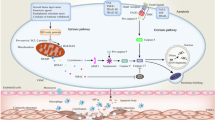
Abstract
To maintain physiological homeostasis, cell turnover occurs every day in the body via a form of programmed cell death called apoptosis. During apoptosis, cells undergo distinct morphological changes culminating in the disassembly of the dying cell into smaller fragments known as apoptotic bodies (ApoBDs). Dysregulation of apoptosis is associated with diseases including infection, cancer and atherosclerosis. Although the development of atherosclerosis is largely attributed to the accumulation of lipids and inflammatory debris in vessel walls, it is also associated with apoptosis of macrophages, smooth muscle cells (SMCs) and endothelial cells. During cellular activation and apoptosis, endothelial cells can release several types of membrane-bound extracellular vesicles (EVs) including exosomes, microvesicles (MVs)/microparticles and ApoBDs. Emerging evidence in the field suggests that these endothelial cell-derived EVs (EndoEVs) can contribute to intercellular communication during the development of atherosclerosis via the transfer of cellular contents such as protein and microRNA, which may prevent or promote disease progression depending on the context. This review provides an up-to-date overview of the known causes and consequences of endothelial cell death during atherosclerosis along with highlighting current methodological approaches to studying EndoEVs and the potential roles of EndoEVs in atherosclerosis development.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR (1972) Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26:239–257
Wajant H (2002) The fas signaling pathway: more than a paradigm. Science (80-) 296:1635–1636
Tait SWG, Green DR (2010) Mitochondria and cell death: outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:621–632. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2952
Nagata S (2010) Apoptosis and autoimmune diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1209:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05749.x
Kalra H, Drummen GPC, Mathivanan S (2016) Focus on extracellular vesicles: introducing the next small big thing. Int J Mol Sci 17:170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020170
Kowal J, Arras G, Colombo M et al (2016) Proteomic comparison defines novel markers to characterize heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:E968–E977. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1521230113
Tricarico C, Clancy J, D’Souza-Schorey C (2017) Biology and biogenesis of shed microvesicles. Small GTPases 8:220–232. https://doi.org/10.1080/21541248.2016.1215283
Lötvall J, Hill AF, Hochberg F et al (2014) Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: a position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v3.26913
Jimenez JJ, Jy W, Mauro LM et al (2003) Endothelial cells release phenotypically and quantitatively distinct microparticles in activation and apoptosis. Thromb Res 109:175–180
Pasquier J, Al Thawadi H, Ghiabi P et al (2014) Microparticles mediated cross-talk between tumoral and endothelial cells promote the constitution of a pro-metastatic vascular niche through Arf6 up regulation. Cancer Microenviron 7:41–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-013-0142-2
Andrews AM, Lutton EM, Merkel SF et al (2016) Mechanical injury induces brain endothelial-derived microvesicle release: implications for cerebral vascular injury during traumatic brain injury. Front Cell Neurosci 10:43
Mallat Z, Hugel B, Ohan J et al (1999) Shed membrane microparticles with procoagulant potential in human atherosclerotic plaques: a role for apoptosis in plaque thrombogenicity. Circulation 99:348–353
Atkin-Smith GK, Poon IKH (2017) Disassembly of the dying: mechanisms and functions. Trends Cell Biol 27:151–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2016.08.011
Tkach M, Théry C (2016) Communication by extracellular vesicles: where we are and where we need to go. Cell 164:1226–1232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.01.043
van Niel G, D’Angelo G, Raposo G (2018) Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19:213–228. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2017.125
Tixeira R, Caruso S, Paone S et al (2017) Defining the morphologic features and products of cell disassembly during apoptosis. Apoptosis 22:475–477
Petrache I, Birukov K, Zaiman AL et al (2003) Caspase-dependent cleavage of myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) is involved in TNF-alpha-mediated bovine pulmonary endothelial cell apoptosis. Faseb J 17:407–416. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.02-0672com
