Abstract
Objective
To examine associations between psychological distress (PD) and chronic health conditions among different age groups in a representative population sample.
Methods
PD measured by the Kessler-10, and the presence of diagnosed chronic conditions were self-reported by respondents aged 18 years and over in a South Australian continuous computer-assisted telephone interviewing surveillance system from July 2002 to June 2007 (n = 26,376).
Results
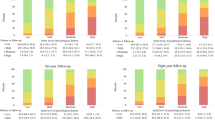
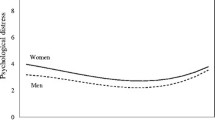
The overall prevalence of PD was 9.8% (95% CI 9.5–10.2). In age-specific adjusted multivariate models, arthritis and mental health conditions remained significantly associated with PD for all age groups, cardiovascular disease was significantly associated with PD among those aged 35 years and over, asthma was associated with PD for respondents aged 50 years and over, and osteoporosis was associated with PD for 50–64 year olds. Being born outside of Australia, United Kingdom or Ireland, current smoking, low level of education, and low income also remained significantly associated with PD for all age groups.
Conclusions
Young people experience a higher prevalence of PD than older age groups, irrespective of the presence of chronic conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Australian Bureau of Statistics (2004) Population by age and sex. South Australia, ABS, Canberra
Australian Centre for Asthma Monitoring (2003) Asthma in Australia 2003. Asthma Series 1. AIHW Cat. no. ACM 1, AIHW, Canberra
Bruce ML, Hoff RA (1994) Social and physical health risk factors for first-onset major depressive disorder in a community sample. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 29:165–171
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2004) Serious psychological distress among persons with diabetes. New York City, 2003 MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 53:1089–1092
Clinical Research Unit for Anxiety and Depression (2007) CRUFAD K10 Test. A WHO Collaborating Center. School of Psychiatry, University of NSW. Available via http://www.crufad.org/selfhelp/k10Test. Accessed 15 July 2009
Cosci F, Corlando A, Fornai E, Pistelli F, Paoletti P, Carrozzi L (2009) Nicotine dependence, psychological distress and personality traits as possible predictors of smoking cessation. Results of a double-blind study with nicotine patch. Addict Behav 34:28–35
Council of Australian Governments (2006) National Action Plan on Mental Health 2006–2011. COAG, Canberra
Dal Grande E, Taylor A, Wilson D (2005) Is there a difference in health estimates between people with listed and unlisted telephone numbers? Aust N Z J Public Health 29:448–456
Dalgard OS, Thapa SB, Hauff E, McCubbin M, Syed HR (2006) Immigration, lack of control and psychological distress: findings from the Oslo Health Study. Scand J Psychol 47:551–558
Department of Health and Ageing (2009) Fourth National Mental Health Plan—an agenda for collaborative government action in mental health 2009–2014. Attorney General’s Department, Canberra
Department of Health SA (2002) South Australian Monitoring and Surveillance System (SAMSS) Brief Report. 2002–20, Department of Health, Adelaide. Available via http://www.health.sa.gov.au/pros/. Accessed 15 July 2009
deShazo RD, Stupka JE (2009) Asthma in US seniors: part 2. Treatment. Seeing through the glass darkly. Am J Med 122:109–113
Dimatteo MR, Lepper HS, Croghan TW (2000) Depression is a risk factor for noncompliance with medical treatment: meta-analysis of the effects of anxiety and depression on patient adherence. Arch Intern Med 160:2101–2107
Geist R, Grdisa V, Otley A (2003) Psychosocial issues in the child with chronic conditions. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 17:141–152
Grzywacz JG, Almeida DM, Neupert SD, Ettner SL (2004) Socioeconomic status and health: a micro-level analysis of exposure and vulnerability to daily stressors. J Health Soc Behav 45:1–16
Guthrie DW, Bartsocas C, Jarosz-Chabot P, Konstantinova M (2003) Psychosocial issues for children and adolescents with diabetes: overview and recommendations. Diabetes Spectr 16:7–12
Hamer M, Molloy GJ, Stamatakis E (2008) Psychological distress as a risk factor for cardiovascular events: pathophysiological and behavioral mechanisms. J Am Coll Cardiol 52:2156–2162
Health West (2001) 2000 Collaborative health and wellbeing survey design and methodology. Western Australian Government, Perth
