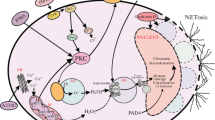
Abstract
Neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation is a hallmark of many disorders that involve neutrophil recruitment, tissue damage, and inflammation. As NET formation is often associated with neutrophil death, the term “NETosis” has become popular. Upon discovery that neutrophils may survive NET release, apparent misnomers, such as “vital NETosis,” have been proposed. Meanwhile, it has become obvious that certain stimuli can trigger neutrophil necroptosis, a process associated with NET-like chromatin release. Here, we discuss the relationship between NET release and neutrophil death in view highlighting that many assays used in the field do not properly distinguish between the two. An updated nomenclature is needed replacing the term “NETosis” to meet the growing variety of settings leading to chromatin release with and without neutrophil death. Dissecting which triggers of NET release involve which signaling pathway will help to define drugable molecular targets that inhibit NET release and/or neutrophil necrosis in specific disorders.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kolaczkowska E, Kubes P (2013) Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 13(3):159–175. doi:10.1038/nri3399
Pillay J, den Braber I, Vrisekoop N, Kwast LM, de Boer RJ, Borghans JA, Tesselaar K, Koenderman L (2010) In vivo labeling with 2H2O reveals a human neutrophil lifespan of 5.4 days. Blood 116:625–627. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-01-259028
Martin C, Burdon PC, Bridger G, Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Williams TJ, Rankin SM (2003) Chemokines acting via CXCR2 and CXCR4 control the release of neutrophils from the bone marrow and their return following senescence. Immunity 19(4):583–593
Colotta F, Re F, Polentarutti N, Sozzani S, Mantovani A (1992) Modulation of granulocyte survival and programmed cell death by cytokines and bacterial products. Blood 80(8):2012–2020
Summers C, Rankin SM, Condliffe AM, Singh N, Peters AM, Chilvers ER (2010) Neutrophil kinetics in health and disease. Trends Immunol 31(8):318–324. doi:10.1016/j.it.2010.05.006
Huber AR, Kunkel SL, Todd RF 3rd, Weiss SJ (1991) Regulation of transendothelial neutrophil migration by endogenous interleukin-8. Science 254(5028):99–102
Brinkmann V, Reichard U, Goosmann C, Fauler B, Uhlemann Y, Weiss DS, Weinrauch Y, Zychlinsky A (2004) Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 303(5663):1532–1535. doi:10.1126/science.1092385
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, El-Deiry WS, Fulda S, Gottlieb E, Green DR, Hengartner MO, Kepp O, Knight RA, Kumar S, Lipton SA, Lu X, Madeo F, Malorni W, Mehlen P, Nunez G, Peter ME, Piacentini M, Rubinsztein DC, Shi Y, Simon HU, Vandenabeele P, White E, Yuan J, Zhivotovsky B, Melino G, Kroemer G (2012) Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell Death Differ 19(1):107–120. doi:10.1038/cdd.2011.96
Jorgensen I, Miao EA (2015) Pyroptotic cell death defends against intracellular pathogens. Immunol Rev 265(1):130–142. doi:10.1111/imr.12287
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y, Huang H, Zhuang Y, Cai T, Wang F, Shao F (2015) Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 526(7575):660–665. doi:10.1038/nature15514
Yipp BG, Kubes P (2013) NETosis: how vital is it? Blood 122(16):2784–2794. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-04-457671
Zhao W, Fogg DK, Kaplan MJ (2015) A novel image-based quantitative method for the characterization of NETosis. J Immunol Methods 423:104–110. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2015.04.027
