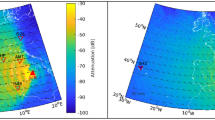
Abstract
Volcanoes generate a broad range of seismo-volcanic and infrasonic signals, whose features and variations are often closely related to volcanic activity. The study of these signals is hence very useful in the monitoring and investigation of volcano dynamics. The analysis of seismo-volcanic and infrasonic signals requires specifically developed techniques due to their unique characteristics, which are generally quite distinct compared with tectonic and volcano-tectonic earthquakes. In this work, we describe analysis methods used to detect and locate seismo-volcanic and infrasonic signals at Mt. Etna. Volcanic tremor sources are located using a method based on spatial seismic amplitude distribution, assuming propagation in a homogeneous medium. The tremor source is found by calculating the goodness of the linear regression fit (R 2) of the log-linearized equation of the seismic amplitude decay with distance. The location method for long-period events is based on the joint computation of semblance and R 2 values, and the location method of very long-period events is based on the application of radial semblance. Infrasonic events and tremor are located by semblance–brightness- and semblance-based methods, respectively. The techniques described here can also be applied to other volcanoes and do not require particular network geometries (such as arrays) but rather simple sparse networks. Using the source locations of all the considered signals, we were able to reconstruct the shallow plumbing system (above sea level) during 2011.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiuppa, A., et al. (2010), Patterns in the recent 2007–2008 activity of Mount Etna volcano investigated by integrated geophysical and geochemical observations, Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 11, Q09008, doi:10.1029/2010GC003168.
Allard, P., Behncke, B., D’Amico, S., Neri, M., and Gambino, S. (2006), Mount Etna 1993 – 2005: Anatomy of an evolving eruptive cycle, Earth Sci. Rev., 78, 85–114, doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2006.04.002.
Almendros, J., Chouet, B., and Dawson, P. (2001), Spatial extent of a hydrothermal system at Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii, determined from array analyses of shallow long-period seismicity 1. Method, J. Geophys. Res. 106(B7), 13,565–13,580, doi:10.1029/2001JB000310.
Almendros, J., Chouet, B., Dawson, P., and Bond, T. (2002), Identifying elements of the plumbing system beneath Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii, from the source locations of very-long period signals, Geophys. J. Int. 148, 303–312.
Almendros, J., and Chouet, B. (2003), Performance of the radial semblance method for the location of very long period volcanic signals, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 93, 1890–1903.
Alparone, S., Cannata, A., and Gresta, S. (2007), Time variation of spectral and wavefield features of volcanic tremor at Mt. Etna (January–June 1999), J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2006.12.012.
Battaglia, J., and Aki, K. (2003), Location of seismic events and eruptive fissures on the Piton de la Fournaise volcano using seismic amplitudes, J. Geophys. Res. 108(B8), 2364, doi:10.1029/2002JB002193.
Battaglia, J., Got, J.-L., and Okubo, P. (2003), Location of long-period events below Kilauea Volcano using seismic amplitudes and accurate relative relocation, J. Geophys. Res., 108(B12), 2553, doi:10.1029/2003JB002517, 2003.
Battaglia, J., Aki, K., and Ferrazzini, V. (2005), Location of tremor sources and estimation of lava output using tremor source amplitude on the Piton de la Fournaise volcano: 1. Location of tremor sources, J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 147, 268–290.
Cannata, A., Hellweg, M., Di Grazia, G., Ford, S., Alparone, S., Gresta, S., Montalto, P., and Patanè, D. (2009a), Long period and very long period events at Mt. Etna volcano: Characteristics, variability and causality, and implications for their sources, J. Volcanol. Geothherm. Res. 187, 227–249, doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2009.09.007.
Cannata, A., Montalto, P., Privitera, E., Russo, G., and Gresta, S. (2009b), Tracking eruptive phenomena by infrasound: May 13, 2008 eruption at Mt. Etna, Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, doi:10.1029/2008GL036738.
Cannata, A., Montalto, P., Privitera, E., and Russo, G. (2009c), Characterization and location of infrasonic sources in active volcanoes: Mt. Etna, September–November 2007, J. Geophys. Res. 114, doi:10.1029/2008JB006007.
Cannata, A., Di Grazia, G., Montalto, P., Ferrari, F., Nunnari, G., Patanè, D., and Privitera, E. (2010a), New insights into banded tremor from the 2008–2009 Mount Etna eruption, J. Geophys. Res. 115, B12318, doi:10.1029/2009JB007120.
