Abstract
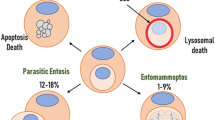
Multiple mechanisms have emerged where the engulfment of whole live cells, leading to the formation of what are called ‘cell-in-cell’ structures, induces cell death. Entosis is one such mechanism that drives cell-in-cell formation during carcinogenesis and development. Curiously, entotic cells participate actively in their own engulfment, by invading into their hosts, and are then killed non-cell-autonomously. Here we review the mechanisms of entosis and entotic cell death and the consequences of entosis on cell populations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abodief WT, Dey P, Al-Hattab O (2006) Cell cannibalism in ductal carcinoma of breast. Cytopathology 17:304–305
Benseler V, Warren A, Vo M, Holz LE, Tay SS, Le Couteur DG, Breen E, Allison AC, van Rooijen N, McGuffog C, Schlitt HJ, Bowen DG, McCaughan GW, Bertolino P (2011) Hepatocyte entry leads to degradation of autoreactive CD8 T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:16735–16740
Brown GC, Vilalta A, Fricker M (2015) Phagoptosis—cell death by phagocytosis—plays central roles in physiology, host defense and pathology. Curr Mol Med 15(9):842–851
Cano CE, Sandi MJ, Hamidi T, Calvo EL, Turrini O, Bartholin L, Loncle C, Secq V, Garcia S, Lomberk G, Kroemer G, Urrutia R, Iovanna JL (2012) Homotypic cell cannibalism, a cell-death process regulated by the nuclear protein 1, opposes to metastasis in pancreatic cancer. EMBO Mol Med 4:964–979
Claveria C, Giovinazzo G, Sierra R, Torres M (2013) Myc-driven endogenous cell competition in the early mammalian embryo. Nature 500:39–44
Coucouvanis E, Martin GR (1995) Signals for death and survival: a two-step mechanism for cavitation in the vertebrate embryo. Cell 83:279–287
de la Cova C, Abril M, Bellosta P, Gallant P, Johnston LA (2004) Drosophila myc regulates organ size by inducing cell competition. Cell 117:107–116
Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap P, Mizushima N, Cuny GD, Mitchison TJ, Moskowitz MA, Yuan J (2005) Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol 1:112–119
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS, Morrison B 3rd, Stockwell BR (2012) Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149:1060–1072
Erdos GW, Raper KB, Vogen LK (1973) Mating types and macrocyst formation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:1828–1830
Fais S, Fauvarque MO (2012) TM9 and cannibalism: how to learn more about cancer by studying amoebae and invertebrates. Trends Mol Med 18:4–5
Florey O, Kim SE, Overholtzer M (2015) Entosis: cell-in-cell formation that kills through entotic cell death. Curr Mol Med 15(9):861–866
Florey O, Kim SE, Sandoval CP, Haynes CM, Overholtzer M (2011) Autophagy machinery mediates macroendocytic processing and entotic cell death by targeting single membranes. Nat Cell Biol 13:1335–1343
Florey O, Overholtzer M (2012) Autophagy proteins in macroendocytic engulfment. Trends Cell Biol 22:374–380
Fujiwara T, Bandi M, Nitta M, Ivanova EV, Bronson RT, Pellman D (2005) Cytokinesis failure generating tetraploids promotes tumorigenesis in p53-null cells. Nature 437:1043–1047
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, El-Deiry WS, Fulda S, Gottlieb E, Green DR, Hengartner MO, Kepp O, Knight RA, Kumar S, Lipton SA, Lu X, Madeo F, Malorni W, Mehlen P, Nunez G, Peter ME, Piacentini M, Rubinsztein DC, Shi Y, Simon HU, Vandenabeele P, White E, Yuan J, Zhivotovsky B, Melino G, Kroemer G (2012) Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell Death Differ 19:107–120
Gonzalez-Pastor JE (2011) Cannibalism: a social behavior in sporulating Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35:415–424
Guadamillas MC, Cerezo A, Del Pozo MA (2011) Overcoming anoikis–pathways to anchorage-independent growth in cancer. J Cell Sci 124:3189–3197
Hahn P, Lindsten T, Ying GS, Bennett J, Milam AH, Thompson CB, Dunaief JL (2003) Proapoptotic bcl-2 family members, Bax and Bak, are essential for developmental photoreceptor apoptosis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:3598–3605
Hoeppner DJ, Hengartner MO, Schnabel R (2001) Engulfment genes cooperate with ced-3 to promote cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 412:202–206
