Abstract
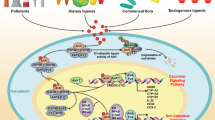
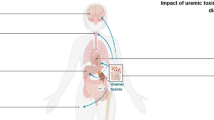
The gut microbiota has a crucial effect on regulating the intestinal mucosal immunity and maintaining intestinal homeostasis both in health and in disease state. Many effects are mediated by gut microbiota-derived metabolites and tryptophan, an essential aromatic amino acid, is considered important among many metabolites in the crosstalk between gut microbiota and the host. Kynurenine, serotonin, and indole derivatives are derived from the three major tryptophan metabolism pathways modulated by gut microbiota directly or indirectly. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) is a cytoplasmic ligand-activated transcription factor involved in multiple cellular processes. Tryptophan metabolites as ligands can activate AHR signaling in various diseases such as inflammation, oxidative stress injury, cancer, aging-related diseases, cardiovascular diseases (CVD), and chronic kidney diseases (CKD). Accumulated uremic toxins in the body fluids of CKD patients activate AHR and affect disease progression. In this review, we will elucidate the relationship between gut microbiota-derived uremic toxins by tryptophan metabolism and AHR activation in CKD and its complications. This review will provide therapeutic avenues for targeting CKD and concurrently present challenges and opportunities for designing new therapeutic strategies against renal fibrosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AHR:
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor
- AHRR:
-
AHR repressor protein
- ARNT:
-
AHR nuclear translocator
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase-2
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular diseases
- CYP:
-
Cytochrome P450 family
- DKD:
-
Diabetic kidney disease
- ESRD:
-
End-stage renal disease
- I3A:
-
Indole-3-aldehyde
- IAA:
-
Indole-3-acetic acid
- IDO:
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
- ILA:
-
Indole-3-lactic acid
- IS:
-
Indoxyl sulfate
- HIF:
-
Hypoxia-inducible transcription factor
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- PAHs:
-
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
- TCDD:
-
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
- TF:
-
Tissue factor
References
Harrill JA, Parks BB, Wauthier E, Rowlands JC, Reid LM, Thomas RS (2015) Lineage-dependent effects of aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists contribute to liver tumorigenesis. Hepatology (Baltimore, MD) 61(2):548–560. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27547
Pessah IN, Lein PJ, Seegal RF, Sagiv SK (2019) Neurotoxicity of polychlorinated biphenyls and related organohalogens. Acta Neuropathol 138(3):363–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-019-01978-1
Corre S, Tardif N, Mouchet N, Leclair HM, Boussemart L, Gautron A, Bachelot L, Perrot A, Soshilov A, Rogiers A, Rambow F, Dumontet E, Tarte K, Bessede A, Guillemin GJ, Marine JC, Denison MS, Gilot D, Galibert MD (2018) Sustained activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor transcription factor promotes resistance to BRAF-inhibitors in melanoma. Nat Commun 9(1):4775. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06951-2
Boström CE, Gerde P, Hanberg A, Jernström B, Johansson C, Kyrklund T, Rannug A, Törnqvist M, Victorin K, Westerholm R (2002) Cancer risk assessment, indicators, and guidelines for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the ambient air. Environ Health Perspect 110(Suppl 3):451–488. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.110-1241197
Poellinger L, Lund J, Gillner M, Hansson LA, Gustafsson JA (1983) Physicochemical characterization of specific and nonspecific polyaromatic hydrocarbon binders in rat and mouse liver cytosol. J Biol Chem 258(22):13535–13542
Denison MS, Wilkinson CF (1985) Identification of the Ah receptor in selected mammalian species and induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase. Eur J Biochem 147(2):429–435. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08767.x
Cheong JE, Sun L (2018) Targeting the IDO1/TDO2-KYN-AhR pathway for cancer immunotherapy—challenges and opportunities. Trends Pharmacol Sci 39(3):307–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2017.11.007
