Abstract
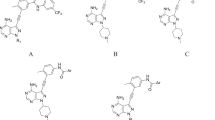
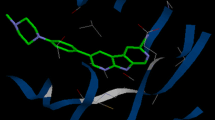
Checkpoint kinase 1(Chk1) is a promising target for cancer treatment. Here three-dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationship (3D-QSAR) studies were performed on 174 1,4-dihydroindeno[1,2-c]pyrazole inhibitors of Chk1 using comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) and comparative molecular similarity indices analysis (CoMSIA). Two satisfactory ligand-based QSAR models were built (CoMFA model: q 2 = 0.541, r 2 = 0.880, CoMSIA model: q 2 = 0.590, r 2 = 0.902). The docking-based studies presented a detailed understanding of interaction between the inhibitors and Chk1. The obtained QSAR models are highly predictable (CoMFA model: q 2 = 0.567, r 2 = 0.891, CoMSIA model: q 2 = 0.596, r 2 = 0.917). The models were further validated by an external testing set obtaining \( r_{\text{pred}}^{2} \) values 0.896 and 0.923 for CoMFA and CoMSIA, respectively. So our models might be helpful for further modification of 1,4-dihydroindeno[1,2-c]pyrazole derivatives.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham RT (2001) Cell cycle checkpoint signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev 15:2177–2196
Baskin II, Tikhonova IG, Palyulin VA, Zefirov NS (2003) Selectivity fields: comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) of the glycine/NMDA and AMPA receptors. J Med Chem 46:4063–4069
Buolamwini JK, Assefa H (2002) CoMFA and CoMSIA 3D QSAR and docking studies on conformationally-restrained cinnamoyl HIV-1 integrase inhibitors: exploration of a binding mode at the active site. J Med Chem 45:841–852
Bush BL, Nachbar RB (1993) Sample-distance partial least squares: PLS optimized for many variables, with application to CoMFA. J Comput Aid Mol Des 7:587–619
Chen Y, Sanchez Y (2004) Chk1 in the DNA damage response: conserved roles from yeasts to mammals. DNA Repair 3:1025–1032
Clark RD, Sprous DG, Leonard JM (2001) Rational approaches to drug design: prous science SA. Barcelona, Spain 475
Cui M, Huang X, Luo X, Briggs JM, Ji R, Chen K, Shen J, Jiang H (2002) Molecular docking and 3D-QSAR studies on gag peptide analogue inhibitors interacting with human cyclophilin A. J Med Chem 45:5249–5259
Foloppe NL, Fisher M, Howes R, Kierstan P, Potter A, Robertson GS, Surgenor AE (2005) Structure-based design of novel Chk1 inhibitors: insights into hydrogen bonding and protein—ligand affinity. J Med Chem 48:4332–4345
Fraley ME, Steen JT, Brnardic EJ, Arrington KL, Spencer KL, Hanney BA, Kim Y, Hartman GD, Stirdivant SM, Drakas BA (2006) 3-(Indol-2-yl)indazoles as Chek1 kinase inhibitors: optimization of potency and selectivity via substitution at C6. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:6049–6053
Gatei M, Sloper K, Sorensen C, Syljuasen R, Falck J, Hobson K, Savage K, Lukas J, Zhou B, Bartek J, Khanna KK (2003) Ataxia-telangiectasia-mutated (ATM) and NBS1-dependent phosphorylation of Chk1 on Ser-317 in response to ionizing radiation. J Biol Chem 278:14806–14811
Huey R, Goodsell DS, Morris GM, Olson AJ (2004) Grid-based hydrogen bond potentials with improved directionality. Lett Drug Des Discov 2:178–183
Huey R, Morris GM, Olson AJ, Goodsell DS (2007) A semiempirical free energy force field with charge-based desolvation. J Comput Chem 28:1145–1152
Kastan MB, Bartek J (2004) Cell-cycle checkpoints and cancer. Nature 432:316–323
Klebe G, Abraham U, Mietzner T (1994) Molecular similarity indices in a comparative analysis (CoMSIA) of drug molecules to correlate and predict their biological activity. J Med Chem 37:4130–4146
Kuerbitz SJ, Plunkett BS, Walsh WV, Kastan MB (1992) Wild-type p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89:7491–7495
Lin NH, Xia P, Kovar P, Park C, Chen Z, Zhang H, Rosenberg SH, Sham HL (2005) Synthesis and biological evaluation of 3-ethylidene-1,3-dihydro- indol-2-ones as novel checkpoint 1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:421–425
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ (2001) Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 46:3
