Abstract
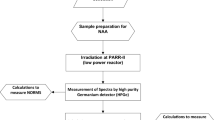
A study was carried out on the concentrations of elements presented in beach black sand samples collected from North of Nile Delta along Mediterranean Coast using instrumental neutron activation analysis (INAA) as an effective analysis technique, especially for monitoring elements. The Egyptian Research Reactor-2 (ETRR-2) as a facility was used for the samples irradiation in the thermal mode of a neutron flux 3 × 1011 n/cm2 s. Natural radioactive elements, rare element and heavy elements as U, Th, La, Lu, Sm, Ce, Nd, Eu, Gd, Sc, Tb, Yb, As, Br, Na, Sb, Ba, Co, Cr, Fe, Hg, Hf, Sr, Ta, Zn and Zr were determined with concentrations average values 16.3, 78.8, 195.4, 3.3, 31.3, 445.1, 223, 7.2, 8.5, 97.1, 3.6, 31.1, 6.1, 24.5, 27,236.8, 1.42, 1327.7, 81.1, 1814.3, 263,735, 0.1, 237.3, 878.7, 20.8, 671.1 and 6225.9 (mg/kg), respectively. The experimental data results were analyzed to evidence any correlations of these elements as well as to know the geological formation in the study area. The elements concentrations in the black sand samples were found higher than the world average crustal soil values except for As and Sb. Results were compared with similar beach black sand in previous studies. The enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index (I geo) for heavy elements were presented to evaluate the contamination rate. We can summarize that exposure for natural radionuclides (U and Th) in this area were still within the acceptable limits due to little time of exposure. Therefore, the black sands from North of Nile Delta are not recommended for use in building constructions due to high radioactive doses.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashraf, H., & Hassan, A. M. (2012). Evaluation of Gd, Sm and Eu in Egyptian monazite samples using the prompt neutron capture gamma-ray technique. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 291, 617–621.
Attiah, A. M. (2011). Environmental Assessment of Rosetta Area, Mediterranean Sea Coast—Egypt (MS.D. Thesis). Fac. Sci., Zagazig University, Egypt.
Badawy, M. W., Ghanim, E. H., Duliu, O. G., El Samman, H., & Frontasyeva, M. V. (2017). Major and trace element distribution in soil and sediments from the Egyptian central Nile Valley. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 131, 53–61.
Collier, D. E., Brown, S. A., Blagojevic, N., Soldenhoff, K. H., & Ring, R. J. (2001). Thorium in mineral products. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 97, 177–180.
Connelly, N. G., & Damhus, T. (2005). Nomenclature of inorganic chemistry: IUPAC recommendations 2005. Cambridge: RSC Publishing.
Donega, H. M., & Burgess, T. E. (1970). Atomic absorption analysis by flameless atomization in a controlled atmosphere. Annali di Chimica, 42, 1521–1524.
Durrance, E. M. (1986). Radioactivity in geology principles and applications. New York: Wiley.
EI-Taher, A., Nossair, A., Azzam, A. H., Kratz, K. L., & Abdel-Halim, A. S. (2004). Determination of traces of uranium and thorium concentration in some Egyptian environmental matrices by instrumental neutron activation analysis. In Proceedings of the Environmental Physics Conference, 24–28 Feb (pp. 141–149). Egypt: Mania.
El-Taher, A. (2010). INAA and DNAA for uranium determination in geological samples from Egypt. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 68, 1189–1192.
Eman, S. (2016). Determination of the elements concentration in Egyptian black sand using the neutron activation analysis technique. Current Science International, 5, 307–313.
Frontasyeva, M. V., Badawy, M. W., Ali, K., El_Samman, M. H., Gundorina, S. F., & Duliu, O. G. (2015). Instrumental neutron activation analysis of soil and sediment samples from Siwa Oasis, Egypt. Physics of Particles and Nuclei Letters, 12, 637–644.
Glascock, D. M. (2014). Overview of neutron activation analysis. Columbia: Missouri University Archaeometry Laboratory.
Grindlay, G., Gras, L., Mora, J., & de Loos-Vollebregt, M. T. C. (2016). Carbon-sulfur and phosphorus-based charge transfer reactions in inductively coupled plasma–atomic emission spectrometry. Spectrochemical Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 115, 8–15.
Hall, G. E. M., & Pelchat, J. C. (1994). Analysis of geological materials for gold, platinum and palladium at low ppb levels by fire assay-ICP mass spectrometry. Chemical Geology, 115(1–2), 61–72.
IAEA. (2003) Thorium fuel utilization: Options and trends. IAEA TECDOC-1319.
Ibrahim, N. (1994). Isotope identification of Langkawi black sand using neutron activation analysis. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 186(6), 489–494.