Hislop AL, Fegan PG, Schlaeppi MJ, Duck M, Yeap BB (2008) Prevalence and associations of psychological distress in young adults with Type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med 25:91–96
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S (1989) Applied logistic regression. Wiley, New York
Keefe FJ, Williams DA (1990) A comparison of coping strategies in chronic pain patients in different age groups. J Gerontol 45:161–165
Kessler R, Mroczek D (1994) Final versions of our non-specific psychological distress scale. Institute for Social Research, University of Michigan, Michigan
Kokkonen E-R, Kokkonen J, Moilanen I (2001) Predictors of delayed social maturation and mental health disorders in young adults chronically ill since childhood. Nord J Psychiatry 55:237–242
Koopmans GT, Lamers LM (2000) Chronic conditions, psychological distress and the use of psychoactive medications. J Psychosom Res 48:115–123
Leavey G, Rozmovits L, Ryan L, King M (2007) Explanations of depression among Irish migrants in Britain. Soc Sci Med 65:231–244
Li C, Ford ES, Zhao G, Strine TW, Dhingra S, Barker L, Berry JT, Mokdad AH (2009) Association between diagnosed diabetes and serious psychological distress among U.S. adults: the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2007. Int J Public Health 54(Suppl 1):43–51
Miech R, Power C, Eaton WW (2007) Disparities in psychological distress across education and sex: a longitudinal analysis of their persistence within a cohort over 19 years. Ann Epidemiol 17:289–295
Myer L, Stein DJ, Grimsrud A, Seedat S, Williams DR (2008) Social determinants of psychological distress in a nationally-representative sample of South African adults. Soc Sci Med 66:1828–1840
National Health and Medical Research Council (2001) Australian alcohol guidelines: Health risks and Benefits. NHMRC, Canberra
National Health Priority Action Council (2006) National chronic disease strategy. Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing, Canberra
Okoro CA, Strine TW, Balluz LS, Crews JE, Dhingra S, Berry JT, Mokdad AH (2009) Serious psychological distress among adults with and without disabilities. Int J Public Health 54(Suppl 1):52–60
Panicker NR, Sharma PN, Al-Duwaisan AR (2008) Psychological distress and associated risk factors in bronchial asthma patients in Kuwait Indian. J Med Sci 62:1–7
Penninx BW, Guralnik JM, Ferrucci L, Simonsick EM, Deeg DJ, Wallace RB (1998) Depressive symptoms and physical decline in community dwelling older persons. JAMA 279:1720–1726
Pratt LA, Dey AN, Cohen AJ (2007) Characteristics of adults with serious psychological distress as measured by the K6 scale: United States, 2001–04. Adv Data 382:1–18
Rasul F, Stansfeld SA, Smith GD, Shlomo YB, Gallacher J (2007) Psychological distress, physical illness and risk of myocardial infarction in the Caerphilly study. Psychol Med 37:1305–1313
Roustit C, Chaix B, Chauvin P (2007) Family breakup and adolescents’ psychosocial maladjustment: public health implications of family disruptions. Pediatrics 120:e984–e991
Schulz AJ, House JS, Israel BA, Mentz G, Dvonch JT, Miranda PY, Kannan S, Koch M (2008) Relational pathways between socioeconomic position and cardiovascular risk in a multiethnic urban sample: complexities and their implications for improving health in economically disadvantaged populations. J Epidemiol Community Health 62:638–646
Shih M, Hootman JM, Strine TW, Chapman DP, Brady TJ (2006) Serious psychological distress in U.S. adults with arthritis. J Gen Intern Med 21:1160–1166
Surtees PG, Wainwright NW, Luben RN, Wareham NJ, Bingham SA, Khaw KT (2008) Psychological distress, major depressive disorder, and risk of stroke. Neurology 70:788–794
Taylor AW, Wilson DH, Wakefield M (1998) Differences in health estimates using telephone and door-to-door survey methods—a hypothetical exercise. Aust N Z J Public Health 22:223–226
Weishaar HB (2008) Consequences of international migration: a qualitative study on stress among Polish migrant workers in Scotland. Public Health 122:1250–1256
World Health Organization (2000) Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. WHO, Geneva
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Strategic Health Research Program of the South Australian Department of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chittleborough, C.R., Winefield, H., Gill, T.K. et al. Age differences in associations between psychological distress and chronic conditions. Int J Public Health 56, 71–80 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-010-0197-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-010-0197-5