Abstract.
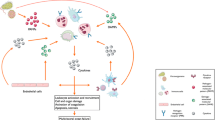
Annexin V belongs to a family of phospholipid binding proteins, the Annexins. It binds in the presence of Ca2+-ions with high affinity to negatively charged phospholipids like phosphatidylserine (PS). On the basis of its protein structure and biological activity Annexin V is considered as a protein exhibiting its hitherto unknown function within the intracellular environment. One argument comes from the understanding that PS is predominantly located in membrane leaflets, which face the cytosol. However, recent findings show that each cell type has the molecular machinery to expose PS at its cell surface. This machinery is activated during the execution of apoptosis. Once PS is exposed at the cell surface it exhibits procoagulant and proinflammatory activities. Annexin V will bind to the PS-exposing apoptotic cell and can inhibit thereby the procoagulant and pro-inflammatory activities of the dying cell. These findings together with the presence of Annexin V in the extracellular space depict a novel (patho)physiological significance for Annexin V in vivo.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reutelingsperger, C., van Heerde, W. Annexin V, the regulator of phosphatidylserine-catalyzed inflammation and coagulation during apoptosis. CMLS, Cell. mol. life sci. 53, 527–532 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180050067
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180050067