Abstract
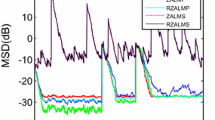
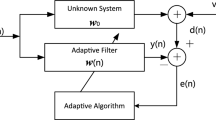
Sparse adaptive filtering algorithms are utilized to exploit system sparsity as well as to mitigate interferences in many applications such as channel estimation and system identification. In order to improve the robustness of the sparse adaptive filtering, a novel adaptive filter is developed in this work by incorporating a correntropy-induced metric (CIM) constraint into the least logarithmic absolute difference (LLAD) algorithm. The CIM as an \(l_{0}\)-norm approximation exerts a zero attraction, and hence, the LLAD algorithm performs well with robustness against impulsive noises. Numerical simulation results show that the proposed algorithm may achieve much better performance than other robust and sparse adaptive filtering algorithms such as the least mean p-power algorithm with \(l_{1}\)-norm or reweighted \(l_{1}\)-norm constraints.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.G. Baraniuk, E.J. Candès, R. Nowak, M. Vetterli, Compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 25(2), 12–13 (2008)
E.J. Candès, J. Romberg, T. Tao, Robust uncertainty principles? Exact signal frequency information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 52(2), 489–509 (2006)
Y. Chen, Y. Gu, A.O. Hero III, A. Hero, A.O.H. Iii, Sparse LMS for system identification, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (2009), pp. 3125–3128
B. Chen, L. Xing, J. Liang, N. Zheng, J.C. Principe, Steady-state mean-square error analysis for adaptive filtering under the maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 21(7), 880–884 (2014)
B. Chen, J.C. Principe, Maximum correntropy estimation is a smoothed MAP estimation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 19(8), 491–494 (2012)
B. Chen, J. Wang, H. Zhao, N. Zheng, J.C. Principe, Convergence of a fixed-point algorithm under maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 22(10), 1723–1727 (2015)
D.L. Donoho, Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 52(4), 1289–1306 (2006)
B. Dumitrescu, A. Onose, P. Helin, I. Tabus, Greedy sparse RLS. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(5), 2194–2207 (2012)
G. Gui, F. Adachi, Stable adaptive sparse filtering algorithms for estimating MIMO channels. IET Commun. 8(7), 1032–1040 (2014)
G. Gui, L. Xu, F. Adachi, Variable step-size based sparse adaptive filtering algorithm for estimating channels in broadband wireless communication systems. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2014(1), 1–10 (2014)
G. Gui, F. Adachi, Sparse Least Mean Fourth Filter with Zero-Attracting L1-Norm Constraint, in 9th International Conference on Information, Communications and Signal Processing (ICICS) (2013), pp. 1–5
G. Gui, L. Xu, F. Adachi, Normalized least mean square-based adaptive sparse filtering algorithms for estimating multiple-input multiple-output channels. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 15(6), 1–10 (2014)
G. Gui, F. Adachi, Improved adaptive sparse channel estimation using least mean square algorithm. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2013(1), 1–18 (2013)
W. Liu, P. Pokharel, J. Príncipe, Correntropy: properties and applications in non-Gaussian signal processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 55(11), 5286–5298 (2007)
Mike Brookes, VOICEBOX: Speech Processing Toolbox for MATLAB. http://www.ee.ic.ac.uk/hp/staff/dmb/voicebox/voicebox.html
NRSC A. M. Preemphasis/Deemphasis and broadcast audio transmission bandwidth specifications (ANSI/EIA-549-88), Standard ANSI/EIA-549-88 (1988)
S.C. Pei, C.C. Tseng, Least mean p-power error criterion for adaptive FIR filter. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 12(9), 1540–1547 (1994)
K. Pelekanakis, M. Chitre, New sparse adaptive algorithms based on the natural gradient and the L0-norm. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 38(2), 323–332 (2013)
G. Su, J. Jin, Y. Gu, J. Wang, Performance analysis of l0 norm constraint least mean square algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(5), 2223–2235 (2012)
M. Shao, C.L. Nikias, Signal processing with fractional lower order moments: stable processes and their applications. Proc. IEEE 81(7), 986–1010 (1993)
J. Shin, J. Yoo, P. Park, Variable step-size affine projection sign algorithm. Electron. Lett. 48(9), 483 (2012)
M.O. Sayin, N.D. Vanli, S.S. Kozat, A novel family of adaptive filtering algorithms based on the logarithmic cost. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(17), 4411–4424 (2013)
S. Seth, J.C. Principe, Compressed Signal Reconstruction Using the Correntropy Induced Metric, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (2008), pp. 3845–3848
A. Singh, J.C. Principe, Using Correntropy as Cost Function in Adaptive Filters, in Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (2009), pp. 2950–2955
R. Tibshirani, Regression Shrinkage and Selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. 58(1), 267–288 (1996)
O. Taheri, S.A. Vorobyov, Sparse Channel Estimation with lp-Norm and Reweighted l1-Norm Penalized Least Mean Squares, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (2011), pp. 2864–2867
O. Taheri, S. Vorobyov, Decimated Least Mean Squares for Frequency Sparse Channel Estimation, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal (ICASSP) (2012), pp. 3181–3184
F. Wen, System identification using reweighted zero attracting least absolute deviation algorithm. 1(1) (2011). arXiv:1110.2907
F. Wen, Diffusion least-mean p-power algorithms for distributed estimation in alpha-stable noise environments. Electron. Lett. 49(21), 1355–1356 (2013)
S. Zhao, B. Chen, J.C. Principe, Kernel Adaptive Filtering with Maximum Correntropy Criterion, in Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (2011), pp. 2012–2017
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. M. N. S. Swamy, the Editor-in-Chief for his help in improving the presentation of the paper. This work was supported by 973 Program (No. 2015CB351703) and National Natural Science Foundation of China Grants (No. 61372152, No. 61401069) as well as Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) research Grants (No. 26889050, No. 15K06072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
In this appendix, we give the evaluations of the computational complexity of (6). First, we rewrite the algorithm as
where \(A(n)=\frac{\mu \tau e(n)}{1+\tau |e(n)|}X(n)\), \(B(n)=-\frac{\rho }{M\sigma ^{3}\sqrt{2\pi }}W(n).^{*}\exp \left( {-\frac{W(n).^{*} W(n)}{2\sigma ^{2}}} \right) \).
The detailed evaluations of the computational complexity per iteration are then shown in Table 2.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, W., Chen, B., Zhao, H. et al. Sparse Least Logarithmic Absolute Difference Algorithm with Correntropy-Induced Metric Penalty. Circuits Syst Signal Process 35, 1077–1089 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-015-0098-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-015-0098-1