Cannata, A., Di Grazia, G., Montalto, P., Aliotta, M., Patanè, D., and Boschi, E. (2010b), Response of Mount Etna to dynamic stresses from distant earthquakes, J. Geophys. Res. 115, B12304, doi:10.1029/2010JB007487.
Cannata, A., Montalto, P., Aliotta, M., Cassisi, C., Pulvirenti, A., Privitera, E., and Patanè, D. (2011a), Clustering and classification of infrasonic events at Mount Etna using pattern recognition techniques, Geophysical Journal International 185, 253–264, doi:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.04951.x.
Cannata, A., Sciotto, M., Spampinato, L. and Spina, L. (2011b), Insights into explosive activity at closely-spaced eruptive vents using infrasound signals: Example of Mt. Etna 2008 eruption, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 208(1–2), 1–11, doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2011.09.003.
Chouet, B. (1996), Long-period volcano seismicity: its source and use in eruption forecasting, Nature 380, 309–316.
Chouet, B. (2003), Volcano seismology, Pure Appl. Geophys. 160, 739–788.
Coltelli, M., Patanè, D., Aiuppa, A., Aliotta, M., Aloisi, M., Behncke, B., Cannata, A., Cannavò, F., Di Grazia, G., Gambino, S., Gurrieri, S., Mattia, M., Montalto, P., Prestifilippo, M., Puglisi, G., Salerno, G., Scandura, D. (2012), Insight into eruptive cyclic behavior of Mount Etna during 2011: geophysical and geochemical constraints, Geophysical Research Abstracts, EGU2012-1992.
Dawson, P. B., Benítez, M. C., Chouet, B. A., Wilson, D., and Okubo, P. G. (2010), Monitoring very‐long‐period seismicity at Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii, Geophys. Res. Lett., 37, L18306, doi:10.1029/2010GL044418.
Davi, R., O’Brien, G.S., De Barros, L., Lokmer, I., Bean, C.J., Lesage, P., Mora, M.M., and Soto, G.J., (2012), Seismic source mechanisms of tremor recorded on Arenal volcano, Costa Rica, retrieved by waveform inversion, J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2011.10.008.
De Barros, L., Lokmer, I., Bean, C. J., O’Brien, G. S., Saccorotti, G., Métaxian, J.‐P., Zuccarello, L., and Patanè, D. (2011), Source mechanism of long‐period events recorded by a high‐density seismic network during the 2008 eruption on Mount Etna, J. Geophys. Res., 116, B01304, doi:10.1029/2010JB007629.
Di Grazia, G., Falsaperla, S., and Langer, H. (2006), Volcanic tremor location during the 2004 Mount Etna lava effusion, Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L04304, doi:10.1029/2005GL025177.
Di Grazia, G., Cannata, A., Montalto, P., Patanè, D., Privitera, E., Zuccarello, L., and Boschi, E. (2009), A new approach to volcano monitoring based on 4D analyzes of seismo‐volcanic and acoustic signals: the 2008 Mt. Etna eruption, Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L18307, doi:10.1029/2009GL039567.
Efron, B., The Jackknife, the Bootstrap and Other Resampling Plans (Soc. for Ind. and Appl. Math., Philadelphia, Pa., 1982).
Falsaperla, S., Alparone, S., D’Amico, S., Di Grazia, G., Ferrari, F., Langer, H., Sgroi, T., and Spampinato, S. (2005), Volcanic tremor at Mt. Etna, Italy, preceding and accompanying the eruption of July–August, 2001, Pure Appl. Geophys. 162, 1–22.
Fee, D., Garcés, M. A., Patrick, M., Chouet, B. A., Dawson, P., and Swanson, D. (2010), Infrasonic harmonic tremor and degassing bursts from Halema’uma’u Crater, Kilauea volcano, Hawaii, J. Geophys. Res. 115, B11316, doi:10.1029/2010JB007642.
Fee, D., and Matoza, R. (2012), An overview of volcano infrasound: From Hawaiian to plinian, local to global, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2012.09.002.
Garces, M., A. Harris, C. Hetzer, J. Johnson, S. Rowland, E. Marchetti, and P. Okubo (2003), Infrasonic tremor observed at Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii, Geophys. Res. Lett. 30(20), 2023, doi:10.1029/2003GL018038.
Giudicepietro, F., D’Auria, L., Martini, M., Caputo, T., Peluso, R., De Cesare, W., Orazi, M., and Scarpato, G., (2009), Changes in the VLP seismic source during the 2007 Stromboli eruption, J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., 182, 162–171, doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2008.11.008.
