Abstract
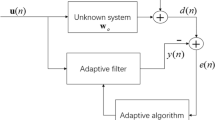
One of the main benefits of the cyclostationary beamforming algorithms is their ability to extract signals from co-channel interference with only a knowledge of the cycle frequency. In this paper, we study the popular cyclostationary beamformers, and propose five new algorithms, namely, the adaptive cyclic adaptive beamforming (ACAB), adaptive cross-SCORE (ACS), constrained least-squares (CLS), adaptive phase-SCORE (APS), and maximal constrained autocorrelation (MCA) algorithms. All these algorithms are adaptive and have a computational complexity of O(n 2) complex multiplications, where n is the number of array elements. A comparative study of these algorithms is made based on numerical simulations. Each of these algorithms has specific application scenarios. The ACS and the APS algorithms are particularly suited for very adverse signal environments. The ACAB, MCA and cyclic adaptive beamforming (CAB, from the work of Wu and Wong) algorithms can provide good performance in the case of medium or weak interference, while the CLS algorithm is especially suitable for weak interference. The CAB algorithm is shown to be a special case of the least-square self-coherent restoral (LS-SCORE) algorithm. Some insights as to how one can assign carrier frequency and symbol rate during digital modulation are also suggested. The proposed adaptive algorithms are easy to implement, and thus are very promising for applications in wireless and mobile communications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agee, B.G., Schell, S.V., Gardner, W.A.: Spectral self-coherence restoral: a new approach to blind adaptive signal extraction using antenna arrays. Proc. IEEE 78(4), 753–767 (1990)
Castedo, L., Figueiras-Vidal, A.R.: An adaptive beamforming technique based on cyclostationary signal properties. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 43(7), 1637–1650 (1995)
Charge, P., Wang, Y., Saillard, J.: Adaptive beamforming for cyclostationary signals. In: IEEE ICASSP, Hong Kong, vol. 5, pp. 349–352 (2003)
Cui, J., Falconer, D.D., Sheikh, A.U.H.: Blind adaptation of antenna arrays using a simple algorithm based on small frequency offsets. IEEE Trans. Commun. 46(1), 61–70 (1998)
Du, K.-L., Swamy, M.N.S.: Simple and practical cyclostationary beamforming algorithms. IEE Proc. Vis. Image Signal Process. 151(3), 175–179 (2004)
Gao, Y., Xiao, X.C., Tang, H.Y.: Estimation of cycle frequency for multiple cyclostationary signals. In: Proc. ICSP’98, Beijing, China, pp. 331–334 (1998)
Gardner, W.A.: Exploitation of spectral redundancy in cyclostationary signals. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 8(2), 14–36 (1991)
Hung, H.S., Hsiao, H.Y., Chien, Y.L.: A new blind adaptive beamformer for underwater communications. In: IEEE Oceans 2003 Proc., San Diego, vol. 3, pp. 1640–1646 (2003)
Lee, J.-H., Lee, Y.-T.: Robust adaptive array beamforming for cyclostationary signals under cycle frequency error. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 47(2), 233–241 (1999)
Lee, J.-H., Lee, Y.-T.: Efficient robust adaptive beamforming for cyclostationary signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 48(7), 1893–1901 (2000)
Monzingo, R.A., Miller, T.W.: Introduction to Adaptive Arrays. Wiley, New York (1980)
Petrus, P., Reed, J.H.: Cochannel interference rejection for AMPS signals using spectral correlation properties and an adaptive array. In: Proc. IEEE 45th Vehicular Technology Conference, Part 1 (of 2), Chicago, IL, USA, vol. 1, pp. 30–34 (1995)
Schell, S.V., Agee, B.G.: Application of the SCORE algorithm and SCORE extensions to sorting in the rank-L spectral self-coherence environment. In: Proc. of 22nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, pp. 274–278 (1988)
Schell, S.V., Gardner, W.A.: Blind adaptive spatio-temporal filtering for wide-band cyclostationary signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 41(5), 1961–1964 (1993)
Stewart, G.W.: Introduction to Matrix Computations. Academic Press, New York (1973)
Tang, H., Wong, K.M., Gershman, A.B., Vorobyov, S.: Blind adaptive beamforming for cyclostationary signals with robustness against cycle frequency mismatch. In: Proc. IEEE Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop, Rosslyn, VA, USA, pp. 18–22 (2002)
Vo, B., Ma, N., Ching, P.C., Wong, K.M.: Tracking moving speech source using cyclic adaptive beamforming. Electron. Lett. 36(19), 1666–1668 (2000)
Wu, Q., Wong, K.M.: Blind adaptive beamforming for cyclostationary signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 44(11), 2757–2767 (1996)
Yu, S.-J., Lee, J.-H.: Adaptive array beamforming for cyclostationary signals. IEEE Trans. Antenna Propag. 44(7), 943–953 (1996)
Zhang, J., Liao, G., Wang, J.: A novel robust adaptive beamforming for cyclostationary signals. In: Proc. IEEE 7th Int. Conf on Signal Processing (ICSP’04), Beijing, China, vol. 1, pp. 339–342 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the NSERC of Canada.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, KL., Swamy, M.N.S. A Class of Adaptive Cyclostationary Beamforming Algorithms. Circuits Syst Signal Process 27, 35–63 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-007-9009-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-007-9009-4