Abstract
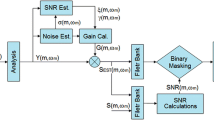
The binary mask approach has been studied recently to reduce the background noise and improve the speech intelligibility and quality in the noisy surroundings. This mask is usually applied at the time–frequency illustration of a noisy speech and discards portions of a speech below a signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) threshold, whereas allowing others to pass over intact. The threshold, however, is normally very low, and considerable residual noise would exist. Moreover, the precise estimate of local instantaneous SNR in practical applications is a difficult task. By modeling the local instantaneous SNR as Fisher–Snedecor distributed random variable, the soft masks for noise reduction are derived by incorporating SNR uncertainty in the frequency domain. Instead of finding a different method to estimate the local instantaneous SNR, the probability of local instantaneous SNR is computed higher than the threshold. The results indicated that soft masks yielded significantly better speech quality in terms of speech distortion and residual noise.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.C. Anzalone, L. Calandruccio, K.A. Doherty, L.H. Carney, Determination of the potential benefit of time-frequency gain manipulation. Ear Hear. 27(5), 480 (2006)
M. Berouti, R. Schwartz, J. Makhoul, Enhancement of speech corrupted by acoustic noise, in IEEE International Conference Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, vol. 4, pp. 208–211 (1979)
J.G. Beerends, J.A. Stemerdink, A perceptual speech-quality measure based on a psychoacoustic sound representation. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 42(3), 115–123 (1994)
S.F. Boll, Suppression of acoustic noise in speech using spectral subtraction. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 27(2), 113–120 (1979)
D.S. Brungart, P.S. Chang, B.D. Simpson, D. Wang, Isolating the energetic component of speech-on-speech masking with ideal time-frequency segregation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 120(6), 4007–4018 (2006)
N. Chatlani, J.J. Soraghan, EMD-based filtering (EMDF) of low-frequency noise for speech enhancement. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 20(4), 1158–1166 (2012)
E. Cho, J.O. Smith, B. Widrow, Exploiting the harmonic structure for speech enhancement, in Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2012, pp. 4569–4572
I. Cohen, B. Berdugo, Noise estimation by minima controlled recursive averaging for robust speech enhancement. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 9(1), 12–15 (2002)
M.A. Cooke, Glimpsing model of speech perception in noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 119(3), 1562–1573 (2006)
M.A. Cooke, P.D. Green, L. Josifovski, A. Vizinho, Robust automatic speech recognition with missing and unreliable acoustic data. Speech Commun. 34(3), 267–285 (2001)
M.A. Cooke, P.D. Green, M. Crawford, Handling missing data in speech recognition, in International Conference of Spoken Language Processing (ICSLP) (1994), pp. 1555–1558
E.J. Diethorn, Y. Huang, J. Benesty, Subband noise reduction methods for speech enhancement, in Audio Signal Processing for Next-Generation Multimedia Communication Systems (2004), pp. 91–115
G.H. Ding, T. Huang, B. Xu, Suppression of additive noise using a power spectral density MMSE estimator. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 11(6), 585–588 (2004)
P. Divenyi, Speech Separation by Humans and Machines (Springer, Berlin, 2004), pp. 13–30
D.L. Donoho, I.M. Johnstone, Adapting to unknown smoothness via wavelet shrinkage. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 90(432), 1200–1224 (1995)
Y. Ephraim, D. Malah, Speech enhancement using a minimum mean-square error log-spectral amplitude estimator. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 33(2), 443–445 (1985)
Y. Ephraim, D. Malah, Speech enhancement using a minimum-mean square error short-time spectral amplitude estimator. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 32(6), 1109–1121 (1984)
W. Etter, G.S. Moschytz, Noise reduction by noise-adaptive spectral magnitude expansion. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 42(5), 341–349 (1994)
C. Faller, J. Chen, Suppressing acoustic echo in a spectral envelope space. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 13(5), 1048–1062 (2005)
B. Gao, W.L. Woo, S.S. Dlay, Unsupervised single-channel separation of nonstationary signals using gammatone filterbank and itakura-saito nonnegative matrix two-dimensional factorizations. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 60(3), 662–675 (2013)
