Abstract
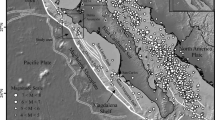
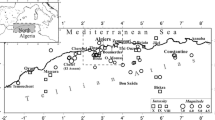
We relocated the hypocentral coordinates of small to moderate-sized earthquakes reported by the National Earthquake Information Center (NEIC) between April 2002 and August 2006 in the Gulf of California region and recorded by the broadband stations of the network of autonomously recording seismographs (NARS–Baja array). The NARS–Baja array consists of 19 stations installed in the Baja California peninsula, Sonora and Sinaloa, Mexico. The events reported by the preliminary determinations of epicenters (PDE) catalog within the period of interest have moment magnitudes (M w) ranging between 1.1 and 6.7. We estimated the hypocentral location of these events using P and S wave arrivals recorded by the regional broadband stations of the NARS–Baja and the RESBAN (Red Sismológica de Banda Ancha) arrays and using a standard location procedure with the HYPOCENTER code (Lienert and Havskov in Seism Res Lett 66:26–36, 1995) as a preliminary step. To refine the location of the initial hypocenters, we used the shrinking box source-specific station term method of Lin and Shearer (J Geophys Res 110, B04304, 2005). We found that most of the seismicity is distributed in the NW–SE direction along the axis of the Gulf of California, following a linear trend that, from north to south, steps southward near the main basins (Wagner, Delfin, Guaymas, Carmen, Farallon, Pescadero and Alarcon) and spreading centers. We compared the epicentral locations reported in the PDE with the locations obtained using regional arrival times, and we found that earthquakes with magnitudes in the range 3.2–5.0 mb differ on the average by as much as 43 km. For the M w magnitude range between 5 and 6.7 the discrepancy is less, differing on the average by about 25 km. We found that the relocated epicenters correlate well with the main bathymetric features of the Gulf.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aragón-Arreola, M., and Martin-Barajas, A. (2007), Westward migration of extension in the Northern Gulf of California, Mexico, Geology 35, 571–574
Castro, R. R., Shearer, P. M., Astiz, L., Suter, M., Jacques-Ayala, C., and Vernon, F. (2010), The Long-lasting aftershock series of the 3 May 1887 M W 7.5 Sonora Earthquake in the Mexican Basin and Range Province, Bull Seism Soc Am 100, 1153–1164
Clayton, R. W., Trampert, J., Rebollar, C. J., Ritsema, J., Persaud, P., Paulssen, H., Pérez-Campos, X., van Wettum, A., Pérez-Vertti, A., and di Luccio, F. (2004), The NARS-Baja array in the Gulf of California R ift zone, Margins Newslett 13, 1–4
DeMets, C. (1995), A reappraisal of seafloor spreading lineations in the Gulf of California: implications for the transfer of Baja California to the Pacific Plate and estimates of Pacific-North America Motion, Geophys Res Lett 22, 3545–3548
Einsele, G. (1982), Mechanism of sill intrusion into soft sediment and expulsion of pore water, Initial Rep Deep Sea Drill Proj 64, 1169–1176
Fabriol, H., Delgado-Argote, L.A., Dañobeitia, J.J., Córdoba, D., González, A., García-Abdeslem, J., Bartolomé, R., and Martín-Atienza, B. (1999), Backscattering and geophysical features of volcanic rifts offshore Santa Rosalía, Baja California Sur, Gulf of California, México, J Volcano Geotherm Res 93, 75–92
Goff, J.A., Bergman, E.A., and Solomon, S.C. (1987), Earthquake source mechanism and transform fault tectonics in the Gulf of California, J Geophys Res 92, 10485–10510
Gonzalez-Fernandez, A., Dañobeitia, J. J., Delgado-Argote, L. A., Michaud, F., Cordoba D., and Bartolomé, R. (2005), Mode of extensión and rifting history of upper Tiburón and upper Delfín basins, Northern Gulf of California, J Geophys Res 110, B01313. doi:10.1029/2003JB002941
Isacks, B., Oliver, J., and Sykes, L. (1968), Seismology and the new global tectonics, J Geophys Res 73, 5855–5899
Lienert, B. R. E., and Havskov, J. (1995), A computer program for locating earthquakes both locally and globally, Seism Res Lett 66, 26–36
Lin, G., and Shearer, P. M. (2005), Test of relative earthquake location techniques using synthetic data, J Geophys Res 110, B04304. doi:10.1029/2004JB003380.
Lomnitz, C., Mooser, F., Allen, C. R., Brune, J. N., and Thatcher, W. (1970), Seismicity and tectonics of the Northern Gulf of California region, Mexico. Preliminary Results, Geof Int 10, 37–48
Lonsdale, P. L., Geology and Tectonics History of the Gulf of California, In: The Geology of North America: The Eastern Pacific Ocean and Hawaii (The Geological Society of America 1989).