Zhao H, Chen L, Yang T, Feng YL, Vaziri ND, Liu BL, Liu QQ, Guo Y, Zhao YY (2019) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation mediates kidney disease and renal cell carcinoma. J Transl Med 17(1):302. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-019-2054-5
Roager HM, Licht TR (2018) Microbial tryptophan catabolites in health and disease. Nat Commun 9(1):3294. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05470-4
Schulte KW, Green E, Wilz A, Platten M, Daumke O (2017) Structural basis for aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated gene activation. Structure (London, England: 1993) 25(7):1025–1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2017.05.008
Fukunaga BN, Probst MR, Reisz-Porszasz S, Hankinson O (1995) Identification of functional domains of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. J Biol Chem 270(49):29270–29278. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.49.29270
Redaelli C, Gaffarogullari EC, Brune M, Pilz C, Becker S, Sonner J, Jäschke A, Gröne HJ, Wick W, Platten M, Lanz TV (2015) Toxicity of teriflunomide in aryl hydrocarbon receptor deficient mice. Biochem Pharmacol 98(3):484–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2015.08.111
Vogel CFA, Ishihara Y, Campbell CE, Kado SY, Nguyen-Chi A, Sweeney C, Pollet M, Haarmann-Stemmann T, Tuscano JM (2019) A protective role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor repressor in inflammation and tumor growth. Cancers 11(5):589. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11050589
Sakurai S, Shimizu T, Ohto U (2017) The crystal structure of the AhRR-ARNT heterodimer reveals the structural basis of the repression of AhR-mediated transcription. J Biol Chem 292(43):17609–17616. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.812974
Wang H, Pan L, Zhang X, Ji R, Si L, Cao Y (2020) The molecular mechanism of AhR-ARNT-XREs signaling pathway in the detoxification response induced by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Environ Res 183:109165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109165
Wang GZ, Zhang L, Zhao XC, Gao SH, Qu LW, Yu H, Fang WF, Zhou YC, Liang F, Zhang C, Huang YC, Liu Z, Fu YX, Zhou GB (2019) The Aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediates tobacco-induced PD-L1 expression and is associated with response to immunotherapy. Nat Commun 10(1):1125. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08887-7
Jaeger C, Tischkau SA (2016) Role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in circadian clock disruption and metabolic dysfunction. Environ Health Insights 10:133–141. https://doi.org/10.4137/ehi.S38343
Singh R, Chandrashekharappa S, Bodduluri SR, Baby BV, Hegde B, Kotla NG, Hiwale AA, Saiyed T, Patel P, Vijay-Kumar M, Langille MGI, Douglas GM, Cheng X, Rouchka EC, Waigel SJ, Dryden GW, Alatassi H, Zhang HG, Haribabu B, Vemula PK, Jala VR (2019) Enhancement of the gut barrier integrity by a microbial metabolite through the Nrf2 pathway. Nat Commun 10(1):89. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07859-7
Bao A, Yang H, Ji J, Chen Y, Bao W, Li F, Zhang M, Zhou X, Li Q, Ben S (2017) Involvements of p38 MAPK and oxidative stress in the ozone-induced enhancement of AHR and pulmonary inflammation in an allergic asthma model. Respir Res 18(1):216. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-017-0697-4
Hu HH, Chen DQ, Wang YN, Feng YL, Cao G, Vaziri ND, Zhao YY (2018) New insights into TGF-β/Smad signaling in tissue fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact 292:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.07.008
Miao H, Cao G, Wu XQ, Chen YY, Chen DQ, Chen L, Vaziri ND, Feng YL, Su W, Gao Y, Zhuang S, Yu XY, Zhang L, Guo Y, Zhao YY (2020) Identification of endogenous 1-aminopyrene as a novel mediator of progressive chronic kidney disease via aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation. Br J Pharmacol 177(15):3415–3435. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.15062
Chen L, Yang T, Lu DW, Zhao H, Feng YL, Chen H, Chen DQ, Vaziri ND, Zhao YY (2018) Central role of dysregulation of TGF-β/Smad in CKD progression and potential targets of its treatment. Biomed Pharmacother 101:670–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.090