Jorge, A. P. S., Enzweiler, J., Shibuya, E. K., Sarkis, J. E. S., & Figueiredo, A. M. G. (1998). Platinum group elements and gold determination in NiS fire assay buttons by UV laser ablation ICPMS. Geostandards Newsletter, 22(1), 47–55.
Knoll, G. F. (2000). Radiation detection and measurement. New York: Wiley Press.
Maiorino, J. R., & Carluccio, T. (2004). A review of thorium utilization as an option for advanced fuel cycle-potential option for brazil in the future. In ANES 2004: Americas Nuclear Energy Symposium, Miami Beach, Florida, 3–6 October.
Majerle, M. (2009). Monte Carlo methods in spallation experiments (Ph.D. thesis). Prague: Czech Technical University.
Maurizio, Barbieri. (2016). The importance of enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index (Igeo) to evaluate the soil contamination. Journal of Geology & Geophysics, 5(1), 1–4.
Moharram, B. M., Shakir, N. S., & Hafez, A. F. (1991). Major, minor, trace elements and natural radioactivity content by NAA of some materials. Isotopenpraxis, 24(7), 199–200.
Nada, A., Abd El-Maksoud, T. M., Abu Zeid, H., El-asy, I. E., Mostafa, S. M. I., & Abd El-Azeem, S. A. (2012). Correlation between radionuclides associated with zircon and monazite in beach sand of Rosetta, Egypt. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 291, 601–610.
Paul, A. C., Pillai, P. M. B., Horidasan, P. P., & Radhakrishnan, S. (1998). Population exposure to airborne thorium at the high natural radiation areas in India. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 40(3), 251–259.
Rahman, M., Molla, N. I., Sharif, A. K. M., Basunia, S., Islam, S., Miah, R. V., et al. (1993). Determination of uranium and thorium in rock samples from Harargaj anticline by instrumental neutron activation analysis. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 173(1), 17–22.
Rekhakutty, R., Saharabudhe, S. G., Chakraborty, P. P., Iyenger, T. S., & Iyer, M. R. (1993). Passive and active measurements of Egyptian monazite samples. Bullatein of Radiation Protection, 16(1–2), 147–150.
Rojkovic, I., Medved, J., & Walzel, E. (1989). Rare earth from uranium mineralization occurrences in the Permian of the Gemericum, the Western Carpathians. Goologicky Zbornik Geologica Carpathica, 40, 453–469.
Tilch, J., Schuster, M., & Schwarzer, M. (2000). Determination of palladium in airborne particulate matter in a German city. Fresenius Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 367(5), 450–453.
Tsai, C. S., & Yeh, S. J. (1997). Determination of rare earth elements in Taiwan monazite by chemical neutron activation analysis. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 216, 241–245.
Tsegaye Birhanu, W., Chaueby, A. K., Tessema Teklemariam, T., Muhammed Dewud, B. B., & Funtua, I. I. (2015). Application of instrumental neutron activation analysis (INAA) in the analysis of essential elements in six endemic Ethiopian medicinal plants. International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR), 19(1), 213–227.
Turekian, K. K., & Wedepohl, K. H. (1961). Distribution of elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 72, 175–192.
U.S. Department of Energy (1993). DOE Fundamentals handbook: Nuclear physics and reactor theory, DOE-HDBK-1019/2-93II.
Vasconcelos, D.C., Oliveira, A.H., Silva, M.R., Penna, R., Santos, T.O., Pereira, C. et al., (2009). Determination of Uranium and thorium activity concentrations using activation analysis beach sands from extreme South Bahia, Brazil. International Nuclear Atlantic Conference 27 September–2 October, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil.
Viers, J., Dupre, B., & Gaillardet, G. (2009). Chemical composition of suspended sediments in World Rivers: New insights from a new database. Science of the Total Environment, 407, 853–868.
Win, D. T. (2004). Neutron activation analysis (NAA). AU Journal of Technology, 8(1), 8–14.
Yuya, K., Kenta, H., & Nakamura, T. (2017). Enhancement of the atomic absorbance of Cr, Zn, Cd, and Pb in metal furnace atomic absorption spectrometry using absorption tubes. Analytical Chemistry Research, 11, 9–12.
Zaim, N. (2016). Neutron activation analysis of soil samples from different parts of Edirne in Turkey. Journal of Applied Spectroscopy, 83(2), 296–300.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, A., Fayez-Hassan, M., Mansour, N.A. et al. Elemental Analysis and Radionuclides Monitoring of Beach Black Sand at North of Nile Delta, Egypt. Pure Appl. Geophys. 175, 2269–2278 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-017-1757-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-017-1757-x