Abstract
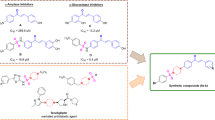
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is an important target for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. A library of 2-amino-6-nitrobenzothiazole-derived hydrazones was evaluated as inhibitors of AChE. The compounds inhibited AChE with IC50 values in nanomolar to micromolar range. N′-(5-chloro-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)-2-(6-nitrobenzothiazol-2-ylamino)acetohydrazide (35) showed strong inhibitory activity against AChE (IC50 = 0.0035 ± 0.005 µM), which was found to be ~0.6-fold active compared to donepezil and ~6.43-fold stronger compared to tacrine. Kinetic studies revealed that compound 35 exhibited a mixed type and reversible mode of enzyme inhibition. SAR studies disclosed several structural aspects significant for potency of these analogs. Molecular docking simulations and binding pose analysis of docked conformations revealed the significance of cumulative effects of hydrogen bonding and π–π interactions for effective stabilization of virtual ligand–AChE complexes. Conformational analysis of lead AChE inhibitor molecules led to the proposal of a five-point pharmacophore model essential for the AChE inhibition. Further, compound 35 presented antioxidant activity higher than ascorbic acid in the in vitro DPPH radical scavenging assay. Additionally, in silico molecular and ADMET properties of the synthesized compounds were predicted to explore their drug likeness for potential oral use as antineurodegenerative agents.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alptuzun V, Prinz M, Horr V, Scheiber J, Radacki K, Fallarero A, Vuorela P, Engels B, Braunschweig H, Erciyas E, Holzgrabe U (2010) Interaction of (benzylidene-hydrazono)-1,4-dihydropyridines with beta-amyloid, acetylcholine, and butyrylcholine esterases. Bioorg Med Chem 18:2049–2059
Alspach JD, Ingraham LL (1977) Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by thiamine. A structure-function study. J Med Chem 20:161–164
Andreani A, Burnelli S, Granaiola M, Guardigli M, Leoni A, Locatelli A, Morigi R, Rambaldi M, Rizzoli M, Varoli L, Roda A (2008) Chemiluminescent high-throughput microassay applied to imidazo [2,1-b]thiazole derivatives as potential acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 43:657–661
Bag S, Tulsan R, Sood A, Datta S, Torok M (2013) Pharmacophore modeling, virtual and in vitro screening for acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and their effects on amyloid-β self-assembly. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des 9:2–14
Brimijoin S (1983) Molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase in brain, nerve and muscle: nature, localization and dynamics. Prog Neurobiol 21:291–322
Carletti E, Colletier J, Dupeux F, Trovaslet M, Masson M, Nachon F (2010) Structural evidence that human acetylcholinesterase inhibited by Tabun ages through O-dealkylation. J Med Chem 53:4002–4008
Castro A, Martinez A (2006) Targeting beta-amyloid pathogenesis through acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Curr Pharm Des 12:4377–4387
Cavalli A, Bolognesi ML, Minarini A, Rosini M, Tumiatti V, Recanatini M, Melchiorre C (2008) Multi-targetdirected ligands to combat neurodegenerative diseases. J Med Chem 51:347–372
Cheung J, Rudolph MJ, Burshteyn F, Cassidy MS, Gary EN, Love J, Franklin MC, Height JJ (2012) Structures of human acetylcholinesterase in complex with pharmacologically important ligands. J Med Chem 55:10282–10286
Chikhale H, Lade K, Joshi P, Kudale S, Nerkar A, Sawant S (2012) In silico design, synthesis and pharmacological screening of some quinazolinones as possible GABAA receptor agonists for anticonvulsant activity. Int. J Pharm Pharm Sci 4:466–469
Dvir H, Silman I, Harel M, Rosenberry TL, Sussman JL (2010) Acetylcholinesterase: from 3D structure to function. Chem Biol Interact 187:10–22
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Feather-Stone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Gella A, Durany N (2009) Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Adh Migr 3:88–93
Geula C, Mesulam MM (1989) Cortical cholinergic fibers in aging and Alzheimer’s disease: a morphometric study. Neuroscience 33:469–481
Goedert M, Spillantini MG (2006) A century of Alzheimer’s disease. Science 314:777–781
Goodsell DS, Morris GM, Olson AJ (1996) Automated docking of flexible ligands: applications of autodock. J Mol Recognit 9:1–5
Grisaru D, Sternfeld M, Eldor A, Glick D, Soreq H (1999) Structural roles of acetylcholinesterase variants in biology and pathology. Eur J Biochem 264:672–686
Heller M, Hanahan DJ (1972) Human erythrocyte membrane bound enzyme acetylcholinesterase. Biochim Biophys Acta 255:251–272
Kryger G, Harel M, Giles K, Toker L, Velan B, Lazar A, Kronman C, Barak D, Ariel N, Shafferman A, Silman I, Sussman JL (2000) Structures of recombinant native and E202Q mutant human acetylcholinesterase complexed with the snake-venom toxin fasciculin-II. Acta Crystallogr Sect D Biol Crystallogr 56:1385–1394
Kryger G, Silman I, Sussman JL (1999) Structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with E2020 (Aricept): implications for the design of new anti-Alzheimer drugs. Structure 7:297–307