Takei H, Araki A, Watanabe H, Ichinose A, Sendo F (1996) Rapid killing of human neutrophils by the potent activator phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) accompanied by changes different from typical apoptosis or necrosis. J Leukoc Biol 59(2):229–240
Fuchs TA, Abed U, Goosmann C, Hurwitz R, Schulze I, Wahn V, Weinrauch Y, Brinkmann V, Zychlinsky A (2007) Novel cell death program leads to neutrophil extracellular traps. J Cell Biol 176(2):231–241. doi:10.1083/jcb.200606027
Metzler KD, Goosmann C, Lubojemska A, Zychlinsky A, Papayannopoulos V (2014) A myeloperoxidase-containing complex regulates neutrophil elastase release and actin dynamics during NETosis. Cell Rep 8(3):883–896. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.06.044
Köcktritz-Blickwede MV, Chow O, Ghochani M, Nizet V (2010) Visualization and functional evaluation of phagocyte extracellular traps. In: Kabelitz D, Kaufmann SHE (eds) Methods in microbiology, vol 37. Elsevier Ltd., pp I39–I60. doi:10.1016/S0580-9517(10)37007-3
Arai Y, Yamashita K, Mizugishi K, Watanabe T, Sakamoto S, Kitano T, Kondo T, Kawabata H, Kadowaki N, Takaori-Kondo A (2013) Serum neutrophil extracellular trap levels predict thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant J Am Soc Blood Marrow Transplant 19(12):1683–1689. doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2013.09.005
Mori Y, Yamaguchi M, Terao Y, Hamada S, Ooshima T, Kawabata S (2012) alpha-Enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae induces formation of neutrophil extracellular traps. J Biol Chem 287(13):10472–10481. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.280321
Francois M, Le Cabec V, Dupont MA, Sansonetti PJ, Maridonneau-Parini I (2000) Induction of necrosis in human neutrophils by Shigella flexneri requires type III secretion, IpaB and IpaC invasins, and actin polymerization. Infect Immun 68(3):1289–1296
Li P, Li M, Lindberg MR, Kennett MJ, Xiong N, Wang Y (2010) PAD4 is essential for antibacterial innate immunity mediated by neutrophil extracellular traps. J Exp Med 207(9):1853–1862. doi:10.1084/jem.20100239
Wang Y, Li M, Stadler S, Correll S, Li P, Wang D, Hayama R, Leonelli L, Han H, Grigoryev SA, Allis CD, Coonrod SA (2009) Histone hypercitrullination mediates chromatin decondensation and neutrophil extracellular trap formation. J Cell Biol 184(2):205–213. doi:10.1083/jcb.200806072
Leshner M, Wang S, Lewis C, Zheng H, Chen XA, Santy L, Wang Y (2012) PAD4 mediated histone hypercitrullination induces heterochromatin decondensation and chromatin unfolding to form neutrophil extracellular trap-like structures. Front Immunol 3:307. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2012.00307
Kumar SV, Kulkarni OP, Mulay SR, Darisipudi MN, Romoli S, Thomasova D, Scherbaum CR, Hohenstein B, Hugo C, Muller S, Liapis H, Anders HJ (2015) Neutrophil extracellular trap-related extracellular histones cause vascular necrosis in severe GN. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN 26(10):2399–2413. doi:10.1681/ASN.2014070673
Knight JS, Zhao W, Luo W, Subramanian V, O’Dell AA, Yalavarthi S, Hodgin JB, Eitzman DT, Thompson PR, Kaplan MJ (2013) Peptidylarginine deiminase inhibition is immunomodulatory and vasculoprotective in murine lupus. J Clin Investig 123(7):2981–2993. doi:10.1172/JCI67390
Knuckley B, Causey CP, Jones JE, Bhatia M, Dreyton CJ, Osborne TC, Takahara H, Thompson PR (2010) Substrate specificity and kinetic studies of PADs 1, 3, and 4 identify potent and selective inhibitors of protein arginine deiminase 3. Biochemistry 49(23):4852–4863. doi:10.1021/bi100363t