Coleman ML, Sahai EA, Yeo M et al (2001) Membrane blebbing during apoptosis results from caspase-mediated activation of ROCK I. Nat Cell Biol 3:339–345. https://doi.org/10.1038/35070009
Moss DK, Betin VM, Malesinski SD, Lane JD (2006) A novel role for microtubules in apoptotic chromatin dynamics and cellular fragmentation. J Cell Sci 119:2362–2374. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02959
Poon IKH, Chiu YH, Armstrong AJ et al (2014) Unexpected link between an antibiotic, pannexin channels and apoptosis. Nature 507:329–334. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13147
Atkin-Smith GK, Tixeira R, Paone S et al (2015) A novel mechanism of generating extracellular vesicles during apoptosis via a beads-on-a-string membrane structure. Nat Commun 6:7439. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8439
Orlando KA, Stone NL, Pittman RN (2006) Rho kinase regulates fragmentation and phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Exp Cell Res 312:5–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.09.012
Zernecke A, Bidzhekov K, Noels H et al (2009) Delivery of microRNA-126 by apoptotic bodies induces CXCL12-dependent vascular protection. Sci Signal 2:81. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2000610
Berda-Haddad Y, Robert S, Salers P et al (2011) Sterile inflammation of endothelial cell-derived apoptotic bodies is mediated by interleukin-1alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:20684–20689. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1116848108
Poon IK, Hulett MD, Parish CR (2010) Molecular mechanisms of late apoptotic/necrotic cell clearance. Cell Death Differ 17:381–397. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.195
Schrijvers DM, De Meyer GR, Kockx MM et al (2005) Phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages is impaired in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:1256–1261. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000166517.18801.a7
Kockx MM, Herman AG (2000) Apoptosis in atherosclerosis: beneficial or detrimental? Cardiovasc Res 45:736–746
Bennett MR, Evan G, Schwartz SM (1995) Apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells derived from normal vessels and coronary atherosclerotic plaques
Gimbrone MAJ, Garcia-Cardena G (2016) Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of atherosclerosis. Circ Res 118:620–636. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306301
Rajendran P, Rengarajan T, Thangavel J et al (2013) The vascular endothelium and human diseases. Int J Biol Sci 9:1057–1069. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.7502
Werner N, Wassmann S, Ahlers P et al (2006) Circulating CD31 +/annexin V + apoptotic microparticles correlate with coronary endothelial function in patients with coronary artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:112–116. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.atv.0000191634.13057.15
Libby P, Okamoto Y, Rocha V, Folco E (2010) Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Circ J 74:213–220
Gerrity RG, Richardson M, Somer JB et al (1977) Endothelial cell morphology in areas of in vivo evans blue uptake in the aorta of young pigs: ultrastructure of the intima in areas of differing permeability to proteins. Am J Pathol 89:313–334
Tricot O, Mallat Z, Heymes C et al (2000) Relation between endothelial cell apoptosis and blood flow direction in human atherosclerotic plaques. Circulation 101:2450–2453
Bombeli T, Karsan A, Tait JF, Harlan JM (1997) Apoptotic vascular endothelial cells become procoagulant. Blood 89:2429–2442
Enomoto S, Sata M, Fukuda D et al (2009) Rosuvastatin prevents endothelial cell death and reduces atherosclerotic lesion formation in ApoE-deficient mice. Biomed Pharmacother 63:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2007.11.002
Oesterle A, Laufs U, Liao JK (2017) Pleiotropic effects of statins on the cardiovascular system. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308537
Li Y, Liu H, Wu Y, Zhu M (2018) Effect of atorvastatin on the apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and its drug mechanism. Pak J Pharm Sci 31:1761–1766
Bao X, Wu C, Lu G (2010) Atorvastatin inhibits homocysteine-induced dysfunction and apoptosis in endothelial progenitor cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31:476–484. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2010.22
Ball RY, Stowers EC, Burton JH et al (1995) Evidence that the death of macrophage foam cells contributes to the lipid core of atheroma. Atherosclerosis 114:45–54
Sata M, Walsh K (1998) Oxidized LDL activates Fas-mediated endothelial cell apoptosis. J Clin Invest 102:1682–1689
