Abstract
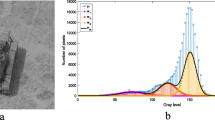
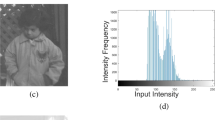
Contrast enhancement has become a vital process in improving the human perception as well as machine perception, due to the enormous application of digital imaging techniques in various fields like medical, aerospace, agriculture, machine vision, automation, surveillance, etc. During contrast enhancement by various existing techniques, the advent of adverse side effects like brightness degradation, intensity saturation and appearance of artifacts in the enhanced images is a critical issue, which needs more research attention. In this paper, an inverted Gaussian histogram specification technique for contrast enhancement of differently skewed images is proposed, in which the pixel concentration on either side of the histogram is increased to overcome the drawbacks in the existing methods. The proposed technique uses parameters like mean, standard deviation and inversion constant to generate various inverted Gaussian specified histograms. Further, transformation and objective functions are used to identify the best desired histogram so as to obtain the best enhanced image for the given image. The performance of the proposed method is compared with other existing techniques on the images taken from various standard databases. The experimental results show that the proposed technique is best suitable for contrast enhancement of images with differently skewed histograms.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
A.N. Avanaki, Exact global histogram specification optimized for structural similarity. Opt. Rev. 16(6), 613–621 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-009-0119-z
S.D. Chen, A.R. Ramli, Contrast enhancement using recursive mean-separate histogram equalization for scalable brightness preservation. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 49(4), 1301–1309 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2003.1261233
S.D. Chen, A.R. Ramli, Minimum mean brightness error bi-histogram equalization in contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 49(4), 1310–1319 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2003.1261234
D. Coltuc, P. Bolon, J.M. Chassery, Exact histogram specification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(5), 1143–1152 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2005.864170
Franzen, R.: Kodak lossless true color image suite. http://r0k.us/graphics/kodak/. Accessed 1 March 2019
R.C. Gonzalez, R.E. Woods, Digital Image Processing, 3rd edn. (Pearson Education, New Jersey, 2008)
Horita, Y., Shibata, K., Kawayoke, Y., Sazzad, Z. P.: MICT image quality evaluation database. http://mict.eng.u-toyama.ac.jp/mictdb.html. Accessed 1 March 2019
G. Jiang, C.Y. Wong, S.C.F. Lin, M.A. Rahman, T.R. Ren, N. Kwok, H. Shi, Y.-H. Yu, T. Wu, Image contrast enhancement with brightness preservation using an optimal gamma correction and weighted sum approach. J. Mod. Opt. 62(7), 536–547 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/09500340.2014.991358
S.W. Jung, Two-dimensional histogram specification using two-dimensional cumulative distribution function. Electron. Lett. 50(12), 872–874 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2014.0287
T. Kim, J. Paik, Adaptive contrast enhancement using gain-controllable clipped histogram equalization. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 54(4), 1803–1810 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2008.4711238
Y.T. Kim, Contrast enhancement using brightness preserving bi-histogram equalization. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 43(1), 1–8 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/30.580378
S. Lal, M. Chandra, Efficient Algorithm for contrast enhancement of natural images. Int. Arab. J. Inf. Technol. 11(1), 95–102 (2014). http://iajit.org/PDF/vol.11,no.1/5307.pdf
E.C. Larson, D.M. Chandler, Most apparent distortion: full-reference image quality assessment and the role of strategy. J. Electron. Imaging 19(1), 011006 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.3267105
D. Martin, C. Fowlkes, D. Tal, J. Malik, A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms. In: Proc. of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition and Measuring Ecological Statistics. 2, 416–423 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2001.937655
A. Nandal, H. Gamboa-Rosales, A. Dhaka et al., Image edge detection using fractional calculus with feature and contrast enhancement. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 37, 3946–3972 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0751-6
M. Nikolova, Y.W. Wen, R. Chan, Exact histogram specification for digital images using a variational approach. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 46(3), 309–325 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-012-0401-8
C.H. Ooi, N.P. Kong, H. Ibrahim, Bi-histogram equalization with a plateau limit for digital image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 55(4), 2072–2080 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2009.5373771
M.E. Reddy, G.R. Reddy, Recursive median and mean partitioned one-to-one gray level mapping transformations for image enhancement. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 38, 3227–3250 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-1013-3
D. Sen, S.K. Pal, Automatic exact histogram specification for contrast enhancement and visual system based quantitative evaluation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20(5), 1211–1220 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2010.2083676
H.R. Sheikh, Z. Wang, L. Cormack, A.C. Bovik, “LIVE image quality assessment database release 2”, http://live.ece.utexas.edu/research/quality. Accessed 1 March 2019
K.S. Sim, C.P. Tso, Y.Y. Tan, Recursive sub-image histogram equalization applied to gray scale images. Pattern. Recognit. Lett. 28(10), 1209–1221 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2007.02.003
C.C. Sun, S.J. Ruan, M.C. Shie, T.W. Pai, Dynamic contrast enhancement based on histogram specification. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 51(4), 1300–1305 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2005.1561859
J.R. Tang, N.A. Mat Isa, Adaptive image enhancement based on bi-histogram equalization with a clipping limit. Comput. Electr. Eng. 40(8), 86–103 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2014.05.017
Test images. http://dragon.larc.nasa.gov/retinex/pao/news/. Accessed 1 March 2019
USC-SIPI image database. http://sipi.usc.edu/database/database.php. Accessed 1 March 2019
Y. Wan, D. Shi, Joint exact histogram specification and image enhancement through the wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16(9), 2245–2250 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2007.902332
Y. Wang, Q. Chen, B. Zhang, Image enhancement based on equal area dualistic sub-image histogram equalization method. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 45(1), 68–75 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/30.754419
B. Xiao, H. Tang, Y. Jiang, W. Li, G. Wang, Brightness and contrast controllable image enhancement based on histogram specification. Neurocomputing. 275, 2798–2809 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.11.057
Y.J. Zhang, Improving the accuracy of direct histogram specification. Electron. Lett. 28(3), 213–214 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1049/el:19920132
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The work is done by the corresponding author S. Jayasankari as a part of her Ph.D. programme under the supervision and direction of Professor Dr. S. Domnic.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest/competing interests
Code Availability (Software Application or Custom Code)
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jayasankari, S., Domnic, S. Contrast Enhancement Using Inverted Gaussian Histogram Specification Technique. Circuits Syst Signal Process 40, 1252–1277 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01515-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01515-6