Hu HH, Cao G, Wu XQ, Vaziri ND, Zhao YY (2020) Wnt signaling pathway in aging-related tissue fibrosis and therapies. Ageing Res Rev 60:101063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101063
Feng YL, Chen H, Chen DQ, Vaziri ND, Su W, Ma SX, Shang YQ, Mao JR, Yu XY, Zhang L, Guo Y (1865) Zhao YY (2019) Activated NF-κB/Nrf2 and Wnt/β-catenin pathways are associated with lipid metabolism in CKD patients with microalbuminuria and macroalbuminuria. Biochim Biophys Acta 9:2317–2332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.05.010
Zhao YY (2013) Metabolomics in chronic kidney disease. Clin Chim Acta 422:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2013.03.033
Feng YL, Cao G, Chen DQ, Vaziri ND, Chen L, Zhang J, Wang M, Guo Y, Zhao YY (2019) Microbiome-metabolomics reveals gut microbiota associated with glycine-conjugated metabolites and polyamine metabolism in chronic kidney disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 74(24):4961–4978. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03155-9
Chen DQ, Cao G, Chen H, Argyopoulos CP, Yu H, Su W, Chen L, Samuels DC, Zhuang S, Bayliss GP, Zhao S, Yu XY, Vaziri ND, Wang M, Liu D, Mao JR, Ma SX, Zhao J, Zhang Y, Shang YQ, Kang H, Ye F, Cheng XH, Li XR, Zhang L, Meng MX, Guo Y, Zhao YY (2019) Identification of serum metabolites associating with chronic kidney disease progression and anti-fibrotic effect of 5-methoxytryptophan. Nat Commun 10(1):1476. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09329-0
Chen YY, Chen DQ, Chen L, Liu JR, Vaziri ND, Guo Y, Zhao YY (2019) Microbiome-metabolome reveals the contribution of gut-kidney axis on kidney disease. J Transl Med 17(1):5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-018-1756-4
Dolivo DM, Larson SA, Dominko T (2018) Tryptophan metabolites kynurenine and serotonin regulate fibroblast activation and fibrosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 75(20):3663–3681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2880-2
Chen DQ, Cao G, Chen H, Liu D, Su W, Yu XY, Vaziri ND, Liu XH, Bai X, Zhang L, Zhao YY (2017) Gene and protein expressions and metabolomics exhibit activated redox signaling and Wnt/β-catenin pathway are associated with metabolite dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease. Redox Biol 12:505–521
Sun M, Ma N, He T, Johnston LJ, Ma X (2019) Tryptophan (Trp) modulates gut homeostasis via aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2019.1598334
Platten M, Nollen EAA, Röhrig UF, Fallarino F, Opitz CA (2019) Tryptophan metabolism as a common therapeutic target in cancer, neurodegeneration and beyond. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 18(5):379–401. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-019-0016-5
Chen L, Chen DQ, Liu JR, Zhang J, Vaziri ND, Zhuang S, Chen H, Feng YL, Guo Y, Zhao YY (2019) Unilateral ureteral obstruction causes gut microbial dysbiosis and metabolome disorders contributing to tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Exp Mol Med 51(3):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-019-0234-2
Gao J, Xu K, Liu H, Liu G, Bai M, Peng C, Li T, Yin Y (2018) Impact of the gut microbiota on intestinal immunity mediated by tryptophan metabolism. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 8:13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2018.00013
Moyer BJ, Rojas IY, Kerley-Hamilton JS, Hazlett HF, Nemani KV, Trask HW, West RJ, Lupien LE, Collins AJ, Ringelberg CS, Gimi B, Kinlaw WB 3rd, Tomlinson CR (2016) Inhibition of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor prevents Western diet-induced obesity. Model for AHR activation by kynurenine via oxidized-LDL, TLR2/4, TGFβ, and IDO1. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 300:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2016.03.011
Agus A, Planchais J, Sokol H (2018) Gut microbiota regulation of tryptophan metabolism in health and disease. Cell Host Microbe 23(6):716–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2018.05.003
Manzella CR, Ackerman M, Singhal M, Ticho AL, Ceh J, Alrefai WA, Saksena S, Dudeja PK, Gill RK (2020) Serotonin modulates AhR activation by interfering with CYP1A1-mediated clearance of AhR ligands. Cell Physiol Biochem 54(1):126–141. https://doi.org/10.33594/000000209