Harada-Shiba M, Kinoshita M, Kamido H, Shimokado K (1998) Oxidized low density lipoprotein induces apoptosis in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells by common and unique mechanisms. J Biol Chem Biol Chem 273:9681–9687
Kannel WB, McGee DL (1979) Diabetes and glucose tolerance as risk factors for cardiovascular disease: the Framingham study. Diabetes Care 2:120–126. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.2.2.120
Sheu ML, Ho FM, Sen Yang R et al (2005) High glucose induces human endothelial cell apoptosis through a phosphoinositide 3-kinase-regulated cyclooxygenase-2 pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:539–545
Ho FM, Liu SH, Liau CS et al (2000) High glucose-induced apoptosis in human endothelial cells is mediated by sequential activations of c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase and caspase-3. Circulation 101:2618–2624
Quagliaro L, Piconi L, Assaloni R et al (2003) Intermittent high glucose enhances apoptosis related to oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: the role of protein kinase C and NAD(P)H-oxidase activation. Diabetes 52:2795–2804
Detaille D, Guigas B, Chauvin C et al (2005) Metformin prevents high-glucose-induced endothelial cell death through a mitochondrial permeability transition-dependent process. Diabetes 54:2179–2187
Korenaga R, Ando J, Tsuboi H et al (1994) Laminar flow stimulates ATP- and shear stress-dependent nitric oxide production in cultured bovine endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 198:213–219. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1994.1030
Förstermann U, Sessa WC (2012) Nitric oxide synthases: regulation and function. Eur Heart J 33:829–837. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehr304
Polte T, Oberle S, Schroder H (1997) The nitric oxide donor SIN-1 protects endothelial cells from tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated cytotoxicity: possible role for cyclic GMP and heme oxygenase. J Mol Cell Cardiol 29:3305–3310. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmcc.1997.0565
Dimmeler S, Rippmann V, Weiland U et al (1997) Angiotensin II induces apoptosis of human endothelial cells. Protective effect of nitric oxide. Circ Res 81:970–976
Irani K (2000) Oxidant signaling in vascular cell growth, death, and survival: a review of the roles of reactive oxygen species in smooth muscle and endothelial cell mitogenic and apoptotic signaling. Circ Res 87:179–183
Hermann C, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S (1997) Shear stress inhibits H2O2-induced apoptosis of human endothelial cells by modulation of the glutathione redox cycle and nitric oxide synthase. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 17:3588 LP-3592
Cominacini L, Garbin U, Pasini AF et al (1998) Oxidized low-density lipoprotein increases the production of intracellular reactive oxygen species in endothelial cells: inhibitory effect of lacidipine. J Hypertens 16:1913–1919
Inoguchi T, Li P, Umeda F et al (2000) High glucose level and free fatty acid stimulate protein kinase c-dependent sctivation of NAD(P)H oxidase in cultured vascular cells. 1939–1945
Basuroy S, Bhattacharya S, Leffler CW, Parfenova H (2009) Nox4 NADPH oxidase mediates oxidative stress and apoptosis caused by TNF-alpha in cerebral vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 296:422–432. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00381.2008
Sima AV, Stancu CS, Simionescu M (2008) Vascular endothelium in atherosclerosis. Cell Tissue Res 335:191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-008-0678-5
Dimmeler S, Haendeler J, Rippmann V et al (1996) Shear stress inhibits apoptosis of human endothelial cells. FEBS Lett 399:71–74
Bartling B, Tostlebe H, Darmer D et al (2000) Shear stress-dependent expression of apoptosis-regulating genes in endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 278:740–746. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2000.3873
Kim M, Kim S, Lim JH et al (2012) Laminar flow activation of ERK5 protein in vascular endothelium leads to atheroprotective effect via NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) activation. J Biol Chem 287:40722–40731. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.381509
Dimmeler S, Fleming I, Fisslthaler B et al (1999) Activation of nitric oxide synthase in endothelial cells by Akt-dependent phosphorylation. Nature 399:601–605. https://doi.org/10.1038/21224
Hu YL, Hur SS, Lei L et al (2017) Shear stress induces apoptosis via cytochrome c release from dynamic mitochondria in endothelial cells. FASEB J 31:689.14