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ (2001) Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 46:3–26
Massoulie J, Pezzementi L, Bon S, Krejci E, Vallette FM (1993) Molecular and cellular biology of cholinesterases. Prog Neurobiol 41:31–91
Matsunaga Y, Tanaka T, Yoshinaga K, Ueki S, Hori Y, Eta R (2011) Acotiamide hydrochloride (Z-338), a new selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, enhances gastric motility without prolonging QT interval in dogs: comparison with cisapride, itopride, and mosapride. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 336:791–800
Molinspiration Cheminformatics, Bratislava, Slovak Republic. http://molinspiration.com/services/properties.html
Mustafa SM, Naira VA, Chittoorb JP, Krishnapillaic S (2004) Synthesis of 1,2,4-triazoles and thiazoles from thiosemicarbazide and its derivatives. Mini Rev Org Chem 1:375–385
Ozturan OE, Tan OU, Ozadali K, Kucukkilinç T, Balkan A, Uçar G (2013) Synthesis, molecular modeling and evaluation of novel N′-2-(4-benzylpiperidin-/piperazin-1-yl)acylhydrazone derivatives as dual inhibitors for cholinesterases and Aβ aggregation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23:440–443
Prinz M, Parlar S, Bayraktar G, Alptuzun V, Erciyas E, Fallarero A, Karlsson D, Vuorela P, Burek M, Forster C, Turunc E, Armagan G, Yalcin A, Schiller C, Leuner K, Krug M, Sotriffer CA, Holzgrabe U (2013) 1,4-Substituted 4-(1H)-pyridylene-hydrazone-type inhibitors of AChE, BuChE, and amyloid-β aggregation crossing the blood-brain barrier. Eur J Pharm Sci 49:603–13
Rajesh MP, Natvar JP (2011) In vitro antioxidant activity of coumarin compounds by DPPH, superoxide and nitric oxide free radical scavenging methods. J Adv Pharm Educ Res 1:52–68
Scarpini E, Scheltens P, Feldman H (2003) Treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: current status and new perspectives. Lancet Neurol 2:539–547
Sengupta AK, Garg M (1980) New 5-arylamino-2[N-(2’-mercaptoacetylamino-4’-arylthiazolo)]thiadiazoles(III): as AChE inhibitors. J Indian Chem Soc 57:1241–1243
Shaw FH, Bentley GA (1953) The pharmacology of some new anticholinesterases. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 31:573–576
Siddiqui N, Arshad MF, Ahsan W, Alam MS (2009) Thiazoles: a valuable insight into the recent advances and biological activities. Int J Pharm Sci Drug Res 1:136–143
Szelenyi JG, Bartha E, Hollan SR (1982) Acetylcholinesterase activity of lymphocyctes: an enzyme characteristic of T-cells. Br J Haematol 50:241–245
Talesa VN (2001) Acetylcholinesterase in Alzheimer’s disease. Mech Ageing Dev 122:1961–1969
Taylor P, Radic Z (1994) The cholinesterases: from genes to proteins. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 34:281–320
Thomas D, Karle CA, Kiehn J (2006) The cardiac hERG/IKr potassium channel as pharmacological target: structure, function, regulation, and clinical applications. Curr Pharm Des 12:2271–2283
Tripathi RKP, Ayyannan SR (2016) Design, synthesis, and evaluation of 2-amino-6-nitrobenzothiazole-derived hydrazones as MAO inhibitors: role of the methylene spacer group. ChemMedChem 11:1551–67
Tripathi RKP, Goshain O, Ayyannan SR (2013) Design, synthesis, in vitro MAO-B inhibitory evaluation and computational studies of some 6-nitrobenzothiazole-derived semicarbazones. ChemMedChem 8:462–474
Tripathi RKP, Krishnamurthy S, Ayyannan SR (2016a) Discovery of 3-hydroxy-3-phenacyloxindole analogues of isatin as potential monoamine oxidase inhibitors. ChemMedChem 11:119–132
Tripathi RKP, Rai GK, Ayyannan SR (2016b) Exploration of a library of 3,4-(methylenedioxy)aniline-derived semicarbazones as dual inhibitors of monoamine oxidase and acetylcholinesterase: design, synthesis, and evaluation. ChemMedChem 11:1145–1160
Trullas R, Skolnick P (1993) Differences in fear motivated behaviors among inbred mouse strains. Psychopharmacology 111:323–331
Utku S, Gokce M, Orhan I, Sahin MF (2011) Synthesis of novel 6-substituted 3(2H)-pyridazinone-2-acetyl-2-(substituted/-nonsubstitutedbenzal)hydrazone derivatives and acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory activities in vitro. Arzneimittelforschung 61:1–7
Yu H, Adedoyin A (2003) ADME-Tox in drug discovery: integration of experimental and computational technologies. Drug Discov Today 8:852–61
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Sairam Krishnamurthy, Associate Professor of Pharmacology, Department of Pharmaceutical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology (Banaras Hindu University), Varanasi for his invaluable assistance in pharmacological screening. First author (Rati K. P. Tripathi) thanks the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi (India) for the award of Senior Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathi, R.K.P., Ayyannan, S.R. Evaluation of 2-amino-6-nitrobenzothiazole derived hydrazones as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: in vitro assays, molecular docking and theoretical ADMET prediction. Med Chem Res 27, 709–725 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-2095-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-2095-3