Abstract
Background and Objectives:
Mandibular advancement appliances are employed in treating snoring and various forms of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS). The splints facilitate the displacement of the mandible anteriorly and widens the pharyngeal lumen during sleep. Two-splint systems are anchored on the dental arches in the maxilla and mandible. The resulting reciprocal forces are transferred onto the teeth, leading to dental side effects when used long-term. We retrospectively examined the dental changes that occurred after patients had worn the Thornton Adjustable Positioner (TAP®) for over two years.
Patients and Methods:
We enrolled all patients consecutively in whom the diagnosis of OSAS was made following polysomnography in a sleep laboratory between January 2004 and December 2005 and who had been treated primarily with a TAP®. We compared the patients’ baseline findings with follow-up findings after more than 24 months of continuous appliance wear.
Results:
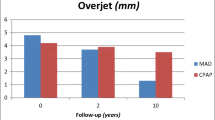
24/47 of the patients were still wearing the splints regularly after an average of 33 ± 9.1 months. Overbite was highly significantly reduced (p = 0.006). We noted a reduction in the frontal overbite of more than 1 mm in ten patients (47.6%), and the overbite of one patient decreased by 4 mm. The maxillary front teeth showed significant palatal tipping and those in the mandible significant labial tipping.
Conclusions:
Clinically small but statistically significant dental side effects predominantly affecting the incisors’ inclination occur after long-term wear of a TAP® appliance. The clinical relevance of these dental changes to the patient can only be judged individually within the scope of an entire assessment.
Zusammenfassung
Hintergrund und Ziel:
Unterkieferprotrusionsschienen (UPS) werden als therapeutische Maßnahme zur Behandlung von Rhonchopathien und bei umschriebenen Formen des obstruktiven Schlafapnoesyndroms (OSAS) angewandt. Mit den Schienen wird der Unterkiefer nach anterior verlagert und das Pharynxlumen im Schlaf erweitert. Zweischienensysteme sind an den Zahnkränzen im Oberund Unterkiefer verankert. Auftretende reziproke Kräfte werden auf die Zähne abgeleitet und führen bei einer Daueranwendung zu dentalen Nebenwirkungen. In der retrospektiven Studie wurden die dentalen Veränderungen bei einer Anwendung des Thornton Adjustable Positioners (TAP®) von mehr als zwei Jahren untersucht.
Patienten und Methodik:
Eingeschlossen wurden in die Studie alle Patienten, die konsekutiv nach der polysomnographisch im Schlaflabor gestellten Diagnose eines OSAS im Zeitraum von Januar 2004 bis Dezember 2005 primär mit einer TAP®-Apparatur versorgt wurden. Verglichen wurden die Situationsmodelle vor Beginn der TAP®-Anwendung mit den Situationsmodellen der Nachuntersuchung nach einer Anwendungsdauer von mehr als 24 Monaten.
Ergebnisse:
Nach durchschnittlich 33 ± 9,1 Monaten wendeten 24 von 47 Patienten die Schiene regelmäßig an. Der Overbite reduzierte sich hochsignifikant (p = 0,006). Eine Reduktion des frontalen Überbisses um mehr als 1 mm wurde bei zehn Patienten (47,6%) festgestellt, bei einem Patienten verringerte sich der Overbite um 4 mm. Die Frontzähne des Oberkiefers kippten signifikant nach palatinal und die des Unterkiefers signifikant nach labial.
Schlussfolgerungen:
Unter der Langzeitanwendung der TAP®-Apparatur treten klinisch geringe, jedoch statistisch signifikante dentale Nebenwirkungen im Ober- und Unterkiefer auf. Diese betreffen vorwiegend die Inklination der Frontzähne. Die klinische Relevanz dieser dentalen Veränderungen für den einzelnen Patienten ist bei einer Gesamtbetrachtung individuell zu bewerten.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghazal, A., Jonas, I.E. & Rose, E.C. Dental Side Effects of Mandibular Advancement Appliances – A 2-year Follow-up. J Orofac Orthop 69, 437–447 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00056-008-0811-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00056-008-0811-9