Liu Q, Guntuku S, Cui X, Matsuoka S, Cortez D, Tamai K, Luo G, Carattini-Rivera S, DeMayo F, Bradley A, Donehower LA, Elledge SJ (2000) Chk1 is an essential kinase that is regulated by ATR and required for the G2/M DNA damage checkpoint. Genes Dev 4:1448–1459
Lyne PD, Kenny PW, Cosgrove DA, Deng C, Zabludoff S, Ashwell S, Wendoloski JJ (2004) Identification of compounds with nanomolar binding affinity for checkpoint kinase-1 using knowledge-based virtual screening. J Med Chem 47:1962–1968
Ni ZJ, Barsanti P, Brammeier N, Diebes A, Poon DJ, Ng S, Pecchi S, Pfister K, Renhowe PA, Ramurthy S, Wagman AS, Le DE, Bussiere V, Zhou Y, Jansen JM, Ma S, Gesner TG (2006) 4-(Aminoalkylamino)-3-benzimidazole-quinolinones as potent CHK-1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:3121–3124
Powell SN, DeFrank JS, Connell P, Eogan M, Preffer F, Dombkowski D, Tang W, Friend S (1995) Differential sensitivity of p53(−) and p53(+) cells to caffeine-induced radiosensitization and override of G2 delay. Cancer Res 55:1643–1648
Richard D, Cramer III, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1988) Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J Am Chem Soc 110:5959–5967
Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Unsal-Kacmaz K, Linn S (2004) Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the DNA damage checkpoints. Annu Rev Biochem 73:39–85
Tao ZF, Lin NH (2006) Chk1 inhibitors for novel cancer treatment. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 6:377–388
Tao ZF, Wang L, Stewart KD, Chen Z, Gu W, Bui M, Merta P, Zhang H, Kovar P, Johnson E, Park C, Judge R, Rosenberg S, Sowin T, Lin NH (2007a) Structure-based design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of potent and selective macrocyclic checkpoint kinase 1 inhibitors. J Med Chem 50:1514–1527
Tao ZF, Li G, Tong YS, Chen ZH, Merta P, Kovar P, Zhang HY, Rosenberg SH, Sham HL, Sowin TJ, Lin NH (2007b) Synthesis and biological evaluation of 4′-(6,7-disubstituted-2,4-dihydro-indeno[1,2-c]pyrazol-3-yl) –biphenyl-4-ol as potent Chk1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:4308
Tao ZF, Li G, Tong YS, Stewart KD, Chen ZH, Bui MH, Merta P, Park C, Kovar P, Zhang HY, Sham HL, Rosenberg SH, Sowin TJ, Lin NH (2007c) Discovery of 4′-(1,4-dihydro-indeno[1,2-c]pyrazol-3-yl)-benzonitriles and 4′-(1,4-dihydro-indeno[1,2-c]pyrazol-3-yl)-pyridine-2′-carbonitriles as potent checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:5944–5951
Tong YS, Claiborne A, Stewart KD, Park C, Kovar P, Chen ZH, Credo RB, Gu WZ, Gwaltney SL, Judge RA, Zhang HY, Rosenberg SH, Sham HL, Sowin TJ, Lin NH (2007a) Discovery of 1,4-dihydroindeno[1,2-c] pyrazoles as a novel class of potent and selective checkpoint kinase 1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 15:2759–2767
Tong YS, Claiborne A, Pyzytulinska M, Tao ZF, Stewart KD, Kovar P, Chen ZH, Credo RB, Guan R, Merta PJ, Zhang HY, Bouska J, Everitt EA, Murry BP, Hickman D, Stratton TJ, Wu J, Rosenberg SH, Sham HL, Sowin TJ, Lin NH (2007b) 1,4-Dihydroindeno[1,2-c]pyrazoles as potent checkpoint kinase 1 inhibitors: extended exploration on phenyl ring substitutions and preliminary ADME/PK studies. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:3618–3623
Wang GT, Li G, Mantei RA, Chen Z, Kovar P, Gu W, Xiao Z, Zhang H, Sham HL, Sowin T (2005) 1-(5-Chloro-2-alkoxyphenyl)-3-(5-cyano-pyrazi-2-yl)ureas as potent and selective inhibitors of Chk1 kinase: synthesis, preliminary SAR, and biological activities. J Med Chem 48:3118–3121
Yarden RI, Pardon-Reoyo S, Sgagias MM, Cowan KH, Body LC (2002) BRCA1 regulates the G2/M checkpoint by activating Chk1 kinase upon DNA damage. Nat Genet 30:285–289
Zhao H, Piwnica-Worms H (2001) ATR-mediated checkpoint pathways regulate phosphorylation and activation of human Chk1. Mol Cell Biol 21:4129–4139
Acknowledgments
The authors are gratefully acknowledged financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21071021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, S., Yu, H., Zhao, L. et al. Molecular docking and 3D-QSAR studies on checkpoint kinase 1 inhibitors. Med Chem Res 22, 4992–5013 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0471-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0471-1