Junxia Z, Zhimei W, Guangfeng ZUO et al (2013) Low shear stress induces human vascular endothelial cell apoptosis by activating Akt signal and increasing reactive oxygen species. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 33:313–317. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2013.03.01
Dong G, Yang S, Cao X et al (2017) Low shear stress-induced autophagy alleviates cell apoptosis in HUVECs. Mol Med Rep 15:3076–3082. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6401
Xu F, Sun Y, Chen Y et al (2009) Endothelial cell apoptosis is responsible for the formation of coronary thrombotic atherosclerotic plaques. Tohoku J Exp Med 218:25–33
Badimon L, Vilahur G (2014) Thrombosis formation on atherosclerotic lesions and plaque rupture. J Intern Med 276:618–632. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12296
Bernal-Mizrachi L, Jy W, Jimenez JJ et al (2003) High levels of circulating endothelial microparticles in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Am Heart J 145:962–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-8703(03)00103-0
Amabile N, Guerin AP, Leroyer A et al (2005) Circulating endothelial microparticles are associated with vascular dysfunction in patients with end-stage renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:3381–3388. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2005050535
Minagar A, Jy W, Jimenez JJ et al (2001) Elevated plasma endothelial microparticles in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 56:1319 LP-1324
Koga H, Sugiyama S, Kugiyama K et al (2005) Elevated levels of VE-cadherin-positive endothelial microparticles in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 45:1622–1630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2005.02.047
Kagawa H, Nomura S, Miyake T et al (1995) Expression of prothrombinase activity and CD9 antigen on the surface of small vesicles from stimulated human endothelial cells. Thromb Res 80:451–460
Combes V, Simon A-C, Grau G-E et al (1999) In vitro generation of endothelial microparticles and possible prothrombotic activity in patients with lupus anticoagulant. J Clin Invest 104:93–102
Jimenez JJ, Jy W, Mauro LM et al (2001) Elevated endothelial microparticles in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: findings from brain and renal microvascular cell culture and patients with active disease. Br J Haematol 112:81–90
Tramontano AF, O’Leary J, Black AD et al (2004) Statin decreases endothelial microparticle release from human coronary artery endothelial cells: implication for the Rho-kinase pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 320:34–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.05.127
Rastogi S, Rizwani W, Joshi B et al (2012) TNF-alpha response of vascular endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells involve differential utilization of ASK1 kinase and p73. Cell Death Differ 19:274–283
Pihusch V, Rank A, Steber R et al (2006) Endothelial cell-derived microparticles in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell recipients. Transplantation 81:1405–1409
Jansen F, Yang X, Hoelscher M et al (2013) Endothelial microparticle-mediated transfer of MicroRNA-126 promotes vascular endothelial cell repair via SPRED1 and is abrogated in glucose-damaged endothelial microparticles. Circulation 128:2026–2038. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.001720
Sapet C, Simoncini S, Loriod B et al (2006) Thrombin-induced endothelial microparticle generation: identification of a novel pathway involving ROCK-II activation by caspase-2. Blood 108:1868–1876. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-04-014175
Hogg N, Browning J, Howard T et al (1999) Apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells caused by serum deprivation, oxidative stress and transforming growth factor-beta. Endothelium 7:35–49
Jimenez JJ, Jy W, Mauro LM et al (2003) Endothelial microparticles released in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura express von Willebrand factor and markers of endothelial activation. Br J Haematol 123:896–902
Simak J, Holada K, Vostal JG (2002) Release of annexin V-binding membrane microparticles from cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells after treatment with camptothecin. BMC Cell Biol 3:11
Hristov M, Erl W, Linder S, Weber PC (2004) Apoptotic bodies from endothelial cells enhance the number and initiate the differentiation of human endothelial progenitor cells in vitro. Blood 104:2761–2766. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2003-10-3614