B. Gao, W.L. Woo, S.S. Dlay, Adaptive sparsity non-negative matrix factorization for single-channel source separation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 5(5), 989–1001 (2011)
Y. Hu, P.C. Loizou, Evaluation of objective measures for speech enhancement. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 16(1), 229–238 (2008)
Y. Hu, P.C. Loizou, Subjective evaluation and comparison of speech enhancement algorithms. Speech Commun. 49, 588–601 (2007)
N. Li, P.C. Loizou, Factors influencing intelligibility of ideal binary-masked speech: implications for noise reduction. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 123(3), 1673–1682 (2008)
Y. Li, D. Wang, On the optimality of ideal binary time-frequency masks. Speech Commun. 51(3), 230–239 (2009)
P.C. Loizou, Speech Enhancement: Theory and Practice (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2013)
R. Martin, Noise power spectral density estimation based on optimal smoothing and minimum statistics. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 9(5), 504–512 (2001)
R. McAulay, M. Malpass, Speech enhancement using a soft-decision noise suppression filter. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 28(2), 137–145 (1980)
S.L. McCabe, M.J. Denham, A model of auditory streaming, in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (1996), pp. 52–58
M.A.B. Messaoud, A. Bouzid, Sparse representations for single channel speech enhancement based on voiced/unvoiced classification. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(5), 1912–1933 (2017)
H. Momeni, H.R. Abutalebi, Generalization of maximum a posteriori amplitude estimator under speech presence uncertainty for speech enhancement. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33(8), 2565–2582 (2014)
S. Rangachari, P.C. Loizou, A noise-estimation algorithm for highly non-stationary environments. Speech Commun. 48(2), 220–231 (2006)
A.W. Rix, J.G. Beerends, M.P. Hollier, A.P. Hekstra, Perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ)-a new method for speech quality assessment of telephone networks and codecs, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processingvol. 2 (2001), pp. 749–752
N. Roman, D. Wang, Pitch-based monaural segregation of reverberant speech. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 120(1), 458–469 (2006)
N. Roman, D. Wang, G.J. Brown, Speech segregation based on sound localization. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 114(4), 2236–2252 (2003)
N. Saleem, Single channel noise reduction system in low SNR. Int. J. Speech Technol. 20(1), 89–98 (2017)
N. Saleem, M. Shafi, E. Mustafa, A. Nawaz, A novel binary mask estimation based on spectral subtraction gain-induced distortions for improved speech intelligibility and quality. Univ. Eng. Technol. Taxila. Tech. J. 20(4), 36 (2015)
N. Saleem, E. Mustafa, A. Nawaz, A. Khan, Ideal binary masking for reducing convolutive noise. Int. J. Speech Technol. 18(4), 547–554 (2015)
P. Scalart, Speech enhancement based on a priori signal to noise estimation, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing vol. 2 (1996), pp. 629–632
B.L. Sim, Y.C. Tong, J.S. Chang, C.T. Tan, A parametric formulation of the generalized spectral subtraction method. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 6(4), 328–337 (1998)
S. Srinivasan, Y. Shao, Z. Jin, D. Wang : A computational auditory scene analysis system for robust speech recognition, in International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (2006)
C.H. Taal, R.C. Hendriks, R. Heusdens, J. Jensen, An algorithm for intelligibility prediction of time-frequency weighted noisy speech. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 19(7), 2125–2136 (2011)
R. Tavares, R. Coelho, Speech enhancement with nonstationary acoustic noise detection in time domain. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23(1), 6–10 (2016)
D. Wang, G.J. Brown, Computational auditory scene analysis: principles, algorithms, and applications (Wiley-IEEE Press, Hoboken, 2006)
D. Wang, Primitive auditory segregation based on oscillatory correlation. Cognitive Sci. 20(3), 409–456 (1996)
L. Zao, R. Coelho, P. Flandrin, Speech enhancement with emd and hurst-based mode selection. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 22(5), 899–911 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editor and the anonymous reviewers for their helpful and constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saleem, N., Irfan, M. Noise Reduction Based on Soft Masks by Incorporating SNR Uncertainty in Frequency Domain. Circuits Syst Signal Process 37, 2591–2612 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0684-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0684-5