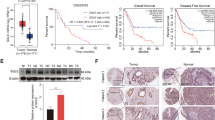
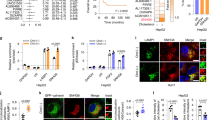
Abstract
Cholesterol biosynthesis plays a critical role in rapidly proliferating tumor cells. X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1), which was first characterized as a basic leucine zipper-type transcription factor, exists in an unspliced (XBP1-u) and spliced (XBP1-s) form. Recent studies showed that unspliced XBP1 (XBP1-u) has unique biological functions independent from XBP1-s and could promote tumorigenesis; however, whether it is involved in tumor metabolic reprogramming remains unknown. Herein, we found that XBP1-u promotes tumor growth by enhancing cholesterol biosynthesis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. Specifically, XBP1-u colocalizes with sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP2) and inhibits its ubiquitination/proteasomal degradation. The ensuing stabilization of SREBP2 activates the transcription of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGCR), a rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis. We subsequently show that the XBP1-u/SREBP2/HMGCR axis is crucial for enhancing cholesterol biosynthesis and lipid accumulation as well as tumorigenesis in HCC cells. Taken together, these findings reveal a novel function of XBP1-u in promoting tumorigenesis through increased cholesterol biosynthesis in hepatocarcinoma cells. Hence, XBP1-u might be a potential target for anti-tumor therapeutic strategies that focus on cholesterol metabolism in HCC.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed duringthis study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100(1):57–70
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144(5):646–674
Li Y, Kasim V, Yan X, Li L, Meliala ITS, Huang C, Li Z, Lei K, Song G, Zheng XJT (2019) Yin Yang 1 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma cell lipid metabolism and tumor progression by inhibiting PGC-1β-induced fatty acid oxidation. Theranostics 9(25):7599
Huang B, Song BL, Xu C (2020) Cholesterol metabolism in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Nat metab 2(2):132–141
Russell DW (1999) Nuclear orphan receptors control cholesterol catabolism. Cell 97(5):539–542
Ikonen E (2006) Mechanisms for cellular cholesterol transport: defects and human disease. Physiol Rev 86(4):1237–1261
Baenke F, Peck B, Miess H, Schulze A (2013) Hooked on fat: the role of lipid synthesis in cancer metabolism and tumour development. Dis Model Mech 6(6):1353–1363
Luo J, Yang H, Song BL (2020) Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21(4):225–245
Silvente-Poirot S, Poirot M (2012) Cholesterol metabolism and cancer: the good, the bad and the ugly. Curr Opin Pharmacol 12(6):673–676
Clendening JW, Pandyra A, Boutros PC, El Ghamrasni S, Khosravi F, Trentin GA, Martirosyan A, Hakem A, Hakem R, Jurisica I, Penn LZ (2010) Dysregulation of the mevalonate pathway promotes transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(34):15051–15056
Thurnher M, Nussbaumer O, Gruenbacher G (2012) Novel aspects of mevalonate pathway inhibitors as antitumor agents. Clin Cancer Res 18(13):3524–3531
Bathaie SZ, Ashrafi M, Azizian M, Tamanoi F (2017) Mevalonate pathway and human cancers. Curr Mol Pharmacol 10(2):77–85
Ding X, Zhang W, Li S, Yang H (2019) The role of cholesterol metabolism in cancer. Am J Cancer Res 9(2):219–227
Chimento A, Casaburi I, Avena P, Trotta F, De Luca A, Rago V, Pezzi V, Sirianni R (2018) Cholesterol and its metabolites in tumor growth: therapeutic potential of statins in cancer treatment. Front Endocrinol 9:1–14
Greenlee JD, Subramanian T, Liu K, King MR (2021) Rafting down the metastatic cascade: the role of lipid rafts in cancer metastasis, cell death, and clinical outcomes. Cancer Res 81(1):5–17
McGregor GH, Campbell AD, Fey SK, Tumanov S, Sumpton D, Blanco GR, Mackay G, Nixon C, Vazquez A, Sansom OJ, Kamphorst JJ (2020) Targeting the metabolic response to statin-mediated oxidative stress produces a synergistic antitumor response. Cancer Res 80(2):175–188
Liou HC, Boothby MR, Finn PW, Davidon R, Nabavi N, Zeleznik-Le NJ, Ting JP, Glimcher LH (1990) A new member of the leucine zipper class of proteins that binds to the HLA DR alpha promoter. Science 247(4950):1581–1584
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, Okada T, Mori K (2001) XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 107(7):881–891
Yanagitani K, Kimata Y, Kadokura H, Kohno K (2011) Translational pausing ensures membrane targeting and cytoplasmic splicing of XBP1u mRNA. Science 331(6017):586–589