Goto, A., and Johnson, J. B. (2011), Monotonic infrasound and Helmholtz resonance at Volcan Villarrica (Chile), Geophys. Res. Lett. 38, L06301, doi:10.1029/2011GL046858.
Gottschammer, E., and Surono, I. (2000), Locating tremor and shock sources recorded at Bromo volcano, J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 101, 199–209.
Gresta, S., Montalto, A., and Patanè, G. (1991), Volcanic tremor at Mt. Etna (January 1984–March 1985): its relationship to the eruptive activity and modelling of the summit feeding system, Bull. Volcanol. 53, 309–320.
Inza, L. A., Mars, J. I., Métaxian, J. P., O’Brien, G. S., and Macedo, O. (2011), Seismo-volcano source localization with triaxial broad-band seismic array : 3C seismic antenna on volcano, Geophysical J. Int., 187(1), 371, doi:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05148.x.
Johnson, J. B. (2003), Generation and propagation of infrasonic airwaves from volcanic explosions, J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., 121, 1–14, doi:10.1016/S0377-0273(02)00408-0.
Johnson, J. B., Aster, R. C., Ruiz, M. C., Malone, S. D., McChesney, P. J., Lees, J. M., and Kyle, P. R. (2003), Interpretation and utility of infrasonic records from erupting volcanoes, J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 121, 15–63, doi:10.1016/S0377-0273(02)00409-2.
Johnson, J.B. (2005), Source location variability and volcanic vent mapping with a small-aperture infrasound array at Stromboli Volcano, Italy, Bull. Volcanol. 67, 1–14.
Johnson, J.B., and Ripepe, M. (2011), Volcano infrasound: A review. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 206(3–4), 61–69, doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2011.06.006.
Jones, K.R., Johnson, J., Aster, R., Kyle, P.R., and McIntosh, W.C. (2008), Infrasonic tracking of large bubble bursts and ash venting at Erebus volcano, Antarctica, J. Volc. Geotherm. Res. 177, doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2008.02.001.
Jones, K.R., and Johnson, J.B. (2010), Mapping complex vent eruptive activity at Santiaguito, Guatemala using network infrasound semblance, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2010.08.006.
Jones, J.P., Carniel, R., and Malone, S.D. (2011), Decomposition, location, and persistence of seismic signals recovered from continuous tremor at Erta’Ale, Ethiopia, J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2011.07.007.
Kaneshima, S., Kawakatsu, H., Matsubayashi, H., Sudo, Y., Tsutsui, T., Ohminato, T., Ito, H., Uhira, K., Yamasato, H., Oikawa, J., Takeo, M., and Iidaka, T. (1996), Mechanism of phreatic eruptions at Aso Volcano inferred from near-field broadband seismic observations, Science 273, 642–645.
Kao, H., and Shan, S.J. (2004), The source-scanning algorithm: mapping the distribution of seismic sources in time and space, Geophysical Journal International 157, 589–594.
Kawakatsu, H., Kaneshima, S., Matsubayashi, H., Ohminato, T., Sudo, Y., Tsutsui, T., Uhira, K., Yamasato, H., Ito, H., and Legrand, D. (2000), Aso94: Aso seismic observation with broadband instruments, J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 101, 129–154.
Kumagai, H., Nakano, M., Maeda, T., Yepes, H., Palacios, P., Ruiz, M., Arrais, S., Vaca, M., Molina, I., and Yamashima, T. (2010), Broadband seismic monitoring of active volcanoes using deterministic and stochastic approaches, J. Geophys. Res. 115, B08303, doi:10.1029/2009JB006889.
Kumagai, H., Saito, T., O’Brien, G., and Yamashina, T. (2011), Characterization of scattered seismic wavefields simulated in heterogeneous media with topography, J. Geophys. Res., 116, B03308, doi:10.1029/2010JB007718.
Langer, H., and Falsaperla, S. (1996), Long‐term observation of volcanic tremor on Stromboli Volcano (Italy): A synopsis, Pre Appl. Geophys. 147, 57–82.
Le Pichon, A., and Cansi, Y. (2003), PMCC for infrasound data processing, Inframatics 2, 1–9.
Lombardo, G., Coco, G., Corrao, M., and Gresta, S. (1996), Features of seismic events and volcanic tremor during the preliminary stages of the 1991–1993 eruption of Mt. Etna, Ann. Geophys. 39, 403–410.