Causey CP, Jones JE, Slack JL, Kamei D, Jones LE, Subramanian V, Knuckley B, Ebrahimi P, Chumanevich AA, Luo Y, Hashimoto H, Sato M, Hofseth LJ, Thompson PR (2011) The development of N-alpha-(2-carboxyl)benzoyl-N(5)-(2-fluoro-1-iminoethyl)-l-ornithine amide (o-F-amidine) and N-alpha-(2-carboxyl)benzoyl-N(5)-(2-chloro-1-iminoethyl)-l-ornithine amide (o-Cl-amidine) as second generation protein arginine deiminase (PAD) inhibitors. J Med Chem 54(19):6919–6935. doi:10.1021/jm2008985
Hemmers S, Teijaro JR, Arandjelovic S, Mowen KA (2011) PAD4-mediated neutrophil extracellular trap formation is not required for immunity against influenza infection. PLoS One 6(7):e22043. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022043
Narasaraju T, Yang E, Samy RP, Ng HH, Poh WP, Liew AA, Phoon MC, van Rooijen N, Chow VT (2011) Excessive neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to acute lung injury of influenza pneumonitis. Am J Pathol 179(1):199–210. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.03.013
Neeli I, Radic M (2013) Opposition between PKC isoforms regulates histone deimination and neutrophil extracellular chromatin release. Front Immunol 4:38. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2013.00038
Kessenbrock K, Krumbholz M, Schonermarck U, Back W, Gross WL, Werb Z, Grone HJ, Brinkmann V, Jenne DE (2009) Netting neutrophils in autoimmune small-vessel vasculitis. Nat Med 15(6):623–625. doi:10.1038/nm.1959
Nakazawa D, Shida H, Tomaru U, Yoshida M, Nishio S, Atsumi T, Ishizu A (2014) Enhanced formation and disordered regulation of NETs in myeloperoxidase-ANCA-associated microscopic polyangiitis. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN 25(5):990–997. doi:10.1681/ASN.2013060606
Sayah DM, Mallavia B, Liu F, Ortiz-Munoz G, Caudrillier A, DerHovanessian A, Ross DJ, Lynch JP 3rd, Saggar R, Ardehali A, Ware LB, Christie JD, Belperio JA, Looney MR (2015) Neutrophil extracellular traps are pathogenic in primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 191(4):455–463. doi:10.1164/rccm.201406-1086OC
Hakkim A, Fuchs TA, Martinez NE, Hess S, Prinz H, Zychlinsky A, Waldmann H (2011) Activation of the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway is required for neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Nat Chem Biol 7(2):75–77. doi:10.1038/nchembio.496
Rohm M, Grimm MJ, D’Auria AC, Almyroudis NG, Segal BH, Urban CF (2014) NADPH oxidase promotes neutrophil extracellular trap formation in pulmonary aspergillosis. Infect Immun 82(5):1766–1777. doi:10.1128/IAI.00096-14
Schauer C, Janko C, Munoz LE, Zhao Y, Kienhofer D, Frey B, Lell M, Manger B, Rech J, Naschberger E, Holmdahl R, Krenn V, Harrer T, Jeremic I, Bilyy R, Schett G, Hoffmann M, Herrmann M (2014) Aggregated neutrophil extracellular traps limit inflammation by degrading cytokines and chemokines. Nat Med 20(5):511–517. doi:10.1038/nm.3547
Papayannopoulos V, Metzler KD, Hakkim A, Zychlinsky A (2010) Neutrophil elastase and myeloperoxidase regulate the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps. J Cell Biol 191(3):677–691. doi:10.1083/jcb.201006052
Metzler KD, Fuchs TA, Nauseef WM, Reumaux D, Roesler J, Schulze I, Wahn V, Papayannopoulos V, Zychlinsky A (2011) Myeloperoxidase is required for neutrophil extracellular trap formation: implications for innate immunity. Blood 117(3):953–959. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-06-290171
Linkermann A, Green DR (2014) Necroptosis. New England J Med 370(5):455–465. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1310050