Yamamoto K, Yoshida H, Kokame K, Kaufman RJ, Mori K (2004) Differential contributions of ATF6 and XBP1 to the activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-responsive cis-acting elements ERSE, UPRE and ERSE-II. J Biochem 136(3):343–350
Yoshida H, Oku M, Suzuki M, Mori K (2006) pXBP1(U) encoded in XBP1 pre-mRNA negatively regulates unfolded protein response activator pXBP1(S) in mammalian ER stress response. J Cell Biol 172(4):565–575
Huang C, Wu S, Ji H, Yan X, Xie Y, Murai S, Zhao H, Miyagishi M, Kasim V (2017) Identification of XBP1-u as a novel regulator of the MDM2/p53 axis using an shRNA library. Sci Adv 3(10):e1701383
Martin D, Li Y, Yang J, Wang G, Margariti A, Jiang Z, Yu H, Zampetaki A, Hu Y, Xu Q, Zeng L (2014) Unspliced X-box-binding protein 1 (XBP1) protects endothelial cells from oxidative stress through interaction with histone deacetylase 3. J Biol Chem 289(44):30625–30634
Zhao Y, Li X, Cai MY, Ma K, Yang J, Zhou J, Fu W, Wei FZ, Wang L, Xie D, Zhu WG (2013) XBP-1u suppresses autophagy by promoting the degradation of FoxO1 in cancer cells. Cell Res 23(4):491–507
Zhao G, Fu Y, Cai Z, Yu F, Gong Z, Dai R, Hu Y, Zeng L, Xu Q, Kong WJC (2017) Unspliced XBP1 confers VSMC homeostasis and prevents aortic aneurysm formation via FoxO4 interaction. Circ Res 121(12):1331–1345
Yang L, Dai R, Wu H, Cai Z, Xie N, Zhang X, Shen Y, Gong Z, Jia Y, Yu FJC (2022) Unspliced XBP1 counteracts β-catenin to inhibit vascular calcification. Circ Res 130(2):213–229
Kasim V, Wu S, Taira K, Miyagishi M (2013) Determination of the role of DDX3 a factor involved in mammalian RNAi pathway using an shRNA-expression library. PLoS ONE 8(3):e59445
Miyagishi M, Taira K (2003) Strategies for generation of an siRNA expression library directed against the human genome. Oligonucleotides 13(5):325–333
Wu S, Wang H, Li Y, Xie Y, Huang C, Zhao H, Miyagishi M, Kasim V (2018) Transcription factor YY1 promotes cell proliferation by directly activating the pentose phosphate pathway. Cancer Res 78(16):4549–4562
Wu S, Kasim V, Kano MR, Tanaka S, Ohba S, Miura Y, Miyata K, Liu X, Matsuhashi A, Chung UI, Yang L, Kataoka K, Nishiyama N, Miyagishi M (2013) Transcription factor YY1 contributes to tumor growth by stabilizing hypoxia factor HIF-1α in a p53-independent manner. Cancer Res 73(6):1787–1799
So JS, Hur KY, Tarrio M, Ruda V, Frank-Kamenetsky M, Fitzgerald K, Koteliansky V, Lichtman AH, Iwawaki T, Glimcher LH, Lee AH (2012) Silencing of lipid metabolism genes through IRE1α-mediated mRNA decay lowers plasma lipids in mice. Cell Metab 16(4):487–499
Casali C, Malvicini R, Erjavec L, Parra L, Artuch A, Fernandez Tomez MC (2020) X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1): a key protein for renal osmotic adaptation. Its role in lipogenic program regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1865(4):1–30
Sundqvist A, Bengoechea-Alonso MT, Ye X, Lukiyanchuk V, Jin J, Harper JW, Ericsson J (2005) Control of lipid metabolism by phosphorylation-dependent degradation of the SREBP family of transcription factors by SCF(Fbw7). Cell Metab 1(6):379–391
Salghetti SE, Kim SY, Tansey WP (1999) Destruction of Myc by ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis: cancer-associated and transforming mutations stabilize Myc. Embo J 18(3):717–726
Nickels JT Jr (2018) New links between lipid accumulation and cancer progression. J Biol Chem 293(17):6635–6636
Kuzu OF, Noory MA, Robertson GP (2016) The role of cholesterol in cancer. Cancer Res 76(8):2063–2070
Jiang S, Wang X, Song D, Liu X, Gu Y, Xu Z, Wang X, Zhang X, Ye Q, Tong Z, Yan B, Yu J, Chen Y, Sun M, Wang Y, Gao S (2019) Cholesterol induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer cells by suppressing degradation of EGFR through APMAP. Cancer Res 79(12):3063–3075
McDonnell DP, Park S, Goulet MT, Jasper J, Wardell SE, Chang C-y, Norris JD, Guyton JR, Nelson ER (2014) Obesity, cholesterol metabolism, and breast cancer pathogenesis. Cancer Res 74(18):4976–4982
Xu H, Xia H, Zhou S, Tang Q, Bi F (2021) Cholesterol activates the Wnt/PCP-YAP signaling in SOAT1-targeted treatment of colon cancer. Cell Death Discov 7(1):1–13
Murillo-Garzón V, Kypta R (2017) WNT signalling in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol 14(11):683–696
Shafique K, McLoone P, Qureshi K, Leung H, Hart C, Morrison DS (2012) Cholesterol and the risk of grade-specific prostate cancer incidence: evidence from two large prospective cohort studies with up to 37 years’ follow up. BMC Cancer 12:1–8
Pelton K, Freeman MR, Solomon KR (2012) Cholesterol and prostate cancer. Opin Pharmacol 12(6):751–759
Tie G, Yan J, Khair L, Messina JA, Deng A, Kang J, Fazzio T, Messina LM (2017) Hypercholesterolemia Increases colorectal cancer incidence by reducing production of NKT and γδ T cells from hematopoietic stem cells. Cancer Res 77(9):2351–2362