Huang H, Chen A, Wang T, Wang M, Ning X, He M, Hu Y, Yuan L, Li S, Wang Q, Liu H, Chen Z, Ren J, Sun Q (2015) Detecting cell-in-cell structures in human tumor samples by E-cadherin/CD68/CD45 triple staining. Oncotarget 6:20278–20287
Huang H, Chen Z, Sun Q (2015) Mammalian Cell Competitions. Cell-in-cell Phenomena and their biomedical implications, Curr Mol Med
Jacob DA, Ray T, Bengston CL, Lindsten T, Wu J, Thompson CB, Forger NG (2008) The role of cell death in sexually dimorphic muscle development: male-specific muscles are retained in female bax/bak knockout mice. Dev Neurobiol 68:1303–1314
Jiang L, Kon N, Li T, Wang SJ, Su T, Hibshoosh H, Baer R, Gu W (2015) Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature 520:57–62
Krajcovic M, Johnson NB, Sun Q, Normand G, Hoover N, Yao E, Richardson AL, King RW, Cibas ES, Schnitt SJ, Brugge JS, Overholtzer M (2011) A non-genetic route to aneuploidy in human cancers. Nat Cell Biol 13:324–330
Krajcovic M, Krishna S, Akkari L, Joyce JA, Overholtzer M (2013) mTOR regulates phagosome and entotic vacuole fission. Mol Biol Cell 24:3736–3745
Krajcovic M, Overholtzer M (2012) Mechanisms of ploidy increase in human cancers: a new role for cell cannibalism. Cancer Res 72:1596–1601
Lee CY, Baehrecke EH (2001) Steroid regulation of autophagic programmed cell death during development. Development 128:1443–1455
Li W, Baker NE (2007) Engulfment is required for cell competition. Cell 129:1215–1225
Li Y, Sun X, Dey SK (2015) Entosis allows timely elimination of the luminal epithelial barrier for embryo implantation. Cell Rep 11:358–365
Lindsten T, Golden JA, Zong WX, Minarcik J, Harris MH, Thompson CB (2003) The proapoptotic activities of bax and bak limit the size of the neural stem cell pool. J Neurosci 23:11112–11119
Lindsten T, Ross AJ, King A, Zong WX, Rathmell JC, Shiels HA, Ulrich E, Waymire KG, Mahar P, Frauwirth K, Chen Y, Wei M, Eng VM, Adelman DM, Simon MC, Ma A, Golden JA, Evan G, Korsmeyer SJ, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB (2000) The combined functions of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members bak and bax are essential for normal development of multiple tissues. Mol Cell 6:1389–1399
Linkermann A, Brasen JH, Darding M, Jin MK, Sanz AB, Heller JO, De Zen F, Weinlich R, Ortiz A, Walczak H, Weinberg JM, Green DR, Kunzendorf U, Krautwald S (2013) Two independent pathways of regulated necrosis mediate ischemia-reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:12024–12029
Linkermann A, Skouta R, Himmerkus N, Mulay SR, Dewitz C, De Zen F, Prokai A, Zuchtriegel G, Krombach F, Welz PS, Weinlich R, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P, Pasparakis M, Bleich M, Weinberg JM, Reichel CA, Brasen JH, Kunzendorf U, Anders HJ, Stockwell BR, Green DR, Krautwald S (2014) Synchronized renal tubular cell death involves ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:16836–16841
Liu Y, Shoji-Kawata S, Sumpter RM Jr, Wei Y, Ginet V, Zhang L, Posner B, Tran KA, Green DR, Xavier RJ, Shaw SY, Clarke PG, Puyal J, Levine B (2013) Autosis is a Na+, K+-ATPase-regulated form of cell death triggered by autophagy-inducing peptides, starvation, and hypoxia-ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:20364–20371
Lolo FN, Casas-Tinto S, Moreno E (2012) Cell competition time line: winners kill losers, which are extruded and engulfed by hemocytes. Cell reports 2:526–539
Lozupone F, Fais S (2015) Cancer cell cannibalism: a primeval option to survive. Curr Mol Med 15(9):836–841
Lugini L, Matarrese P, Tinari A, Lozupone F, Federici C, Iessi E, Gentile M, Luciani F, Parmiani G, Rivoltini L, Malorni W, Fais S (2006) Cannibalism of live lymphocytes by human metastatic but not primary melanoma cells. Cancer Res 66:3629–3638
Mailleux AA, Overholtzer M, Schmelzle T, Bouillet P, Strasser A, Brugge JS (2007) BIM regulates apoptosis during mammary ductal morphogenesis, and its absence reveals alternative cell death mechanisms. Dev Cell 12:221–234
Mocarski ES, Guo H, Kaiser WJ (2015) Necroptosis: the Trojan horse in cell autonomous antiviral host defense. Virology 479–480:160–166
Morata G, Ripoll P (1975) Minutes: mutants of drosophila autonomously affecting cell division rate. Dev Biol 42:211–221
