Abstract
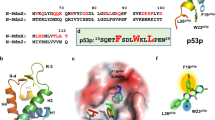
The tumor suppressor protein p53 is inhibited while mouse double minute 2 (MDM2) protein binds on its transactivation domain. Overexpression of MDM2 impairs p53 function and are observed in many human tumors. Disruption of MDM2–p53 interaction leads to increased p53 level and restores p53 transcriptional activity. Restoration of p53 activity through inhibiting the interaction between p53 and MDM2 represents a promising approach for cancer therapy. A number of small-molecule p53–MDM2 binding inhibitors have been developed during the past several years. Nutlin-3 has shown a potent and selective small-molecule MDM2 antagonist which has a considerable promise in pre-clinical studies. In this study we investigated theoretically the interaction of Nutlin-3 with MDM2 at atomistic level, and compared to the interaction of p53 with MDM2 to explore the molecular basis of inhibition. In MDM2–p53 model, there are three hydrogen bonding interactions between MDM2 and p53. The lengths of the hydrogen bonds are found to be 2.45, 2.46, and 1.89 Å whereas interaction energies are −3.82, −3.76, and −5.32 kcal/mol, respectively. The sum of three hydrogen bonding energy is −12.90 kcal/mol. On the other hand, in MDM2–Nutlin-3 model there are four hydrogen bond interactions between MDM2 and Nutlin-3. The bond lengths are found to be 2.29, 1.77, 2.48, and 2.39 Å whereas interaction energies are −4.21, −6.63, −3.65, and −3.63 kcal/mol, respectively. The sum of three hydrogen bonding energy is −18.12 kcal/mol. From the comparison between two models, it is revealed that MDM2–Nutlin3 model has four hydrogen bonds whereas MDM2–p53 model has three hydrogen bonds. The interaction energy in MDM2–Nutlin-3 is relatively more stable than MDM2–p53 interaction. Due to stronger hydrogen bond interaction with higher interaction energy, Nutlin-3 blocks the p53-binding pocket of MDM2 and thus disrupts the MDM2–p53 interaction and helps to activate p53 pathway of apoptosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balint E, Bates S, Vousden KH (1999) Mdm2 binds p73 alpha without targeting degradation. Oncogene 18:3923–3929
Calzaferri G, Forss L, Kamber I (1989) Molecular geometries by the extended huckel molecular orbital method. J Phys Chem 93:5366–5371
Case DA, Darden TA, Cheatham TEI, Simmerling CL, Wang J, Duke RE, Luo R, Merz KM, Pearlman DA, Crowley M, Walker RC, Zhang W, Wang B, Hayik S, Roitberg A, Seabra G, Wong FK, Paesani F, Wu X, Brozell S, Tsui V, Gohlke H, Yang L, Tan C, Mongan J, Hornak V, Cui G, Beroza P, Mathews DH, Schafmeister C, Ross WS, Kollmana PA (2006) AMBER 9. University of California, San Francisco
Chene P (2003) Inhibiting the p53-MDM2 interaction: an important target for cancer therapy. Nature Rev Cancer 3:102–109
Coll Mulet L, Iglesias Serret D, Santidrian AF, Cosialls AM, de Frias M, Castano E (2006) MDM2 antagonists activate p53 and synergies with genotoxic drugs in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 107:4109–4114
Darden T, York D, Pedersen L (1993) Particle Mesh Ewald-an N.Log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J Chem Phys 98:10089–10092
Del Carpio MCA, Yoshimori A (1999) A novel system for assessment of macromolecular interaction in condensed phases. (2) interaction site inference by molecular shape, electrostatic complementarity. Genome Inf 11:3–12
Del Carpio MCA, Yoshimori A (2000) MIAX: a novel system for assessment of macromolecular interaction. (3) parallel hybrid GA for flexible protein docking. Genome Inf 12:205–214
Del Carpio MCA, Ichiishi E, Yoshimori A, Oshikawa T (2002) MIAX: a new paradigm to model bio-molecular interaction and complex formation in condensed phases. PROTEINS: Struct Funct Genet 48:696–732
Del Carpio MCA, Peissker T, Yoshimori A, Ichiishi E (2003) Docking unbound proteins with MIAX: a novel algorithm for protein-protein soft docking. Genome Inf 14:238–249
Elanany M, Sasata K, Yokosuka T, Takami S, Kubo M, Miyamoto A, Iimamura A (2000) Computational methods for the design of zeolitic materials. Stud Surf Sci Catal 142:1867–1876