Matoza, R.S., Hedlin, M., and Garces, M. (2007), An infrasound array study of Mount St. Helens, J. Volc. Geotherm. Res. 160, 249–262.
Matoza, R. S., Fee, D., and Garcés, M. A. (2010), Infrasonic tremor wavefield of the Pu`u `Ō`ō crater complex and lava tube system, Hawaii, in April 2007, J. Geophys. Res. 115, B12312, doi:10.1029/2009JB007192.
Matsubara, W., Yomogida, K., Koyama, J., Kasahara, M., Ichiyanagi, M., Kawakatsu, H., and Yamamoto, M. (2004), Distribution and characteristics in waveform and spectrum of seismic events associated with the 2000 eruption of Mt. Usu, J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 136, 141–158.
Metaxian, J.-P., Lesage, P., and Dorel, J. (1997), The permanent tremor of Masaya volcano, Nicaragua: wave field analysis and source location, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 22529–22545.
Montalto, P., Cannata, A., Privitera, E., Gresta, S., Nunnari, G., and Patanè, D. (2010), Towards an automatic monitoring system for infrasonic events at Mt. Etna: Strategies for source location and modelling, Pure Appl. Geophys. 167, 1215–1231, doi:10.1007/s00024-010-0051-y.
Neidell, N., and Taner, M.T. (1971), Semblance and other coherency measures for multichannel data, Geophysics 36, 482–497.
Neuberg, J. (2000), External modulation of volcanic activity, Geophys. J. Int. 142, 232–240.
Neuberg, J., and Pointer, T. (2000), Effects of volcano topography on seismic broad-band waveforms, Geophys. J. Int., 143, 239–248.
Nishimura, T., Nakamichi, H., Tanaka, S., Sato, M., Kobayashi, T., Ueki, S., Hamaguchi, H., Ohtake, M., and Sato, H. (2000), Source process of very-long-period seismic events associated with the 1998 activity of Iwate Volcano, northeastern Japan, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 19135–19147.
Ohminato, T., Chouet, B., Dawson, P., and Kedar, S. (1998), Waveform inversion of very long period impulsive signals associated with magmatic injection beneath Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 23839–23862.
Patanè, D., Barberi, G., Cocina, O., De Gori, P., and Chiarabba, C. (2006), Time-resolved seismic tomography detects magma intrusions at Mount Etna, Science 313, 821–823.
Patanè, D., Di Grazia, G., Cannata, A., Montalto, P., and Boschi, E. (2008), The shallow magma pathway geometry at Mt. Etna volcano, Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 9, Q12021, doi:10.1029/2008GC002131.
Ripepe, M., and Marchetti, E. (2002), Array tracking of infrasonic sources at Stromboli volcano, Geophys. Res. Lett. 29(22), 2076, doi:10.1029/2002GL015452.
Ripepe, M., Poggi, P., and Marchetti, E. (2004), Small aperture infrasonic array monitors activity of Stromboli volcano, Inframatics 7, 1–14.
Ripepe, M., Marchetti, E., and Ulivieri, G. (2007), Infrasonic monitoring at Stromboli volcano during the 2003 effusive eruption: insights on the explosive and degassing process of an open conduit system, J. Geophys. Res. 112, B09207. doi:10.1029/2006JB004613.
Ripepe, M., Marchetti, E., Bonadonna, C., Harris, A. J. L., Pioli, L., and Ulivieri, G. (2010), Monochromatic infrasonic tremor driven by persistent degassing and convection at Villarrica Volcano, Chile, Geophys. Res. Lett. 37, L15303, doi:10.1029/2010GL043516.
Saccorotti, G., Lokmer, I., Bean, C. J., Di Grazia, G., and Patane, D. (2007), Analysis of sustained long-period activity at Etna Volcano, Italy, J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., 160, 340–354.
Uhira, K., and Takeo, M. (1994), The source of explosive eruptions of Sakuajima volcano, Japan, J. Geophys. Res., 99, 17775–17789.
Withers, M., Aster, R., Young, C., Beiriger, J., Harris, M., Moore, S., and Trujillo, J. (1998), A comparison of select trigger algorithms for automated global seismic phase and event detection, Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 88, 95–106.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Phil Dawson and an anonymous reviewer for their useful suggestions that greatly improved the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cannata, A., Di Grazia, G., Aliotta, M. et al. Monitoring Seismo-volcanic and Infrasonic Signals at Volcanoes: Mt. Etna Case Study. Pure Appl. Geophys. 170, 1751–1771 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-012-0634-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-012-0634-x