Abstract
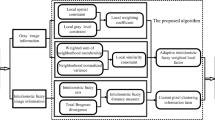
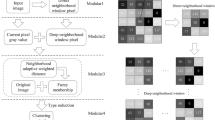
To improve the segmentation performance and anti-noise robustness of existing weighted kernel intuitionistic fuzzy clustering, a robust kernelized total Bregman divergence-based fuzzy local information clustering motivated by intuitionistic fuzzy information is proposed. In this algorithm, a kernelized total Bregman divergence is extended by a polynomial kernel function, and the corresponding intuitionistic kernelized total Bregman divergence is put forward to measure the difference between intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Then, the weighted local information is introduced into the objective function of intuitionistic fuzzy clustering, and the similarity between the current pixel and its neighborhood pixels is constructed to better describe the influence of neighborhood pixels on the current pixel. Finally, the square root of the deviation between the current pixel and the mean value of its neighboring pixels is used to adjust the local spatial information to improve the robustness to noise or outliers and further enhance the anti-noise ability of the algorithm. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm has better clustering performance and stronger anti-noise robustness than existing state-of-the-art fuzzy clustering-related algorithms.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The MR brain images generated and analyzed during this study are available in the Kaggle brain tumor dataset: https://www.kaggle.com/hasimdev/brain-mri-dataset. The natural images generated and analysed during this study are available in the Berkeley Segmentation Dataset: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2001.937655. The remote sensing images generated and analysed during this study are available in the UC Merced Land Use dataset: http://vision.ucmerced.edu/datasets/landuse.html and NWPU-RESISC45: http://www.escience.cn/people/JunweiHan/NWPU-RESISC45.html.
References
M.N. Ahmed, S.M. Yamany, N. Mohamed et al., A modified fuzzy C-means algorithm for bias field estimation and segmentation of MRI data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 21(3), 193–199 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/42.996338
S. Alipour, J. Shanbehzadeh, Fast automatic medical image segmentation based on spatial kernel fuzzy c-means on level set method. Mach. Vis. Appl. 25(6), 1469–1488 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-014-0606-5
J. Arora, M. Tushir, A new semi-supervised intuitionistic fuzzy c-means clustering. ICST Trans. Scalable Inf. Syst. 7(24), 159622 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4108/eai.13-7-2018.159622
M.A. Balafar, A.R. Ramli, M.I. Saripan, S. Mashohor, Review of brain MRI image segmentation methods. Artif. Intell. Rev. 33(3), 261–274 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-010-9155-0
A. Banerjee, S. Merugu, I.S. Dhillon et al., Clustering with Bregman divergences. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 6(4), 1705–1749 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1137/1.9781611972740.22
J.C. Bezdek, Pattern recognition with fuzzy objective function algorithms (Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-0450-1
J.C. Bezdek, Cluster validity with fuzzy sets. J. Cybern. 3(3), 58–73 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1080/01969727308546047
L.M. Bregman, The relaxation method of finding the common points of convex sets and its application to the solution of problems in convex programming. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 7(3), 200–217 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1016/0041-5553(67)90040-7
W. Cai, S. Chen, D. Zhang, Fast and robust fuzzy c-means clustering algorithms incorporating local information for image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 40(3), 825–838 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2006.07.011
T. Chaira, A novel intuitionistic fuzzy c means clustering algorithm and its application to medical images. Appl. Soft Comput. 11(2), 1711–1717 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2010.05.005
T. Chaira, A. Panwar, An Atanassov’s intuitionistic fuzzy kernel clustering for medical image segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 7(2), 360–370 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/18756891.2013.865830
S.V. Carata, V.E. Neagoe, A pulse-coupled neural network approach for image segmentation and its pattern recognition application, in 2016 International Conference on Communications (COMM) (IEEE, 2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICComm.2016.7528317
L. Chen, C. Chen, M. Lu, A multiple-kernel fuzzy C-means algorithm for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B Cybern. 41(5), 1263–1274 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2011.2124455
X. Chen, B.P. Nguyen, C.K. Chui, S.H. Ong, Automated brain tumor segmentation using kernel dictionary learning and superpixel-level features, in IEEE International Conference on Systems, man, and cybernetics (SMC), (IEEE, 2017), pp. 002,547–002,552 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/SMC.2016.7844622
S. Chen, D. Zhang, Robust image segmentation using FCM with spatial constraints based on new kernel-induced distance measure. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 34(4), 1907–1916 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2004.831165
I. Despotović, E. Ansteenkiste, W. Philips, Spatially coherent fuzzy clustering for accurate and noise-robust image segmentation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 20(4), 295–298 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2013.2244080
