Abstract
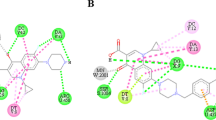
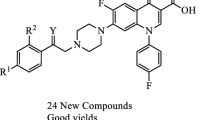
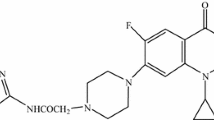
Gatifloxacin is a synthetic broad-spectrum fluorquinolone antibacterial agent with a 3-methylpiperazinyl-side chain at position 7 and a methoxy group at position 8 of the quinolone ring. In the present study different analogues of gatifloxacin were prepared; the piperazinyl ring was chosen as the center of reaction for synthesizing this series of derivatives. The structures of these derivatives were established using spectroscopic techniques such as IR, 1H NMR, and EIMS. In vitro antibacterial and antifungal activities were evaluated by disc diffusion method and these derivatives were compared with in-use fluoroquinolones like gatifloxacin, sparfloxacin, and gemifloxacin. Derivative A proved very potent against Gram-negative organisms, especially Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Shigella flexeneri, and Klebseilla pneumoniae, and derivatives A–C exhibited good antifungal activity compared to in-use quinolones. In addition, gatifloxacin and derivatives were investigated for immunomodulating activities. Derivative B has good anti-inflammatory activity, with IC50 < 12.5 μg/ml.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailly HC, Kok MR, Baum BJ, Tak PP (1990) Gatifloxacin as cytokine production inhibitor. Int J Immunopharmacol 12:31–36
Bryskier A, Chantot JF (1995) Subsitituent on the piperazine ring can shift excretion of the compound from kidney to liver and therefore increase its half-life. This is useful in patient with impaired liver function. Drugs 49:16–18
Dahlgren C, Briheim G (1985) Comparison between the luminal dependant cheminescence of polymorphnuclear leukocytes and of the myeloperoxidase hydrogen peroxide system: influence of pH, cations and protein. Photochem Photobiol 41:605–610
de Almeida MV, Maurício FS, de Souza MVN, da Costa CF, Felipe RCV, Maria CSL (2007) Synthesis and antitubercular activity of lipophilic moxifloxacin and gatifloxacin derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:5661–5664
Deborah HS, Virginia LM (1999) Bacterial phospholipases and pathogenesis. Microbes Infect 1:1103–1112
Domagala JM, Heifetz CL, Hutt MP, Mich TF, Nichols JB, Solomon M, Worth DF (1988) 1-Substituted 7-[3-[(ethylamino)methyl]-1-pyrrolidinyl]-6,8-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinoline carboxylic acids. New quantitative structure activity relationships at N1 for the quinolone antibacterials. J Med Chem 31:991–1001
Drusano GL, Wolfson JS, Hooper DC (1989) Quinolone antimicrobial agents. Am Soc Microbiol 71:105
Emami S, Shafiee A, Foroumadi A (2006) Structural features of new quinolones and relationship to antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria. Mini-Rev Med Chem 6:375–386
Haklar G, Ozveri ES, Yuksel M, Aktan A, Yalcin AS (2001) Different kinds of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species were detected in colon and breast tumors. Cancer Lett 165:219–224
Helfand S, Werkmeister J, Roader J (1982) Chemiluminescence response of human natural killer cells. I. The relationship between target cell binding, chemiluminescence, and cytolysis. J Exp Med 156:492–505
Hoshino K, Kitamura A, Morrissey I, Sato K, Kato J, Ikeda H (1994) Comparison of inhibition of Escherichia coli topoisomerase IV by quinolones with DNA gyrase inhibition. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38:2623–2627
Jensen G, Wandall DA, Gaarsler K (1996) Antibiotic resistance in Shigella and Salmonella in region of Lithuania. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 15:872–876
Kabir OA, Olukayode O, Chidi EO, Christopher CI, Kehinde EF (2005) Screening of crude extracts of six medicinal plants used in South-West Nigerian unorthodox medicine for antimethicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus activity. BMC Compl Alt Med 5:1472–1483
Keiser J, Burri C (2001) Evaluation of quinolone derivatives for antitrypanosomal activity. Trop Med Int Health 6:369–389
Kenneth T (2007) The mechanisms of bacterial pathogenicity. Todar’s Online Textbook of Bacteriology
Nakajima R, Kitamura K, Someya K, Tanaka M, Sato K (1995) In vitro and in vivo antifungal activities of DU-6859a, a fluoroquinolone, in combination with amphotericin B and fluconazole against pathogenic fungi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 39:1517–1521
National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (1993) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility tests, 5th edn. NCCLS document M2-A5. NCCLS, Villanova, PA
Ronald AR, Low DE (2003) Fluoroquinolones antibiotics. Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel
Scheld WM (1989) Quinolone therapy for infections of the central nervous system. Rev Infect Dis 11:1194–1202
Shen LL, Fostel JM (1994) DNA topoisomerase inhibitors as antifungal agents. Adv Pharmacol 29:227–244
Siddiqui R, Sultana N, Khan KM, Akber N, Arayne MS (2007) Effect of skeletal modifications of ciprofloxacin on antibacterial, antifungal and cytotoxic activities. J Chinese Clin Med 21:188–195
Tokushige H, Yokogaki S, Naka H (2003) Gatifloxacin as cytokine production inhibitor. European Patent EP1312364
Walsh C (2003) Antibiotics, actions, origins, resistance. Harvard Medical School. ASM Press, Boston
WHO (2003) Manual for the laboratory identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of bacterial pathogens of public health importance in the developing world. Who Health Organization, Geneva, pp 103–162
Yong HL, Yun ZT, Xue FH, Ren GX (2004) The crystal structure of a gatifloxacin complex and its fluorescent property. Z Anorg Allg Chem 631:639–641
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sultana, N., Naz, A., Khan, B. et al. Synthesis, characterization, antibacterial, antifungal, and immunomodulating activities of gatifloxacin derivatives. Med Chem Res 19, 1210–1221 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-009-9264-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-009-9264-y