Gao K, Mu CL, Farzi A, Zhu WY (2019) Tryptophan metabolism: a link between the gut microbiota and brain. Adv Nutr 11(3):709–723. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmz127
Luan H, Wang X, Cai Z (2019) Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics: targeting the crosstalk between gut microbiota and brain in neurodegenerative disorders. Mass Spectrom Rev 38(1):22–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/mas.21553
Jin Q, Black A, Kales SN, Vattem D, Ruiz-Canela M, Sotos-Prieto M (2019) Metabolomics and microbiomes as potential tools to evaluate the effects of the mediterranean diet. Nutrients 11(1):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010207
Yacoub R, Wyatt CM (2017) Manipulating the gut microbiome to decrease uremic toxins. Kidney Int 91(3):521–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2017.01.003
Vogel CFA, Van Winkle LS, Esser C, Haarmann-Stemmann T (2020) The aryl hydrocarbon receptor as a target of environmental stressors—Implications for pollution mediated stress and inflammatory responses. Redox Biol 34:101530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101530
Milanesi S, Garibaldi S, Saio M, Ghigliotti G, Picciotto D, Ameri P, Garibotto G, Barisione C, Verzola D (2019) Indoxyl sulfate induces renal fibroblast activation through a targetable heat shock protein 90-dependent pathway. Oxid Med Cell Long 2019:2050183. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2050183
Liu Y, Li X, Zhang B, Fu Y, Yang A, Zhang H, Zhang H, Niu Y, Nie J, Yang J (2019) CYP1A1 methylation mediates the effect of smoking and occupational polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons co-exposure on oxidative DNA damage among Chinese coke-oven workers. Environ Health 18(1):69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-019-0508-0
Trikha P, Lee DA (2020) The role of AhR in transcriptional regulation of immune cell development and function. Biochim Biophys Acta 1:188335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.188335
Wang M, Chen DQ, Chen L, Cao G, Zhao H, Liu D, Vaziri ND, Guo Y, Zhao YY (2018) Novel inhibitors of the cellular renin-angiotensin system components, poricoic acids, target Smad3 phosphorylation and Wnt/β-catenin pathway against renal fibrosis. Br J Pharmacol 175(13):2689–2708. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14333
Addi T, Poitevin S, McKay N, El Mecherfi KE, Kheroua O, Jourde-Chiche N, de Macedo A, Gondouin B, Cerini C, Brunet P, Dignat-George F, Burtey S, Dou L (2019) Mechanisms of tissue factor induction by the uremic toxin indole-3 acetic acid through aryl hydrocarbon receptor/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway in human endothelial cells. Arch Toxicol 93(1):121–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2328-3
Gondouin B, Cerini C, Dou L, Sallee M, Duval-Sabatier A, Pletinck A, Calaf R, Lacroix R, Jourde-Chiche N, Poitevin S, Arnaud L, Vanholder R, Brunet P, Dignat-George F, Burtey S (2013) Indolic uremic solutes increase tissue factor production in endothelial cells by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway. Kidney Int 84(4):733–744. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2013.133
Addi T, Dou L, Burtey S (2018) Tryptophan-derived uremic toxins and thrombosis in chronic kidney disease. Toxins 10(10):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100412
Wolf D, Ley K (2019) Immunity and inflammation in atherosclerosis. Circ Res 124(2):315–327. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.118.313591
Dou L, Sallee M, Cerini C, Poitevin S, Gondouin B, Jourde-Chiche N, Fallague K, Brunet P, Calaf R, Dussol B, Mallet B, Dignat-George F, Burtey S (2015) The cardiovascular effect of the uremic solute indole-3 acetic acid. J Am Soc Nephrol 26(4):876–887. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2013121283
Lee WJ, Liu SH, Chiang CK, Lin SY, Liang KW, Chen CH, Tien HR, Chen PH, Wu JP, Tsai YC, Lai DW, Chang YC, Sheu WH, Sheu ML (2016) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor deficiency attenuates oxidative stress-related mesangial cell activation and macrophage infiltration and extracellular matrix accumulation in diabetic nephropathy. Antioxid Redox Signal 24(4):217–231. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2015.6310