Elanany M, Selvam P, Yokosuka T, Takami S, Kubo M, Imamura A, Miyamoto A (2003) A quantum molecular dynamics simulation study of the initial hydrolysis step in Sol-Gel prosess. J Phys Chem B 107:1518–1524
Freedman D, Levine AJ (1999) Functions of the MDM2 oncoprotein. Cell Mol Life Sci 5:96–107
Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD, Impey RW, Klein ML (1983) Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys 79:926–935
Jung C, Ito Y, Endou A, Kubo M, Imamura A, Selvam P, Miyamoto A (2003) A Quantum-chemical study on the supported precious metal catalyst. Catal Today 87:43–50
Kadakia M, Slader C, Berberich SJ (2001) Regulation of p63 function by Mdm2 and MdmX. DNA Cell Biol 20:321–330
Katchalski Katzir E, Shariv I, Einstein M, Friesen AA, Aalo C, Wodak SJ (1992) Molecular surface recognition: determination of geometric fit between proteins and their ligands by correlation techniques. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:2195–2199
Kubo M, Ando M, Sakahara S, Jung C, Seki K, Kusagaya T, Endou A, Takami S, Imamura A, Miyamoto A (2004) Development of tight-binding, chemical-reaction dynamics simulator for combinatorial computational chemistry. Appl Surf Sci 223:188–195
Kussie PH et al (1996) Structure of the MDM2 oncoprotein bound to the p53 tumor suppressor transactivation domain. Science 274:948–953
Lane D (1999) Br J Cancer 80:1342–1349
Laurie NA, Donovan SL, Shih CS, Zhang J, Mills N, Fuller C (2006) Inactivation of the p53 pathway in retinoblastoma. Nature 444:61–66
Levine AJ (1997) p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 88:323–331
Luo Y, Selvam P, Ito S, Takami Y, Kubo M, Imamura A, Miyamoto A (2003) Ring opening of methylenecyclopropane over lanthanocene catalyst: a quantum-chemical molecular dynamics simulation study. Organometallics 22:2181–2183
Lwin TZ, Luo R (2006) Force field influences in beta-hairpin folding simulations. Protein Sci 15:2642–2655
Michael D, Oren M (2003) The p53-Mdm2 module and the ubiquitin system. Semin Cancer Biol 13:49–58
Momand J, Jung D, Wilczynski S, Niland J (1998) The MDM2 gene amplification database. Nucleic Acids Res 26:3453–3459
Price SL (2000) Towards more accurate model intermolecular potentials for organic molecules. Rev Comput Chem 14:225–289
Rauf SMA, Ismael M, Sahu KK, Suzuki A, Koyama M, Tsuboi H, Hatakeyama N, Endou A, Takaba H, Del Carpio MCA, Kubo M, Miyamoto A (2010) The effect of R249S carcinogenic and H168R–R249S suppressor mutations on p53–DNA interaction, a multi scale computational study. Comput Biol Med 40:498–508
Ryckaert JP, Ciccotti G, Berendsen HJC (1977) Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J Comput Phys 23:327–341
Sasata K, Yokosuka T, Kurokawa H, Takami S, Kubo M, Imamura A, Shinmura T, Kanoh M, Selvam P, Miyamoto A (2003) Quantum chemical molecular dynamics simulation of the plasma etching processes. Jpn J Appl Phys 42:1859–1864
Stone AJ (1996) The Theory of Intermolecular Forces (Edi.). Clarendon Press, Oxford
Van Maerken T, Speleman F, Vermeulen J, Lambertz I, De Clercq S, De Smet E (2006) Small-molecule MDM2 antagonists as a new therapy concept for neuroblastoma. Cancer Res 66:9646–9655
Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D, Podlaski F, Filipovic Z, Norman K, Ursula K, Christine L, Christian K, Nader F, Emily AL (2004) In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science 303:844–848
Wang JM, Cieplak P, Kollman PA (2000) How well does a restrained electrostatic potential (RESP) model perform in calcluating conformational energies of organic and biological molecules? J Comput Chem 21:1049–1074
Zeng X, Chen L, Jost CA, Maya R, Keller D, Wang X et al (1999) MDM2 suppresses p73 function without promoting p73 degradation. Mol Cell Biol 19:3257–3266
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdur Rauf, S.M., Takaba, H., Del Carpio, C.A. et al. How Nutlin-3 disrupts the MDM2–p53 interaction: a theoretical investigation. Med Chem Res 23, 1998–2006 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0792-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0792-0