Coumans FAW, Brisson AR, Buzas EI et al (2017) Methodological guidelines to study extracellular vesicles. Circ Res 120:1632–1648
Sluijter JPG, Davidson SM, Boulanger CM et al (2018) Extracellular vesicles in diagnostics and therapy of the ischaemic heart: position Paper from the Working Group on Cellular Biology of the Heart of the European Society of Cardiology. Cardiovasc Res 114:19–34. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvx211
Heloire F, Weill B, Weber S, Batteux F (2003) Aggregates of endothelial microparticles and platelets circulate in peripheral blood. Variations during stable coronary disease and acute myocardial infarction. Thromb Res 110:173–180
Arteaga RB, Chirinos JA, Soriano AO et al (2006) Endothelial microparticles and platelet and leukocyte activation in patients with the metabolic syndrome. Am J Cardiol 98:70–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2006.01.054
Boulanger CM, Amabile N, Guerin AP et al (2007) In vivo shear stress determines circulating levels of endothelial microparticles in end-stage renal disease. Hypertension 49:902–908. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000259667.22309.df
Jansen F, Yang X, Baumann K et al (2015) Endothelial microparticles reduce ICAM-1 expression in a microRNA-222-dependent mechanism. J Cell Mol Med 19:2202–2214. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12607
Baranyai T, Herczeg K, Onódi Z et al (2015) Isolation of exosomes from blood plasma: qualitative and quantitative comparison of ultracentrifugation and size exclusion chromatography methods. PLoS One 10:e0145686
Cvjetkovic A, Lötvall J, Lässer C (2014) The influence of rotor type and centrifugation time on the yield and purity of extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles 3:23111. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v3.23111
Arroyo JD, Chevillet JR, Kroh EM, et al (2011) Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:5003 LP-5008
Van Deun J, Mestdagh P, Sormunen R et al (2014) The impact of disparate isolation methods for extracellular vesicles on downstream RNA profiling. J Extracell vesicles. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v3.24858
Lobb RJ, Becker M, Wen SW et al (2015) Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J Extracell vesicles 4:27031
Njock M-S, Cheng HS, Dang LT et al (2015) Endothelial cells suppress monocyte activation through secretion of extracellular vesicles containing anti-inflammatory microRNAs. Blood 125:3202–3212. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-11-611046
Jiang L, Paone S, Caruso S et al (2017) Determining the contents and cell origins of apoptotic bodies by flow cytometry. Sci Rep 7:14444. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14305-z
Boulanger CM, Scoazec A, Ebrahimian T et al (2001) Circulating microparticles from patients with myocardial infarction cause endothelial dysfunction. Circulation 104:2649–2652. https://doi.org/10.1161/hc4701.100516
VanWijk MJ, Nieuwland R, Boer K et al (2002) Microparticle subpopulations are increased in preeclampsia: possible involvement in vascular dysfunction? Am J Obstet Gynecol 187:450–456
Leroyer AS, Isobe H, Leseche G et al (2007) Cellular origins and thrombogenic activity of microparticles isolated from human atherosclerotic plaques. J Am Coll Cardiol 49:772–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2006.10.053
Hergenreider E, Heydt S, Treguer K et al (2012) Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nat Cell Biol 14:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2441
Holnthoner W, Bonstingl C, Hromada C et al (2017) Endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles size-dependently exert procoagulant activity detected by thromboelastometry. Sci Rep 7:3707. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03159-0
Boulanger CM, Loyer X, Rautou P-E, Amabile N (2017) Extracellular vesicles in coronary artery disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 14:259–272. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2017.7
Zhan R, Leng X, Liu X et al (2009) Heat shock protein 70 is secreted from endothelial cells by a non-classical pathway involving exosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 387:229–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.06.095
Cunningham KS, Gotlieb AI (2004) The role of shear stress in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Lab Investig 85:9
Boon RA, Leyen TA, Fontijn RD et al (2010) KLF2-induced actin shear fibers control both alignment to flow and JNK signaling in vascular endothelium. Blood 115:2533–2542