Wu J, Jiang Z, Zhang H, Liang W, Huang W, Zhang H, Li Y, Wang Z, Wang J, Jia Y, Liu B, Wu H (2018) Sodium butyrate attenuates diabetes-induced aortic endothelial dysfunction via P300-mediated transcriptional activation of Nrf2. Free Radical Biol Med 124:454–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.06.034
Assefa EG, Yan Q, Gezahegn SB, Salissou MTM, He S, Wu N, Zuo X, Ying C (2019) Role of resveratrol on indoxyl sulfate-induced endothelial hyperpermeability via aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR)/src-dependent pathway. Oxid Med Cell Long 2019:5847040. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5847040
Brito JS, Borges NA, Anjos JSD, Nakao LS, Stockler-Pinto MB, Paiva BR, Cardoso-Weide LC, Cardozo L, Mafra D (2019) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and uremic toxins from the gut microbiota in chronic kidney disease patients: is there a relationship between them? Biochemistry 58(15):2054–2060. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.8b01305
Wu PH, Lin YT, Wu PY, Lee HH, Lee SC, Hung SC, Chen SC, Kuo MC, Chiu YW (2020) Association between circulation indole-3-acetic acid levels and stem cell factor in maintenance hemodialysis patients: a cross-sectional study. J Clin Med 9(1):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010124
Imhann F, Vich Vila A, Bonder MJ, Fu J, Gevers D, Visschedijk MC, Spekhorst LM, Alberts R, Franke L, van Dullemen HM, Ter Steege RWF, Huttenhower C, Dijkstra G, Xavier RJ, Festen EAM, Wijmenga C, Zhernakova A, Weersma RK (2018) Interplay of host genetics and gut microbiota underlying the onset and clinical presentation of inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 67(1):108–119. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312135
Beaumont M, Neyrinck AM, Olivares M, Rodriguez J, de Rocca Serra A, Roumain M, Bindels LB, Cani PD, Evenepoel P, Muccioli GG, Demoulin JB, Delzenne NM (2018) The gut microbiota metabolite indole alleviates liver inflammation in mice. FASEB J. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201800544
Xiang F, Cao X, Shen B, Chen X, Guo M, Ding X, Zou J (2020) Transcriptome profiling reveals indoxyl sulfate should be culpable of impaired T cell function in chronic kidney disease. Front Med 7:178. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2020.00178
Schroeder JC, Dinatale BC, Murray IA, Flaveny CA, Liu Q, Laurenzana EM, Lin JM, Strom SC, Omiecinski CJ, Amin S, Perdew GH (2010) The uremic toxin 3-indoxyl sulfate is a potent endogenous agonist for the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Biochemistry 49(2):393–400. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi901786x
Koehler S, Kuczkowski A, Kuehne L, Jüngst C, Hoehne M, Grahammer F, Eddy S, Kretzler M, Beck BB, Höhfeld J, Schermer B, Benzing T, Brinkkoetter PT, Rinschen MM (2020) Proteome analysis of isolated podocytes reveals stress responses in glomerular sclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 31(3):544–559. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2019030312
Hung SC, Kuo KL, Huang HL, Lin CC, Tsai TH, Wang CH, Chen JW, Lin SJ, Huang PH, Tarng DC (2016) Indoxyl sulfate suppresses endothelial progenitor cell-mediated neovascularization. Kidney Int 89(3):574–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2015.11.020
Zhao T, Zhang H, Yin X, Zhao H, Ma L, Yan M, Peng L, Wang Q, Dong X, Li P (2020) Tangshen formula modulates gut Microbiota and reduces gut-derived toxins in diabetic nephropathy rats. Biomed Pharmacother 129:110325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110325
Kim JT, Kim SS, Jun DW, Hwang YH, Park WH, Pak YK, Lee HK (2013) Serum arylhydrocarbon receptor transactivating activity is elevated in type 2 diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Investig 4(5):483–491. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.12081
Matsuoka K, Kato K, Takao T, Ogawa M, Ishii Y, Shimizu F, Masuda J, Takada A (2017) Concentrations of various tryptophan metabolites are higher in patients with diabetes mellitus than in healthy aged male adults. Diabetol Int 8(1):69–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-016-0282-y
