Abstract
Aim:
Treatment options in orthodontics have been expanded by skeletal anchorage via mini-implants over the last few years. Sufficient primary stability is imperative to minimize implant loss rate. The aim of this study was to quantitatively analyze the factors influencing primary stability: bone quality, implant-design, diameter, and depth of pilot drilling.
Material and Methods:
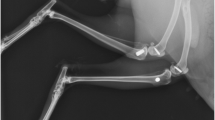
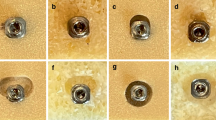
Thirty-six pelvic bone segments (ilium) of country pigs were dissected and embedded in resin. To determine the primary stability, we measured the insertion torque of five different mini-implant types (tomas®-pin [Dentaurum, Ispringen, Germany] 08 and 10 mm, and Dual Top [Jeil Medical Corporation, Seoul, Korea] 1.6 × 8 and 10 mm plus 2 × 10 mm). Twenty-five or 30 implants were inserted into each pelvic bone segment following preparation of the implant sites using pilot drill diameters of 1.0, 1.1, 1.2 and 1.3 mm and pilot drill depths of 1, 2, 3, 6 and 10 mm. Five implants were inserted for reference purposes to establish comparability. Thicknesses of bone compacta were measured via micro-computer tomography.
Results:
Insertion torques of orthodontic mini-implants and therefore primary stability varied greatly, depending on bone quality, implant-design, and preparation of implant site. Compared with the tomas®-pin, the Dual Top screw showed significantlygreater primary stability. Torque moments beyond 230 Nmm caused fractures of 9 Dual Top screws.
Conclusion:
Compacta thickness, implant design and implant site preparation have a strong impact on the primary stability of mini-implants for orthodontic anchorage. Depending on the insertion site and local bone quality, the clinician should choose an optimum combination of implant and pilot-drilling diameter and depth.
Zusammenfassung
Einleitung und Ziel:
Die skelettale Verankerung mit Mini-Implantaten hat die Behandlungsmöglichkeiten der Kieferorthopädie in den letzten Jahren stark erweitert. Zur Minimierung der Verlustrate ist es erforderlich, eine ausreichende Primärstabilität zu erzielen. Ziel der Studie war es, die beeinflussenden Faktoren quantitativ zu analysieren: Knochenqualität, Schraubendesign, Pilotbohrtiefe und -durchmesser.
Material und Methodik:
36 Beckenknochen (Ilium) vom Landschwein wurden präpariert und in Kunststoff eingebettet. Für die Bestimmung der Primärstabilität wurde das Eindrehmoment von fünf verschiedenen Mini-Implantat-Typen (tomas®-pin [Dentaurum, Ispringen, Deutschland] 08 und 10 mm, Dual Top [Jeil Medical Corporation, Seoul, Korea] 1,6 × 8 und 10 mm sowie 2 × 10 mm) gemessen und als Funktion zum Drehwinkel aufgezeichnet. Nach unterschiedlicher Aufbereitung des Implantatlagers (Pilotbohrdurchmesser: 1,0, 1,1, 1,2 und 1,3 mm; Pilotbohrtiefe: 1, 2, 3, 6 und 10 mm) wurden pro Beckenknochen 25 bzw. 30 Implantate gesetzt. Jeweils fünf Referenz-Implantate wurden inseriert, um eine Vergleichbarkeit zwischen den Präparaten herzustellen. Die Dicke der Kompakta wurde mittels Mikro-Computertomographie ermittelt.
Ergebnisse:
Das Eindrehmoment und damit die Primärstabilität der untersuchten kieferorthopädischen Mini-Implantate zeigte je nach Knochenqualität, Form und Größe des Implantates sowie der Vorbereitung des Implantatlagers große Unterschiede. Die Dual-Top-Schraube erreichte im Vergleich mit dem tomas®-pin eine signifikant höhere Primärstabilität. Bei Eindrehmomenten von über 230 Nmm kam es bei neun Dual-Top-Schrauben zur Implantatfraktur.
Schlussfolgerung:
Kompaktadicke, Schraubenart und die Vorbereitung des Implantatlagers spielen bei Mini-Implantaten zu Verankerungszwecken in Bezug auf die Primärstabilität eine wichtige Rolle. Je nach der Insertionsregion und der damit verbundenen Knochenqualität sollte eine optimale Kombination von Vorbohrtiefe, Vorbohrdurchmesser und Implantat gewählt werden.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilmes, B., Rademacher, C., Olthoff, G. et al. Parameters Affecting Primary Stability of Orthodontic Mini-implants. J Orofac Orthop 67, 162–174 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00056-006-0611-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00056-006-0611-z