Ebrahim M, Mulay SR, Anders HJ, Thomasova D (2015) MDM2 beyond cancer: podoptosis, development, inflammation, and tissue regeneration. Histol Histopathol 30(11):1271–1282. doi:10.14670/HH-11-636
Wartha F, Henriques-Normark B (2008) ETosis: a novel cell death pathway. Sci Signal 1(21):pe25. doi:10.1126/stke.121pe25
Desai J, Vr SK, Mulay SR, Konrad L, Romoli S, Schauer C, Herrmann M, Bilyy R, Muller S, Popper B, Nakazawa D, Weidenbusch M, Thomasova D, Krautwald S, Linkermann A, Anders HJ (2015) Neutrophil extracellular trap formation can involve RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL signalling. Eur J Immunol. doi:10.1002/eji.201545605
Mulay SR, Desai J, Kumar VRS, Eberhard JN, Thomasova D, Romoli S, Grigorescu M, Kulkarni OP, Popper B, Vielhauer V, Zuchtriegel G, Reichel C, Bräsen JH, Romagnani P, Bilyy R, Munoz LE, Herrmann M, Liapis H, Krautwald S, Linkermann A, Anders HJ (2016) Cytotoxicity of crystals involves RIPK3-MLKL-mediated necroptosis. Nat Commun 7:10274. doi:10.1038/ncomms10274
Pilsczek FH, Salina D, Poon KK, Fahey C, Yipp BG, Sibley CD, Robbins SM, Green FH, Surette MG, Sugai M, Bowden MG, Hussain M, Zhang K, Kubes P (2010) A novel mechanism of rapid nuclear neutrophil extracellular trap formation in response to Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol 185(12):7413–7425. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1000675
Yipp BG, Petri B, Salina D, Jenne CN, Scott BN, Zbytnuik LD, Pittman K, Asaduzzaman M, Wu K, Meijndert HC, Malawista SE, de Boisfleury Chevance A, Zhang K, Conly J, Kubes P (2012) Infection-induced NETosis is a dynamic process involving neutrophil multitasking in vivo. Nat Med 18(9):1386–1393. doi:10.1038/nm.2847
Clark SR, Ma AC, Tavener SA, McDonald B, Goodarzi Z, Kelly MM, Patel KD, Chakrabarti S, McAvoy E, Sinclair GD, Keys EM, Allen-Vercoe E, Devinney R, Doig CJ, Green FH, Kubes P (2007) Platelet TLR4 activates neutrophil extracellular traps to ensnare bacteria in septic blood. Nat Med 13(4):463–469. doi:10.1038/nm1565
Byrd AS, O’Brien XM, Johnson CM, Lavigne LM, Reichner JS (2013) An extracellular matrix-based mechanism of rapid neutrophil extracellular trap formation in response to Candida albicans. J Immunol 190(8):4136–4148. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1202671
Peschel A, Hartl D (2012) Anuclear neutrophils keep hunting. Nat Med 18(9):1336–1338. doi:10.1038/nm.2918
Yousefi S, Mihalache C, Kozlowski E, Schmid I, Simon HU (2009) Viable neutrophils release mitochondrial DNA to form neutrophil extracellular traps. Cell Death Differ 16(11):1438–1444. doi:10.1038/cdd.2009.96
Chow OA, von Kockritz-Blickwede M, Bright AT, Hensler ME, Zinkernagel AS, Cogen AL, Gallo RL, Monestier M, Wang Y, Glass CK, Nizet V (2010) Statins enhance formation of phagocyte extracellular traps. Cell Host Microbe 8(5):445–454. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2010.10.005
Parker H, Dragunow M, Hampton MB, Kettle AJ, Winterbourn CC (2012) Requirements for NADPH oxidase and myeloperoxidase in neutrophil extracellular trap formation differ depending on the stimulus. J Leukoc Biol 92(4):841–849. doi:10.1189/jlb.1211601
Amini P, Stojkov D, Wang X, Wicki S, Kaufmann T, Wong WW, Simon HU, Yousefi S (2015) NET formation can occur independently of RIPK3 and MLKL signaling. Eur J Immunol. doi:10.1002/eji.201545615
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desai, J., Mulay, S.R., Nakazawa, D. et al. Matters of life and death. How neutrophils die or survive along NET release and is “NETosis” = necroptosis?. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 73, 2211–2219 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2195-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2195-0