Kim HY, Yoo TH, Cho JY, Kim HC, Lee WW (2019) Indoxyl sulfate-induced TNF-α is regulated by crosstalk between the aryl hydrocarbon receptor, NF-κB, and SOCS2 in human macrophages. FASEB J 33(10):10844–10858. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201900730R
Shivanna S, Kolandaivelu K, Shashar M, Belghasim M, Al-Rabadi L, Balcells M, Zhang A, Weinberg J, Francis J, Pollastri MP, Edelman ER, Sherr DH, Chitalia VC (2016) The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is a critical regulator of tissue factor stability and an antithrombotic target in uremia. J Am Soc Nephrol 27(1):189–201. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2014121241
Chitalia VC, Shivanna S, Martorell J, Balcells M, Bosch I, Kolandaivelu K, Edelman ER (2013) Uremic serum and solutes increase post-vascular interventional thrombotic risk through altered stability of smooth muscle cell tissue factor. Circulation 127(3):365–376. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.112.118174
Sallee M, Dou L, Cerini C, Poitevin S, Brunet P, Burtey S (2014) The aryl hydrocarbon receptor-activating effect of uremic toxins from tryptophan metabolism: a new concept to understand cardiovascular complications of chronic kidney disease. Toxins 6(3):934–949. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6030934
Neuen BL, Ohkuma T, Neal B, Matthews DR, de Zeeuw D, Mahaffey KW, Fulcher G, Desai M, Li Q, Deng H, Rosenthal N, Jardine MJ, Bakris G, Perkovic V (2018) Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with Canagliflozin according to baseline kidney function. Circulation 138(15):1537–1550. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.118.035901
Kim HY, Yoo TH, Hwang Y, Lee GH, Kim B, Jang J, Yu HT, Kim MC, Cho JY, Lee CJ, Kim HC, Park S, Lee WW (2017) Indoxyl sulfate (IS)-mediated immune dysfunction provokes endothelial damage in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Sci Rep 7(1):3057. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03130-z
Lin YT, Wu PH, Tsai YC, Hsu YL, Wang HY, Kuo MC, Kuo PL, Hwang SJ (2019) Indoxyl sulfate induces apoptosis through oxidative stress and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway inhibition in human astrocytes. J Clin Med 8(2):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020191
Shang F, Wang SC, Hsu CY, Miao Y, Martin M, Yin Y, Wu CC, Wang YT, Wu G, Chien S, Huang HD, Tarng DC, Shiu YT, Cheung AK, Huang PH, Chen Z, Shyy JY (2017) MicroRNA-92a mediates endothelial dysfunction in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 28(11):3251–3261. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2016111215
Huang M, Wei R, Wang Y, Su T, Li P, Chen X (2018) The uremic toxin hippurate promotes endothelial dysfunction via the activation of Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission. Redox biology 16:303–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.03.010
Nakano T, Katsuki S, Chen M, Decano JL, Halu A, Lee LH, Pestana DVS, Kum AST, Kuromoto RK, Golden WS, Boff MS, Guimaraes GC, Higashi H, Kauffman KJ, Maejima T, Suzuki T, Iwata H, Barabasi AL, Aster JC, Anderson DG, Sharma A, Singh SA, Aikawa E, Aikawa M (2019) Uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate promotes proinflammatory macrophage activation via the interplay of OATP2B1 and Dll4-notch signaling. Circulation 139(1):78–96. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.118.034588
Xiang HC, Lin LX, Hu XF, Zhu H, Li HP, Zhang RY, Hu L, Liu WT, Zhao YL, Shu Y, Pan HL, Li M (2019) AMPK activation attenuates inflammatory pain through inhibiting NF-κB activation and IL-1β expression. J Neuroinflamm 16(1):34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1411-x
Ito S, Osaka M, Edamatsu T, Itoh Y, Yoshida M (2016) Crucial role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in indoxyl sulfate-induced vascular inflammation. J Atheroscl Thromb 23(8):960–975. https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.34462
Islam J, Sato S, Watanabe K, Watanabe T, Ardiansyah Hirahara K, Aoyama Y, Tomita S, Aso H, Komai M, Shirakawa H (2017) Dietary tryptophan alleviates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis through aryl hydrocarbon receptor in mice. J Nutr Biochem 42:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.12.019