R.R. Gharieb, Incorporating local data and KL membership divergence into hard C-means clustering for fuzzy and noise-robust data segmentation. Mach. Learn. Data Min. 2018, 35–53 (2018). https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.74514
N. Giordana, W. Pieczynski, Estimation of generalized multisensor hidden Markov chains and unsupervised image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 19(5), 465–475 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1109/34.589206
M. Gong, Y. Liang, J. Shi et al., Fuzzy C-means clustering with local information and kernel metric for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(2), 573–584 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2012.2219547
Y. Guo, A. Sengur, A novel color image segmentation approach based on neutrosophic set and modified fuzzy c-means. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 32(4), 1699–1723 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-012-9531-x
M.A. Hasnat, O. Alata, A. Tremeau, Model-based hierarchical clustering with Bregman divergences and Fishers mixture model: application to depth image analysis. Stats. Comput. 26(4), 861–880 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-015-9576-3
X. Hua, Y. Cheng, H. Wang, Y. Qin, D. Chen, Geometric target detection based on total Bregman divergence. Digit. Signal Process. 75(75), 232–241 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2018.01.008
H.C. Huang, Y.Y. Chuang, C.S. Chen, Multiple kernel fuzzy clustering. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 20(1), 120–134 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2011.2170175
C.W. Huang, K.P. Lin, M.C. Wu, et al., Intuitionistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm with neighborhood attraction in segmenting medical image. Pattern Anal. Appl. 18(1), 459–470 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-014-1264-2
P. Kaur, Intuitionistic fuzzy sets based credibilistic fuzzy C-means clustering for medical image segmentation. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 9(4), 345–351 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-017-0039-2
P. Kaur, A.K. Soni, A. Gosain, A robust kernelized intuitionistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm in segmentation of noisy medical images. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 34(2), 163–175 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2012.09.015
D. Koundal, B. Sharma, E. Gandotra, Spatial intuitionistic fuzzy set-based image segmentation. Imaging Med. 9(4), 95–101 (2017)
T. Krassimir, Atanassov. Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 20(1), 87–96 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0114(86)80034-3
S. Krinidis, V. Chatzis, A robust fuzzy local information c-means clustering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19(5), 1328–1337 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2010.2040763
R. Krishnapuram, J.M. Keller, A possibilistic approach to clustering. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 1(2), 98–110 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1109/91.227387
D. Kumar, H. Verma, Mehra, R.K. Agrawal, A modified intuitionistic fuzzy c-means clustering approach to segment human brain MRI image. Multimed Tools Appl. 78(6), 1–25 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-5954-0
D. Kumar, R.K. Agrawal, H. Verma, Kernel intuitionistic fuzzy entropy clustering for MRI image segmentation. Soft Comput. 24(6), 4003–4026 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04169-y
A.W.C. Liew, S.H. Leung, W.H. Lau, Fuzzy image clustering incorporating spatial continuity. IEE Proc. Vis. Image Signal Proc. 147(2), 185–192 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1049/ip-vis:20000218
K.P. Lin, A novel evolutionary kernel intuitionistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 22(5), 1074–1087 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2013.2280141
M. Liu, Total Bregman Divergence, a Robust Divergence Measure, and its Applications (University of Florida, Gainesville, 2011)
M. Liu, B.C. Vemuri, S. Amari et al., Shape retrieval using hierarchical total Bregman soft clustering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(12), 2407–2419 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2012.44
J. Luo, Y. Wang, Q. Wang et al., Automatic image segmentation of grape based on computer vision, in Recent Developments in Intelligent Systems and Interactive Applications (2016), pp. 365–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49568-2_52
D. Martin, C. Fowlkes, D. Tal et al., A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics, in Proceedings Eighth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. ICCV 2001 (2001), pp. 416–423. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2001.937655
C.E. Shannon, A mathematical theory of communication. Bell. Labs. Tech. J. 27(4), 379–423 (1948). https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb00917.x
J. Shawetaylor, N. Cristianini, Kernel methods for pattern analysis: ranking, clustering and data visualization. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 101(476), 1730–1730 (2004)
L. Szilagyi, Z. Benyo, S.M. Szilagyi, H.S. Adam, MR brain image segmentation using an enhanced fuzzy c-means algorithm, in Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (IEEE, 2003), pp. 724–726. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2003.1279866
E. Szmidt, J. Kacprzyk, Distances between intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 114(3), 505–518 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0114(98)00244-9
H. Verma, R.K. Agrawal, A. Sharan, An improved intuitionistic fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm incorporating local information for brain image segmentation. Appl. Soft Comput. 46(C), 543–557 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.12.022
