Abstract.
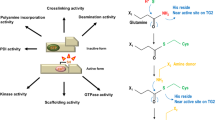
The unique structure in which six cysteine residues in a sequence of 38 or 39 amino acid residues form three disulphide bonds in a 1-5, 2-4 and 3-6 configuration constitutes the basic elements of a trefoil domain. Today three mammalian trefoil factors (TFF1, TFF2 and TFF3) containing one or two trefoil domains are known. Trefoil factors are usually associated with the mucin layer of the gastrointestinal tract. Early studies on trefoil factors concentrated on structure elucidation and sites of expression in health and disease, whereas studies over the last 3–5 years have focused on the mechanism of action and the search for specific receptors. This review summarises our present knowledge of trefoil peptide structures, their sites of expression, and their protection and repair functions, with a focus on the mechanism by which these peptides exert their biological function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thim, L. Trefoil peptides: from structure to function. CMLS, Cell. mol. life sci. 53, 888–903 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180050108
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180050108