Moreno E, Basler K (2004) dMyc transforms cells into super-competitors. Cell 117:117–129
Nelson C, Ambros V, Baehrecke EH (2014) miR-14 regulates autophagy during developmental cell death by targeting ip3-kinase 2. Mol Cell 56:376–388
Nizak C, Fitzhenry RJ, Kessin RH (2007) Exploitation of other social amoebae by Dictyostelium caveatum. PLoS One 2:e212
O’Day DH, Keszei A (2012) Signalling and sex in the social amoebozoans. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 87:313–329
Overholtzer M, Brugge JS (2008) The cell biology of cell-in-cell structures. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:796–809
Overholtzer M, Mailleux AA, Mouneimne G, Normand G, Schnitt SJ, King RW, Cibas ES, Brugge JS (2007) A nonapoptotic cell death process, entosis, that occurs by cell-in-cell invasion. Cell 131:966–979
Overholtzer M, Wang X (2015) Editorial: cell-in-cell: a century-old mystery comes to the table. Curr Mol Med 15(9):802–804
Purvanov V, Holst M, Khan J, Baarlink C, Grosse R (2014) G-protein-coupled receptor signaling and polarized actin dynamics drive cell-in-cell invasion. Elife 3
Rathmell JC, Lindsten T, Zong WX, Cinalli RM, Thompson CB (2002) Deficiency in bak and bax perturbs thymic selection and lymphoid homeostasis. Nat Immunol 3:932–939
Reddien PW, Cameron S, Horvitz HR (2001) Phagocytosis promotes programmed cell death in C. elegans. Nature 412:198–202
Rusconi JC, Hays R, Cagan RL (2000) Programmed cell death and patterning in Drosophila. Cell Death Differ 7:1063–1070
Saga Y, Yanagisawa K (1982) Macrocyst development in Dictyostelium discoideum. I. Induction of synchronous development by giant cells and biochemical analysis. J Cell Sci 55:341–352
Schwegler M, Wirsing AM, Schenker HM, Ott L, Ries JM, Buttner-Herold M, Fietkau R, Putz F, Distel LV (2015) Prognostic value of homotypic cell Internalization by nonprofessional phagocytic cancer cells. BioMed Res Int 2015:359392
Sierro F, Tay SS, Warren A, Le Couteur DG, McCaughan GW, Bowen DG, Bertolino P (2015) Suicidal emperipolesis: a process leading to cell-in-cell structures, T cell clearance and immune homeostasis. Curr Mol Med 15(9):819–827
Sun Q, Cibas ES, Huang H, Hodgson L, Overholtzer M (2014) Induction of entosis by epithelial cadherin expression. Cell Res 24:1288–1298
Sun Q, Luo T, Ren Y, Florey O, Shirasawa S, Sasazuki T, Robinson DN, Overholtzer M (2014) Competition between human cells by entosis. Cell Res 24:1299–1310
Villa del Campo C, Claveria C, Sierra R, Torres M (2014) Cell competition promotes phenotypically silent cardiomyocyte replacement in the mammalian heart. Cell Rep 8:1741–1751
Waddell DR, Duffy KT (1986) Breakdown of self/nonself recognition in cannibalistic strains of the predatory slime mold, Dictyostelium caveatum. J Cell Biol 102:298–305
Wan Q, Liu J, Zheng Z, Zhu H, Chu X, Dong Z, Huang S, Du Q (2012) Regulation of myosin activation during cell-cell contact formation by Par3-Lgl antagonism: entosis without matrix detachment. Mol Biol Cell 23:2076–2091
Wang M, Ning X, Chen A, Huang H, Ni C, Zhou C, Yu K, Lan S, Wang Q, Li S, Liu H, Wang X, Chen Z, Ma L, Sun Q (2015) Impaired formation of homotypic cell-in-cell structures in human tumor cells lacking alpha-catenin expression. Sci Rep 5:12223
Wang S, He MF, Chen YH, Wang MY, Yu XM, Bai J, Zhu HY, Wang YY, Zhao H, Mei Q, Nie J, Ma J, Wang JF, Wen Q, Ma L, Wang Y, Wang XN (2013) Rapid reuptake of granzyme B leads to emperitosis: an apoptotic cell-in-cell death of immune killer cells inside tumor cells. Cell Death Dis 4:e856
Wang X (2015) Cell-in-cell phenomenon: a new Paradigm in life sciences. Curr Mol Med 15(9):810–818
Wang Y, Wang X (2015) Entosis and related forms of cell death within cells. Curr Mol Med 15(9):805–809
Ward KA, Li WI, Zimmer S, Davis T (1991) Viscoelastic properties of transformed cells: role in tumor cell progression and metastasis formation. Biorheology 28:301–313
Acknowledgments
This article was Funded by a Grant from the National Cancer Institute (R01CA154649, to M.O.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishna, S., Overholtzer, M. Mechanisms and consequences of entosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 73, 2379–2386 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2207-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2207-0