Abstract.
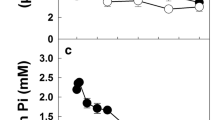
The influence of the anti-fungal agent phosphonate (Phi) on the response of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L. cv. Jet Neuf ) cell suspensions to inorganic phosphate (Pi) starvation was examined. Subculture of the cells for 7 d in the absence of Pi increased acid phosphatase (APase; EC 3.1.3.2) and pyrophosphate (PPi)-dependent phosphofructokinase (PFP; EC 2.7.1.90) activities by 4.5- and 2.8-fold, respectively, and led to a 19-fold increase in V max and a 14-fold decrease in K m (Pi) for Pi uptake. Addition of 2 mM Phi to the nutrient media caused dramatic reductions in the growth and Pi content of the Pi-starved, but not Pi-sufficient cells, and largely abolished the Pi-starvation-dependent induction of PFP, APase, and the high-affinity plasmalemma Pi translocator. Immunoblotting indicated the cells contain three APase isoforms that are synthesized de novo following Pi stress, and that Phi treatment represses this process. Phosphonate treatment of Pi-starved cells significantly altered the relative extent of in-vivo 32P-labelling of polypeptides having Mrs of 66, 55, 45 and 40 kDa. However, Phi had no effect on the total adenylate pool of Pi-starved cells which was about 32% lower than that of Pi-sufficient cells by day 7. Soluble protein levels, and activities of pyruvate kinase (EC 2.7.1.40) and ATP-dependent phosphofructokinase (EC 2.7.1.11) were unaffected by Pi starvation and/or Phi treatment. The effects of Phi on the growth, and APase and PFP activities of Pi-starved B. napus seedlings were similar to those observed in the suspension cells. The results are consistent with the hypothesis that a primary site of Phi action in higher plants is at the level of the signal transduction chain by which plants perceive and respond to Pi stress at the molecular level.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 30 December 1996 / Accepted: 19 February 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carswell, M., Grant, B. & Plaxton, W. Disruption of the phosphate-starvation response of oilseed rape suspension cells by the fungicide phosphonate. Planta 203, 67–74 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00050166
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00050166