Bhattarai Y, Williams BB, Battaglioli EJ, Whitaker WR, Till L, Grover M, Linden DR, Akiba Y, Kandimalla KK, Zachos NC, Kaunitz JD, Sonnenburg JL, Fischbach MA, Farrugia G, Kashyap PC (2018) Gut microbiota-produced tryptamine activates an epithelial G-protein-coupled receptor to increase colonic secretion. Cell Host Microbe 23(6):775–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2018.05.004
Zelante T, Iannitti RG, Cunha C, De Luca A, Giovannini G, Pieraccini G, Zecchi R, D’Angelo C, Massi-Benedetti C, Fallarino F, Carvalho A, Puccetti P, Romani L (2013) Tryptophan catabolites from microbiota engage aryl hydrocarbon receptor and balance mucosal reactivity via interleukin-22. Immunity 39(2):372–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.08.003
Hou Q, Ye L, Liu H, Huang L, Yang Q, Turner JR, Yu Q (2018) Lactobacillus accelerates ISCs regeneration to protect the integrity of intestinal mucosa through activation of STAT3 signaling pathway induced by LPLs secretion of IL-22. Cell Death Differ 25(9):1657–1670. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0070-2
Krishnan S, Ding Y, Saedi N, Choi M, Sridharan GV, Sherr DH, Yarmush ML, Alaniz RC, Jayaraman A, Lee K (2018) Gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites modulate inflammatory response in hepatocytes and macrophages. Cell Rep 23(4):1099–1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.109
Yu J, Luo Y, Zhu Z, Zhou Y, Sun L, Gao J, Sun J, Wang G, Yao X, Li W (2019) A tryptophan metabolite of the skin microbiota attenuates inflammation in patients with atopic dermatitis through the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. J Allergy Clin Immunol 143(6):2108–2119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2018.11.036e2112
Cervantes-Barragan L, Chai JN, Tianero MD, Di Luccia B, Ahern PP, Merriman J, Cortez VS, Caparon MG, Donia MS, Gilfillan S, Cella M, Gordon JI, Hsieh CS, Colonna M (2017) Lactobacillus reuteri induces gut intraepithelial CD4(+)CD8αα(+) T cells. Science (New York, NY) 357(6353):806–810. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aah5825
Meng D, Sommella E, Salviati E, Campiglia P, Ganguli K, Djebali K, Zhu W, Walker WA (2020) Indole-3-lactic acid, a metabolite of tryptophan, secreted by Bifidobacterium longum subspecies infantis is anti-inflammatory in the immature intestine. Pediatr Res 88(2):209–217. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-019-0740-x
Sakurai T, Odamaki T, Xiao JZ (2019) Production of indole-3-lactic acid by Bifidobacterium strains isolated from human infants. Microorganisms 7(9):340. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7090340
Xue Z, Li D, Yu W, Zhang Q, Hou X, He Y, Kou X (2017) Mechanisms and therapeutic prospects of polyphenols as modulators of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Food Funct 8(4):1414–1437. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6fo01810f
Mexia N, Gaitanis G, Velegraki A, Soshilov A, Denison MS, Magiatis P (2015) Pityriazepin and other potent AhR ligands isolated from Malassezia furfur yeast. Arch Biochem Biophys 571:16–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2015.02.023
Chen DQ, Feng YL, Cao G, Zhao YY (2018) Natural products as a source for antifibrosis therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci 39(11):937–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2018.09.002
Feng YL, Chen DQ, Vaziri ND, Guo Y, Zhao YY (2020) Small molecule inhibitors of epithelial-mesenchymal transition for the treatment of cancer and fibrosis. Med Res Rev 40(1):54–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21596
Chen YY, Yu XY, Chen L, Vaziri ND, Ma SC, Zhao YY (2019) Redox signaling in aging kidney and opportunity for therapeutic intervention through natural products. Free Radical Biol Med 141:141–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.06.012
Chen DQ, Feng YL, Chen L, Liu JR, Wang M, Vaziri ND, Zhao YY (2019) Poricoic acid A enhances melatonin inhibition of AKI-to-CKD transition by regulating Gas6/Axl NFκB/Nrf2 axis. Free Radical Biol Med 134:484–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.01.046
