Abstract.
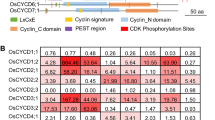
Although the majority of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) play a key role in cell cycle progression, recent evidence has shown that CDKs are also implicated in transcription regulation. Here, we describe two Arabidopsis CDKs designated Arath;CDKC;1 and Arath; CDKC;2. These CDKs share a PITAIRE signature in the cyclin-binding domain and the structural characteristics of mammalian CDK9. Yeast two-hybrid screens and immunoprecipitation assays identified CDKC-interacting proteins with homology to the animal cyclin T/cyclin K group. We suggest that these Arabidopsis CDKCs may be part of a kinase complex similar to the animal positive transcription elongation factor b, whose activity is essential for transcription control. Expression studies showed that Arath; CDKC transcripts are mainly confined to epidermal tissues and are most abundant in flower tissues. No expression was detected in actively dividing Arabidopsis tissues, suggesting a role for the CDKC proteins in differentiated cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 23 October 2002; received after revision 17 December 2002; accepted 20 December 2002
RID="*"
ID="*"Corresponding author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barrôco, R., De Veylder, L., Magyar, Z. et al. Novel complexes of cyclin-dependent kinases and a cyclin-like protein from Arabidopsis thaliana with a function unrelated to cell division. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 60, 401–412 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180300033
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180300033