Villa GR, Hulce JJ, Zanca C, Bi J, Ikegami S, Cahill GL, Gu Y, Lum KM, Masui K, Yang H, Rong X, Hong C, Turner KM, Liu F, Hon GC, Jenkins D, Martini M, Armando AM, Quehenberger O, Cloughesy TF, Furnari FB, Cavenee WK, Tontonoz P, Gahman TC, Shiau AK, Cravatt BF, Mischel PS (2016) An LXR-cholesterol axis creates a metabolic co-dependency for brain cancers. Cancer Cell 30(5):683–693
Stopsack KH, Gerke TA, Andrén O, Andersson S-O, Giovannucci EL, Mucci LA, Rider JR (2017) Cholesterol uptake and regulation in high-grade and lethal prostate cancers. Carcinogenesis 38(8):806–811
Yue S, Li J, Lee SY, Lee HJ, Shao T, Song B, Cheng L, Masterson TA, Liu X, Ratliff TL, Cheng JX (2014) Cholesteryl ester accumulation induced by PTEN loss and PI3K/AKT activation underlies human prostate cancer aggressiveness. Cell Metab 19(3):393–406
Gill S, Stevenson J, Kristiana I, Brown AJ (2011) Cholesterol-dependent degradation of squalene monooxygenase, a control point in cholesterol synthesis beyond HMG-CoA reductase. Cell Metab 13(3):260–273
Maione F, Oliaro-Bosso S, Meda C, Di Nicolantonio F, Bussolino F, Balliano G, Viola F, Giraudo E (2015) The cholesterol biosynthesis enzyme oxidosqualene cyclase is a new target to impair tumour angiogenesis and metastasis dissemination. Sci Rep 5:1–12
Calfon M, Zeng H, Urano F, Till JH, Hubbard SR, Harding HP, Clark SG, Ron D (2002) IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing the XBP-1 mRNA. Nature 415(6867):92–96
Ikonen E (2008) Cellular cholesterol trafficking and compartmentalization. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9(2):125–138
Mostaghel EA, Solomon KR, Pelton K, Freeman MR, Montgomery RB (2012) Impact of circulating cholesterol levels on growth and intratumoral androgen concentration of prostate tumors. PLoS ONE 7(1):e30062
Jacobs RJ, Voorneveld PW, Kodach LL, Hardwick JC (2012) Cholesterol metabolism and colorectal cancers. Curr Opin Pharmacol 12(6):690–695
Ginestier C, Monville F, Wicinski J, Cabaud O, Cervera N, Josselin E, Finetti P, Guille A, Larderet G, Viens P, Sebti S, Bertucci F, Birnbaum D, Charafe-Jauffret E (2012) Mevalonate metabolism regulates Basal breast cancer stem cells and is a potential therapeutic target. Stem Cells 30(7):1327–1337
Xue L, Qi H, Zhang H, Ding L, Huang Q, Zhao D, Wu BJ, Li X (2020) Targeting SREBP-2-regulated mevalonate metabolism for cancer therapy. Front Oncol 10:1–20
Larsson O (1996) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors: role in normal and malignant cells. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 22(3):197–212
Li N, Zhou ZS, Shen Y, Xu J, Miao HH, Xiong Y, Xu F, Li BL, Luo J, Song BL (2017) Inhibition of the sterol regulatory element-binding protein pathway suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma by repressing inflammation in mice. Hepatology 65(6):1936–1947
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Professor Xia Zhang (Institute of Pathology, Southwest Hospital, Third Military Medical University) for his helpful comments in preparing this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China No. 31871367 (V. Kasim), No. 32070715 (V. Kasim), No. 81872273 (S. Wu), and No. 82173029 (S. Wu).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VK and SW conceived the project, designed the experiments, analyzed and interpreted the experimental results, and wrote the manuscript; MW, UN, AH performed most of the experiments and analyzed the experimental data; CH and YL carried out part of the experiments, constructed the vectors and interpreted the data; MM designed the shRNA target sequences and provided part of experimental materials for vector constructions.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Our studies did not include human participants, human data or human tissue. For the animal studies, a protocol detailing experimental procedures following the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Chongqing University Cancer Hospital guidelines was submitted to—and approved by—the Laboratory Animal Welfare and Ethics Committee of Chongqing University Cancer Hospital.
Consent for publication
We have obtained consent to publish this paper from all the participants of this research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, M., Nurjanah, U., Herkilini, A. et al. Unspliced XBP1 contributes to cholesterol biosynthesis and tumorigenesis by stabilizing SREBP2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 79, 472 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-022-04504-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-022-04504-x