López-Pineda, L., and Rebollar, C.J. (2005), Source characteristics of the Mw 6.2 Loreto earthquake of 12 March 2003 that occurred in a transform fault in the middle of the Gulf of California, Mexico, Bull Seism Soc Am 95, 419–430
López-Pineda, L., Rebollar, C. J., and Quintanar, L. (2007), Crustal Thickness estimates for Baja California, Sonora, and Sinaloa, Mexico, using disperse surface waves, J Geophys Res, 112, B04308. doi:10.1029/2005JB003899
Molnar, P. (1973), Fault plane solutions of earthquakes and direction of motion in the Gulf of California and on the rivera fracture zone, Geol Soc Am Bull 84, 1651–1658
Nava, F. A., and Brune, J. N. (1982), An earthquake-explosion reversed refraction line in the peninsular ranges of southern California and Baja California Norte, Bull Seism Soc Am 72, 1195–1206
Pacheco, J. F., and Sykes, L. R. (1992), Seismic moment catalog of large shallow earthquakes, 1900 to 1989, Bull Seism Soc Am 82, 1306–1349
Persaud, P., Stock, J. M., Steckler, M. S., Martin-Barajas, A., Diebold, J. B., Gonzalez-Fernandez, A., and Mountain, G. S. (2003), Active deformation and shallow structure of the Wagner, Consag, and Delfin basins, northern Gulf of California, Mexico, J Geophys Res 108(B7), 2355. doi:10.1029/2002JB001937.
Phillips, R.P. (1964), Seismic refraction Studies in the Gulf of California, in Marine Geology of the Gulf of California, In Van Andel T. H., and Shor G.G., AAPG Mem 3, 90–121
Rebollar, C. J., Quintanar, L., Castro, R. R., Day, S. M., Madrid, J., Brune, J. N., Astiz, L., and Vernon, F. (2001), Source characteristics of a 5.5 magnitude earthquake that occurred in the transform fault system of the Delfin basin in the Gulf of California, Bull Seism Soc Am 91, 781–791
Reichle, M., and Reid, I. (1977), Detailed study of earthquake swarms from the Gulf of California, Bull Seism Soc Am 67, 159–171
Reid, I., Reichle, M., Brune, J., and Bradner, H. (1973), Microearthquake studies using sonobuoys, preliminary results from the Gulf of California, J R Astronom Soc 34, 365–379
Richards-Dinger, K. and Shearer P. (2000), Earthquake locations in southern California obtained using source-specific station terms, J Geophys Res, 105, 10939–10960
Rodriguez-Lozoya, H. E., Quintanar, L., Ortega, R., Rebollar, C. J., and Yagi, Y. (2008), Ruptura process of four medium-size earthquakes that occurred in the gulf of california, J Geophys Res, 113, B10301. doi:10.1029/2007JB005323.
Sykes, L. R. (1968), Seismological Evidence for Transform Faults, Sea-floor Spreading and Continental Drift, in the History of the Earth’s Crust, In (ed. Phinney), pp 120–150, Princeton Univ. Press, Princeton
Sykes, L. R., (1970), Focal mechanism solutions for earthquakes along the world rift system, Bull Seismol Soc Am 60, 1749–1752
Thatcher, W., and Brune, J. (1971), Seismic study of an oceanic ridge earthquake swarm in the Gulf of California, Geophys J R Astron Soc 22, 473–489
Trampert, J., Paulsen, H., Van Wettum, A., Ritsema, J., Clayton, R., Castro, R., Rebollar, C., and Pérez-Vertti, A. (2003), New array monitors seismic activity near the Gulf of California in México, EOS, Trans Am Geoph Union 84, 29–32
Zhang, X., Paulsen, H., Lebedev, S. and Meier, T. (2007), Surface Wave Tomography of the Gulf of California, Geophys Res Lett, 34, L15305. doi:10.1029/2007GL030631
Acknowledgments
The operation of the RESBAN array (Red Sismológica de Banda Ancha) has been possible thanks to the financial support of the Mexican National Council for Science and Technology (CONACYT) by means of the projects 48852 and COC022. The NARS–Baja array was the result of a collaboration project among Utrecht University, California Institute of Technology and CICESE. The operation and data acquisition was possible thanks to Arie van Wettum, Robert Clayton, Jeannot Trampert and Hanneke Paulssen. Part of the analysis of this paper was made while one of the authors (RRC) was a UC MEXUS-CONACYT Visiting Scholar at the University of California, San Diego, IGPP-SIO. Peter Shearer kindly provided the modified version of the COMPLOC code. The useful comments and suggestions of the editor William Lee Bandy help us to improve the manuscript. We also thank the two anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castro, R.R., Perez-Vertti, A., Mendez, I. et al. Location of Moderate-Sized Earthquakes Recorded by the NARS–Baja Array in the Gulf of California Region Between 2002 and 2006. Pure Appl. Geophys. 168, 1279–1292 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-010-0177-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-010-0177-y