Abstract
Objectives
To assess the validity of the San Antonio heart study (SAHS) diabetes prediction model in a large representative Iranian population.
Methods
A risk function derived from data in the SAHS to predict the 7.5-year risk of diabetes, was tested for its ability to predict incident diabetes in 3,242 individuals aged ≥20 years. The performance or ability to accurately predict diabetes risk, of the SAHS function compared with the performance of risk functions developed specifically from the Tehran lipid and glucose study. Comparisons included goodness of fit, discrimination, and calibration.
Results
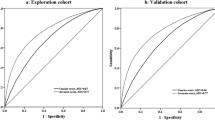
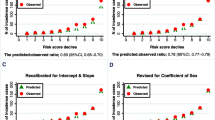
The participants were followed for 6.3 years. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AROC) for diabetes of SAHS model was 0.83 (95% CI 0.80–0.86). The model overestimated the risk of diabetes in TLGS population with the overall bias of 111%. After the recalibration, the model-predicted probability agreed well with the actual observed 6-year risk of diabetes.
Discussion and conclusion
The American SAHS was a prediction model for diabetes with good discrimination in an Iranian target population after calibration.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Ghani MA, Williams K, DeFronzo RA, Stern M (2007) What is the best predictor of future type 2 diabetes? Diabetes Care 30:1544–1548. doi:10.2337/dc06-1331
Azizi F, Ghanbarian A, Momenan AA, Hadaegh F, Mirmiran P, Hedayati M et al (2009) Prevention of non-communicable disease in a population in nutrition transition: Tehran lipid and glucose study phase II. Trials 10:5. doi:10.1186/1745-6215-10-5
Chien K, Cai T, Hsu H, Su T, Chang W, Chen M et al (2009) A prediction model for type 2 diabetes risk among Chinese people. Diabetologia 52:443–450. doi:10.1007/s00125-008-1232-4
Colagiuri S, Cull CA, Holman RR (2002) Are lower fasting plasma glucose levels at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes associated with improved outcomes? Diabetes Care 25:1410–1417. doi:10.2337/diacare.25.8.1410
Colagiuri S, Hussain Z, Zimmet P, Cameron A, Shaw J (2004) Screening for type 2 diabetes and impaired glucose metabolism. Diabetes Care 27:367–371. doi:10.2337/diacare.27.2.367
Conen D, Ridker PM, Mora S, Buring JE, Glynn RJ (2007) Blood pressure and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus: The Women’s Health Study. Eur Heart J; 28:2937–2943. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehm400
DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL (1988) Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics 44:837–845
Friedwald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS (1972) Estimation of the concentration of low density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 18:419–503
Genuth S, Alberti KG, Bennett P, Buse J, Defronzo R, Kahn R et al (2003) Follow-up report on the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 26:3160–3167. doi:10.2337/diacare.26.11.3160
Glumer C, Carstensen B, Sandbaek A, Lauritzen T, Jorgensen T, Borch-Johnsen K (2004) A Danish diabetes risk score for targeted screening: the Inter99 study. Diabetes Care 27:727–733. doi:10.2337/diacare.27.3.727
Glumer C, Vistisen D, Borch-Johnsen K, Colagiuri S (2006) Risk scores for type 2 diabetes can be applied in some populations but not all. Diabetes Care 29:410–414. doi:10.2337/diacare.29.02.06.dc05-0945
Hadaegh F, Bozorgmanesh MR, Ghasemi A, Harati H, Saadat N, Azizi F (2008) High prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes and abnormal glucose tolerance in the Iranian urban population: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. BMC Public Health 8:176. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-8-176
Hadaegh F, Shafiee G, Azizi F (2009) Anthropometric predictors of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus in Iranian women. Ann Saudi Med 29:194–200
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ (1982) The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 143:29–36
Herman WH (2009) Predicting risk for diabetes: choosing (or building) the right model. Ann Int Med 150:812–814. doi:10.1059/0003-4819-150-11-200906020-00010
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S (2000). Applied logistic regression. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Johnson SL, Tabaei BP, Herman WH (2005) The efficacy and cost of alternative strategies for systematic screening for type 2 diabetes in the US population 45–74 years of age. Diabetes Care 28:307–311
Justice AC, Covinsky KE, Berlin JA (1999) Assessing the generalizability of prognostic information. Ann Intern Med 130:515–524
Kahn HS, Cheng YJ, Thompson TJ, Imperatore G, Gregg EW (2009) Two risk-scoring systems for predicting incident diabetes mellitus in US adults age 45 to 64 years. Ann Intern Med 150:741–751
Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, Walker EA et al (2002) Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med 346:393–403. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa012512
Kolberg JA, Jorgensen T, Gerwien RW, Hamren S, McKenna MP, Moler E et al (2009) Development of a type 2 diabetes risk model from a panel of serum biomarkers from the Inter99 cohort. Diabetes Care 32:1207–1212. doi:10.2337/dc08-1935
Lindstrom J, Tuomilehto J (2003) The diabetes risk score: a practical tool to predict type 2 diabetes risk. Diabetes Care 26:725–731. doi:10.2337/diacare.26.3.725
MacKay MF, Haffner SM, Wagenknecht LE, D’Agostino RB, Hanley AJG (2009) Prediction of type 2 diabetes using alternate anthropometric measures in a multi-ethnic cohort. Diabetes Care 32:956–958. doi:10.2337/dc08-1663
McNeely MJ, Boyko EJ, Leonetti DL, Kahn SE, Fujimoto WY (2003) Comparison of a clinical model, the oral glucose tolerance test, and fasting glucose for prediction of type 2 diabetes risk in Japanese Americans. Diabetes Care 26:758–763
Nyamdorj R, Qiao Q, Soderberg S, Pitkaniemi JM, Zimmet PZ, Shaw JE et al (2009) BMI compared with central obesity indicators as a predictor of diabetes incidence in Mauritius. Obesity (Silver Spring) 17:342–348. doi:10.1038/oby.2008.503
Pan XR, Li GW, Hu YH, Wang JX, Yang WY, An ZX et al (1997) Effects of diet and exercise in preventing NIDDM in people with impaired glucose tolerance. The Da Qing IGT and Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 20:537–544
Rahman M, Simmons RK, Harding AH, Wareham NJ, Griffin SJ (2008) A simple risk score identifies individuals at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study. Fam Pract 25:191–196
Rathmann W, Martin S, Haastert B, Icks A, Holle R, Lowel H et al (2005) Performance of screening questionnaires and risk scores for undiagnosed diabetes: the KORA Survey 2000. Arch Intern Med 165:436–441
Schulze M, Joost H (2009) Rapid responses to: Henry S. Kahn, Yiling J. Cheng, Theodore J. Thompson, Giuseppina Imperatore, and Edward W. Gregg. Two risk-scoring systems for predicting incident diabetes mellitus in US adults age 45 to 64 years in Ann Intern Med 2009; 150:741–751: Integer points based scoring systems for diabetes prediction: The German Diabetes Risk Score (18 June). Retrieved 15 Jul 2009, from http://www.annals.org/cgi/eletters/150/11/741#114512
Schulze MB, Hoffmann K, Boeing H, Linseisen J, Rohrmann S, Mohlig M et al (2007) An accurate risk score based on anthropometric, dietary, and lifestyle factors to predict the development of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 30:510–515
Schulze MB, Weikert C, Pischon T, Bergmann MM, Al-Hasani H, Schleicher E et al (2009) Use of multiple metabolic and genetic markers to improve the prediction of type 2 diabetes: the EPIC-Potsdam Study. Diabetes Care 32:2116–2119. doi:10.2337/dc09-0197
Stern MP, Williams K, Haffner SM (2002) Identification of persons at high risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus: do we need the oral glucose tolerance test? Ann Intern Med 136:575–581
Talmud PJ Hingorani AD Cooper JA, Marmot MG, Brunner EJ, Kumari M et al (2010) Utility of genetic and non-genetic risk factors in prediction of type 2 diabetes: Whitehall II prospective cohort study. BMJ 340:b4838. doi:10.1136/bmj.b4838
Tulloch-Reid MK, Williams DE, Looker HC, Hanson RL, Knowler WC (2003) Do measures of body fat distribution provide information on the risk of type 2 diabetes in addition to measures of general Obesity? Diabetes Care 26:2556–2561. doi:10.2337/diacare.26.9.2556
Wang Y, Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Hu FB (2005) Comparison of abdominal adiposity and overall obesity in predicting risk of type 2 diabetes among men. Am J Clin Nutr 81:555–563
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H (2004) Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 27:1047–1053
Wilson PWF, Meigs JB, Sullivan L, Fox CS, Nathan DM, D’Agostino R B Sr (2007) Prediction of incident diabetes mellitus in middle-aged adults: The Framingham offspring study. Arch Intern Med 167:1068–1074. doi:10.1001/archinte.167.10.1068
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grant No. 121 from the National Research Council of the Islamic Republic of Iran. We express our appreciation to the participants of district-13 of Tehran for their enthusiastic support in this study.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bozorgmanesh, M., Hadaegh, F., Zabetian, A. et al. San Antonio heart study diabetes prediction model applicable to a Middle Eastern population? Tehran glucose and lipid study. Int J Public Health 55, 315–323 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-010-0130-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-010-0130-y