Abstract
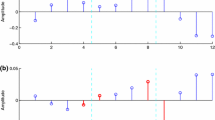
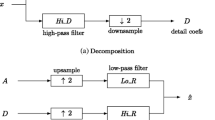
A scheme jointly exploring the rational dither modulation (RDM) and auditory masking properties in the discrete wavelet transform (DWT) domain is proposed to achieve effective blind audio watermarking. The embedding of binary information is carried out by modulating coefficient vectors in the 5th-level approximation subband using the quantization steps estimated from past watermarked vectors. The robustness and payload capacity of the proposed scheme are maneuverable by varying vector dimensions, while the imperceptibility is ensured by constraining quantization noise below the auditory masking threshold. Furthermore, the periodic characteristic inherited in the RDM formulation can be used to re-establish synchronization for accurate watermark extraction. Experimental results show that the proposed DWT–RDM approach renders a near-zero objective difference grade in the perceptual evaluation of audio quality even when the signal-to-noise ratio maintains at a level near 20 dB. In most digital signal processing attacks, the bit error rates of retrieved watermarks are sufficiently low as compared to other recently developed methods with fewer payload capacities.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Al-Haj, A. Mohammad, L. Bata, DWT-based audio watermarking. Int. Arab J. Inf. Technol. 8(3), 326–333 (2011)
P. Bassia, I. Pitas, N. Nikolaidis, Robust audio watermarking in the time domain. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 3(2), 232–241 (2001)
V. Bhat, I. Sengupta, A. Das, An adaptive audio watermarking based on the singular value decomposition in the wavelet domain. Digit. Signal Process. 20(6), 1547–1558 (2010)
V. Bhat, I. Sengupta, A. Das, A new audio watermarking scheme based on singular value decomposition and quantization. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 30(5), 915–927 (2011)
B. Chen, G.W. Wornell, Quantization index modulation: a class of provably good methods for digital watermarking and information embedding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 47(4), 1423–1443 (2001)
I.J. Cox, J. Kilian, F.T. Leighton, T. Shamoon, Secure spread spectrum watermarking for multimedia. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 6(12), 1673–1687 (1997)
M. Fallahpour, D. Megias, DWT-based high capacity audio watermarking. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. E93–A(1), 331–335 (2010)
J.J. Garcia-Hernandez, M. Nakano-Miyatake, H. Perez-Meana, Data hiding in audio signal using Rational Dither Modulation. IEICE Electron. Express 5(7), 217–222 (2008)
X. He, M.S. Scordilis, An enhanced psychoacoustic model based on the discrete wavelet packet transform. J. Frankl. Inst. 343(7), 738–755 (2006)
H.-T. Hu, L.-Y. Hsu, H.-H. Chou, Perceptual-based DWPT-DCT framework for selective blind audio watermarking. Signal Process. 105, 316–327 (2014)
H.-T. Hu, L.-Y. Hsu, H.-H. Chou, Variable-dimensional vector modulation for perceptual-based DWT blind audio watermarking with adjustable payload capacity. Digit. Signal Process. 31, 115–123 (2014)
H.-T. Hu, W.-H. Chen, A dual cepstrum-based watermarking scheme with self-synchronization. Signal Process. 92(4), 1109–1116 (2012)
ITU-R Recommendation, BS. 1387, Method for objective measurements of perceived audio quality. (1998)
P. Kabal, An examination and interpretation of ITU-R BS.1387: perceptual evaluation of audio quality, TSP Lab Technical Report, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, McGill University, (2002)
S. Katzenbeisser, F.A.P. Petitcolas (Eds.), Information hiding techniques for steganography and digital watermarking (Artech House, Boston, 2000)
B.Y. Lei, I.Y. Soon, Z. Li, Blind and robust audio watermarking scheme based on SVD–DCT. Signal Process. 91(8), 1973–1984 (2011)
B. Lei, I.Y. Soon, F. Zhou, Z. Li, H. Lei, A robust audio watermarking scheme based on lifting wavelet transform and singular value decomposition. Signal Process. 92(9), 1985–2001 (2012)
X. Li, H.H. Yu, Transparent and robust audio data hiding in cepstrum domain. IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, (2000), pp. 397–400