H. Verma, R.K. Agrawal, Possibilistic intuitionistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm for MRI brain image segmentation. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Tools 24(5), 1550016 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218213015500165
I.K. Vlachos, G.D. Sergiadis, Towards intuitionistic fuzzy image processing, in International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Modelling, Control and Automation and International Conference on Intelligent Agents, Web Technologies and Internet Commerce (CIMCA-IAWTIC) (2005), pp. 2–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/CIMCA.2005.1631233
G.S. Wang, Properties and construction methods of kernel in support vector machine. Comput. Sci. 33(6), 178–182 (2006). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-137X.2006.06.047
N. Wang, M. Guo, Survey on application of fuzzy connectedness in image segmentation. Sci. Technol. Eng. 8(16), 4588–4592 (2008). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2008.16.037. (in Chinese)
Z. Wang, J. Fan, H. Lou et al., Intuitionistic fuzzy c-mean clustering algorithm incorporating local information for image segmentation. Appl. Res. Comput. 31(9), 2864–2872 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2014.09.073. (in Chinese)
K. Wu, M. Yang, Alternative C-means clustering algorithms. Pattern Recognit. 35(10), 2267–2278 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3203(01)00197-2
C. Wu, J. Sun, Adaptive robust picture fuzzy clustering algorithm based on total divergence. Binggong Xuebao 40(9), 1890–1901 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.09.014. (in Chinese)
C. Wu, X. Yang, Robust credibilistic fuzzy local information clustering with spatial information constraints. Digit. Signal Process. 97, 102615 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2019.102615
C. Wu, X. Zhang, Total Bregman divergence-based fuzzy local information C-means clustering for robust image segmentation. Appl. Soft Comput. 94, 106468 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106468
C. Wu, C. Huang, J. Zhang, Intuitionistic fuzzy information-driven total Bregman divergence fuzzy clustering with multiple local information constraints for image segmentation. Vis. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-021-02319-8
Z. Xu, J. Wu, Intuitionistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithms. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 21(4), 580–590 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-4132.2010.04.009
Y. Xu, Q. Ye, Generalized mercer kernels and reproducing kernel Banach spaces. Mem. Am. Math. Soc. 258(1243), 1–122 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1090/memo/1243
R.R. Yager, On the measure of fuzziness and negation. II. Lattices. Inf. Control 44(3), 236–260 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0019-9958(80)90156-4
R.R. Yager, On the measure of fuzziness and negation part I: membership in the unit interval. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 5(4), 221–229 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1080/03081077908547452
L.A. Zadeh, Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8(3), 338–353 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0019-9958(65)90241-X
S. Zeng, X.Y. Wang, H. Cui, C.J. Zheng, D. Feng, A unified collaborative multi-kernel fuzzy clustering for multiview data. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26(3), 1671–1687 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2017.2743679
S. Zeng, Z. Wang, R. Huang, L. Chen, D. Feng, A study on multi-kernel intuitionistic fuzzy C-means clustering with multiple attributes. Neurocomputing 335, 59–71 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.01.042
F. Zhao, Z. Zeng, H. Liu, R. Lan, J. Fan, Semi-supervised approach to surrogate-assisted multi objective kernel intuitionistic fuzzy clustering algorithm for color image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 28(6), 1023–1034 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2973121
F. Zhao, W.J. Sun, H.Q. Liu et al., Intuitionistic fuzzy clustering image segmentation based on flower pollination optimization with nearest neighbor searching. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 42(4), 1006–1012 (2020). https://doi.org/10.11999/JEIT190428
D. Zhang, S. Chen, Kernel-based fuzzy clustering incorporating spatial constraints for image segmentation, in Proceedings of the 2003 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics (IEEE, 2003), pp. 2189–2192. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMLC.2003.1259869
C. Zhong, Z. Liu, Y. Yang et al., Improved FCM algorithm based on neighboring membership constraint for image segmentation. J. Jilin Univ. (Inf. Sci. Ed.) 31(6), 627–633 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-5896.2013.06.012
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62071378) (Grant No. 61671377, 51709228) and the Shaanxi Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 2016JM8034, 2017JM6107, 2018JM4018, 2021JM-459, 2022JM-370).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CW was involved in the conceptualization, data curation, funding acquisition, methodology, project administration, resources, supervision, validation, visualization. CH contributed to the formal analysis, investigation, software, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. JZ contributed to writing—review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., Huang, C. & Zhang, J. Local Information-Driven Intuitionistic Fuzzy C-Means Algorithm Integrating Total Bregman Divergence and Kernel Metric for Noisy Image Segmentation. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 1522–1572 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02175-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02175-4