Chen DQ, Cao G, Zhao H, Chen L, Yang T, Wang M, Vaziri ND, Guo Y, Zhao YY (2019) Combined melatonin and poricoic acid A inhibits renal fibrosis through modulating the interaction of Smad3 and β-catenin pathway in AKI-to-CKD continuum. Ther Adv Chron Dis 10:2040622319869116. https://doi.org/10.1177/2040622319869116
Yang T, Feng YL, Chen L, Vaziri ND, Zhao YY (2019) Dietary natural flavonoids treating cancer by targeting aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Crit Rev Toxicol 49(5):445–460. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408444.2019.1635987
Wang K, Feng C, Li C, Yao J, Xie X, Gong L, Luan Y, Xing G, Zhu X, Qi X, Ren J (2015) Baicalin protects mice from aristolochic acid I-induced kidney injury by induction of cyp1a through the aromatic hydrocarbon receptor. Int J Mol Sci 16(7):16454–16468. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160716454
Feng C, Xie X, Wu M, Li C, Gao M, Liu M, Qi X, Ren J (2013) Tanshinone I protects mice from aristolochic acid I-induced kidney injury by induction of CYP1A. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36(3):850–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2013.07.017
Ichii O, Otsuka-Kanazawa S, Nakamura T, Ueno M, Kon Y, Chen W, Rosenberg AZ, Kopp JB (2014) Podocyte injury caused by indoxyl sulfate, a uremic toxin and aryl-hydrocarbon receptor ligand. PLoS ONE 9(9):108448. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108448
Kolachalama VB, Shashar M, Alousi F, Shivanna S, Rijal K, Belghasem ME, Walker J, Matsuura S, Chang GH, Gibson CM, Dember LM, Francis JM, Ravid K, Chitalia VC (2018) Uremic solute-aryl hydrocarbon receptor-tissue factor axis associates with thrombosis after vascular injury in humans. J Am Soc Nephrol 29(3):1063–1072. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2017080929
Belghasem M, Roth D, Richards S, Napolene MA, Walker J, Yin W, Arinze N, Lyle C, Spencer C, Francis JM, Thompson C, Andry C, Whelan SA, Lee N, Ravid K, Chitalia VC (2019) Metabolites in a mouse cancer model enhance venous thrombogenicity through the aryl hydrocarbon receptor-tissue factor axis. Blood 134(26):2399–2413. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2019001675
Orlando IMC, Lafleur VN, Storti F, Spielmann P, Crowther L, Santambrogio S, Schodel J, Hoogewijs D, Mole DR, Wenger RH (2019) Distal and proximal hypoxia response elements cooperate to regulate organ-specific erythropoietin gene expression. Haematologica. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2019.236406
Garrison AM, Parrott JM, Tuñon A, Delgado J, Redus L, O’Connor JC (2018) Kynurenine pathway metabolic balance influences microglia activity: targeting kynurenine monooxygenase to dampen neuroinflammation. Psychoneuroendocrinology 94:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.04.019
Faust D, Nikolova T, Watjen W, Kaina B, Dietrich C (2017) The Brassica-derived phytochemical indolo[3,2-b]carbazole protects against oxidative DNA damage by aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation. Arch Toxicol 91(2):967–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1672-4
Wang Q, Yang K, Han B, Sheng B, Yin J, Pu A, Li L, Sun L, Yu M, Qiu Y, Xiao W, Yang H (2018) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor inhibits inflammation in DSS induced colitis via the MK2/pMK2/TTP pathway. Int J Mol Med 41(2):868–876. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2017.3262
Mohammadi-Bardbori A, Omidi M, Arabnezhad MR (2019) Impact of CH223191-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction on Its Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonistic and Antagonistic Activities. Chem Res Toxicol 32(4):691–697. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.8b00371
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81603271, 81673578, 81872985) and National Key Research and Development Project of China (2019YFC1709405).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, JR., Miao, H., Deng, DQ. et al. Gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolism mediates renal fibrosis by aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling activation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 78, 909–922 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03645-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03645-1