W.-N. Lie, L.-C. Chang, Robust and high-quality time-domain audio watermarking based on low-frequency amplitude modification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 8(1), 46–59 (2006)
S.C. Liu, S.D. Lin, BCH code-based robust audio watermarking in cepstrum domain. J. Inf. Sci. Eng. 22(3), 535–543 (2006)
J. Liu, K. She, A hybrid approach of DWT and DCT for rational dither modulation watermarking. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 31(2), 797–811 (2012)
D. Megías, J. Serra-Ruiz, M. Fallahpour, Efficient self-synchronised blind audio watermarking system based on time domain and FFT amplitude modification. Signal Process. 90(12), 3078–3092 (2010)
G.R. Naik, D.K. Kumar, An overview of independent component analysis and its applications. Inform. Int. J. Comput. Inform. 35(1), 63–81 (2009)
G.R. Naik, W. Wang, Audio analysis of statistically instantaneous signals with mixed Gaussian probability distributions. Int. J. Electron. 99(10), 1333–1350 (2012)
T. Painter, A. Spanias, Perceptual coding of digital audio. Proc. IEEE 88(4), 451–515 (2000)
F. Perez-Gonzalez, C. Mosquera, M. Barni, A. Abrardo, Rational dither modulation: a high-rate data-hiding method invariant to gain attacks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53(10), 3960–3975 (2005)
J. Seok, Audio watermarking using independent component analysis. J. Inf. Commun. Converg. Eng. 10(2), 175–180 (2012)
R. Tachibana, S. Shimizu, S. Kobayashi, T. Nakamura, An audio watermarking method using a two-dimensional pseudo-random array. Signal Process. 82(10), 1455–1469 (2002)
I.D. Toolbox, http://cogsys.imm.dtu.dk/toolbox/ica/
X. Wang, W. Qi, P. Niu, A new adaptive digital audio watermarking based on support vector regression. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 15(8), 2270–2277 (2007)
H. Wang, R. Nishimura, Y. Suzuki, L. Mao, Fuzzy self-adaptive digital audio watermarking based on time-spread echo hiding. Appl. Acoust. 69(10), 868–874 (2008)
X.-Y. Wang, P.-P. Niu, H.-Y. Yang, A robust digital audio watermarking based on statistics characteristics. Pattern Recognit. 42(11), 3057–3064 (2009)
X.-Y. Wang, P.-P. Niu, M.-Y. Lu, A robust digital audio watermarking scheme using wavelet moment invariance. J. Syst. Softw. 84(8), 1408–1421 (2011)
X. Wang, P. Wang, P. Zhang, S. Xu, H. Yang, A norm-space, adaptive, and blind audio watermarking algorithm by discrete wavelet transform. Signal Process. 93(4), 913–922 (2013)
X.-Y. Wang, H. Zhao, A novel synchronization invariant audio watermarking scheme based on DWT and DCT. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(12), 4835–4840 (2006)
L. Wei, X. Xiangyang, L. Peizhong, Localized audio watermarking technique robust against time-scale modification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 8(1), 60–69 (2006)
S. Wu, J. Huang, D. Huang, Y.Q. Shi, Efficiently self-synchronized audio watermarking for assured audio data transmission. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 51(1), 69–76 (2005)
H.-T. Wu, Y.-M. Cheung, Secure watermarking on 3D geometry via ICA and orthogonal transformation, in Transactions on Data Hiding and Multimedia Security VII, ed. by Y. Shi (Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, 2012), pp. 52–62
S. Xiang, H.J. Kim, J. Huang, Audio watermarking robust against time-scale modification and MP3 compression. Signal Process. 88(10), 2372–2387 (2008)
S. Xiang, Audio watermarking robust against D/A and A/D conversions. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2011(1), 1–14 (2011)
I.-K. Yeo, H.J. Kim, Modified patchwork algorithm: a novel audio watermarking scheme. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 11(4), 381–386 (2003)
X. Zhao, Y. Guo, J. Liu, Y. Yan, Quantization index modulation audio watermarking system using a psychoacoustic model, in 8th International Conference on Information, Communications and Signal Processing (ICICS) (2011),pp. 1–4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, ROC under Grant MOST 103-2221-E-197-020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, HT., Hsu, LY. A DWT-Based Rational Dither Modulation Scheme for Effective Blind Audio Watermarking. Circuits Syst Signal Process 35, 553–572 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-015-0074-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-015-0074-9