Downs JR, Clearfield M, Weis S et al (1998) Primary prevention of acute coronary events with lovastatin in men and women with average cholesterol levels: results of AFCAPS/TexCAPS. Air Force/Texas Coronary Atherosclerosis Prevention Study. JAMA 279:1615–1622
Suades R, Padró T, Alonso R et al (2013) Lipid-lowering therapy with statins reduces microparticle shedding from endothelium, platelets and inflammatory cells. Thromb Haemost 110:366–377. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH13-03-0238
Huang B, Cheng Y, Xie Q et al (2012) Effect of 40 mg versus 10 mg of atorvastatin on oxidized low-density lipoprotein, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, circulating endothelial-derived microparticles, and endothelial progenitor cells in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. Clin Cardiol 35:125–130. https://doi.org/10.1002/clc.21017
Jenkins NT, Padilla J, Boyle LJ et al (2013) Disturbed blood flow acutely induces activation and apoptosis of the human vascular endothelium. Hypertension 61:615–621. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.00561
Chirinos JA, Zambrano JP, Virani SS et al (2005) Correlation between apoptotic endothelial microparticles and serum interleukin-6 and c-reactive protein in healthy men. Am J Cardiol 95:1258–1260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.01.063
Komiyama Y, Pedersen AH, Kisiel W (1990) Proteolytic activation of human factors IX and X by recombinant human factor VIIa: effects of calcium, phospholipids, and tissue factor. Biochemistry 29:9418–9425
Owens AP, Mackman N (2011) Microparticles in hemostasis and thrombosis. Circ Res 108:1284–1297. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.233056
Mallat Z, Benamer H, Hugel B et al (2000) Elevated levels of shed membrane microparticles with procoagulant potential in the peripheral circulating blood of patients with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 101:841–843
Keyel PA, Tkacheva OA, Larregina AT, Salter RD (2012) Coordinate stimulation of macrophages by microparticles and TLR ligands induces foam cell formation. J Immunol 189:4621–4629. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1200828
Huber J, Vales A, Mitulovic G et al (2002) Oxidized membrane vesicles and blebs from apoptotic cells contain biologically active oxidized phospholipids that induce monocyte-endothelial interactions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:101–107
Atkin-Smith GK, Paone S, Zanker DJ et al (2017) Isolation of cell type-specific apoptotic bodies by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Sci Rep 7:39846
Dickhout A, Koenen RR (2018) Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Disease. Chances and Risks. Front Cardiovasc Med 5:113. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2018.00113
Schiro A, Wilkinson FL, Weston R et al (2014) Endothelial microparticles as conveyors of information in atherosclerotic disease. Atherosclerosis 234:295–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.03.019
Amabile N, Cheng S, Renard JM et al (2014) Association of circulating endothelial microparticles with cardiometabolic risk factors in the Framingham Heart Study. Eur Heart J 35:2972–2979. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehu153
Jayachandran M, Litwiller RD, Lahr BD et al (2011) Alterations in platelet function and cell-derived microvesicles in recently menopausal women: relationship to metabolic syndrome and atherogenic risk. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 4:811–822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-011-9296-9
Bernal-Mizrachi L, Jy W, Fierro C et al (2004) Endothelial microparticles correlate with high-risk angiographic lesions in acute coronary syndromes. Int J Cardiol 97:439–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2003.10.029
Pérez-Casal M, Downey C, Cutillas-Moreno B et al (2009) Microparticle-associated endothelial protein C receptor and the induction of cytoprotective and anti-inflammatory effects. Haematologica 94:387–394. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.13547
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (GNT1125033) to I.K.H.P. and (GNT1141732) to A.A.B., and Australian Research Council (DP170103790) to I.K.H.P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have anything to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paone, S., Baxter, A.A., Hulett, M.D. et al. Endothelial cell apoptosis and the role of endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles in the progression of atherosclerosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 76, 1093–1106 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2983-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2983-9