Abstract
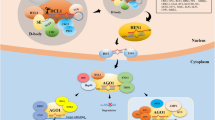
microRNAs (miRNAs) are important regulators of gene expression. After excised from primary miRNA transcript by dicer-like1 (DCL1, an RNAse III enzyme), miRNAs bind and guide their effector protein named argonaute 1 (AGO1) to silence the expression of target RNAs containing their complementary sequences in plants. miRNA levels and activities are tightly controlled to ensure their functions in various biological processes such as development, metabolism and responses to abiotic and biotic stresses. Studies have identified many factors that involve in miRNA accumulation and activities. Characterization of these factors in turn greatly improves our understanding of the processes related to miRNAs. Here, we review recent progress of mechanisms underlying miRNA expression and functions in plants.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Baulcombe D (2004) RNA silencing in plants. Nature 431:356–363
Bologna NG, Voinnet O (2014) The diversity, biogenesis, and activities of endogenous silencing small RNAs in Arabidopsis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65:473–503
Rogers K, Chen X (2013) Biogenesis, turnover, and mode of action of plant microRNAs. Plant Cell 25:2383–2399
Reinhart BJ, Weinstein EG, Rhoades MW, Bartel B, Bartel DP (2002) MicroRNAs in plants. Genes Dev 16:1616–1626
Park W, Li J, Song R, Messing J, Chen X (2002) Carpel factory, a dicer homolog, and HEN1, a novel protein, act in microRNA metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Biol 12:1484–1495
Llave C, Kasschau KD, Rector MA, Carrington JC (2002) Endogenous and silencing-associated small RNAs in plants. Plant Cell 14:1605–1619
Meyers BC, Souret FF, Lu C, Green PJ (2006) Sweating the small stuff: microRNA discovery in plants. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:139–146
Chen X (2009) Small RNAs and their roles in plant development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 25:21–44
Martin RC, Liu PP, Goloviznina NA, Nonogaki H (2010) microRNA, seeds, and Darwin?: diverse function of miRNA in seed biology and plant responses to stress. J Exp Bot 61:2229–2234
Poethig RS (2009) Small RNAs and developmental timing in plants. Curr Opin Genet Dev 19:374–378
Moreno-Risueno MA, Van Norman JM, Benfey PN (2012) Transcriptional switches direct plant organ formation and patterning. Curr Top Dev Biol 98:229–257
Chuck G, Candela H, Hake S (2009) Big impacts by small RNAs in plant development. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:81–86
Seo JK, Wu J, Lii Y, Li Y, Jin H (2013) Contribution of small RNA pathway components in plant immunity. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact : MPMI 26:617–625
Sunkar R, Li YF, Jagadeeswaran G (2012) Functions of microRNAs in plant stress responses. Trends Plant Sci 17:196–203
Khraiwesh B, Zhu JK, Zhu J (2012) Role of miRNAs and siRNAs in biotic and abiotic stress responses of plants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1819:137–148
Yu B, Yang Z, Li J, Minakhina S, Yang M, Padgett RW, Steward R, Chen X (2005) Methylation as a crucial step in plant microRNA biogenesis. Science 307:932–935
Park MY, Wu G, Gonzalez-Sulser A, Vaucheret H, Poethig RS (2005) Nuclear processing and export of microRNAs in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:3691–3696
Baumberger N, Baulcombe DC (2005) Arabidopsis ARGONAUTE1 is an RNA Slicer that selectively recruits microRNAs and short interfering RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:11928–11933
Mourrain P, Beclin C, Elmayan T, Feuerbach F, Godon C, Morel JB, Jouette D, Lacombe AM, Nikic S, Picault N, Remoue K, Sanial M, Vo TA, Vaucheret H (2000) Arabidopsis SGS2 and SGS3 genes are required for posttranscriptional gene silencing and natural virus resistance. Cell 101:533–542
Wu L, Zhang Q, Zhou H, Ni F, Wu X, Qi Y (2009) Rice MicroRNA effector complexes and targets. Plant Cell 21:3421–3435
Nozawa M, Miura S, Nei M (2012) Origins and evolution of microRNA genes in plant species. Genome Biol Evol 4:230–239
Coruh C, Shahid S, Axtell MJ (2014) Seeing the forest for the trees: annotating small RNA producing genes in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 18C:87–95
Xie ZX, Allen E, Fahlgren N, Calamar A, Givan SA, Carrington JC (2005) Expression of Arabidopsis MIRNA genes. Plant Physiol 138:2145–2154
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S, Enright AJ (2008) miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D154–D158
Yang GD, Yan K, Wu BJ, Wang YH, Gao YX, Zheng CC (2012) Genomewide analysis of intronic microRNAs in rice and Arabidopsis. J Genet 91:313–324
Piriyapongsa J, Jordan IK (2008) Dual coding of siRNAs and miRNAs by plant transposable elements. RNA 14:814–821
Kim YJ, Zheng B, Yu Y, Won SY, Mo B, Chen X (2011) The role of Mediator in small and long noncoding RNA production in Arabidopsis thaliana. EMBO J 30:814–822
Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP (2004) Computational identification of plant microRNAs and their targets, including a stress-induced miRNA. Mol Cell 14:787–799
Zhang BH, Pan XP, Wang QL, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2005) Identification and characterization of new plant microRNAs using EST analysis. Cell Res 15:336–360
Hajheidari M, Farrona S, Huettel B, Koncz Z, Koncz C (2012) CDKF;1 and CDKD protein kinases regulate phosphorylation of serine residues in the C-terminal domain of Arabidopsis RNA polymerase II. Plant Cell 24:1626–1642
Yu B, Bi L, Zheng B, Ji L, Chevalier D, Agarwal M, Ramachandran V, Li W, Lagrange T, Walker JC, Chen X (2008) The FHA domain proteins DAWDLE in Arabidopsis and SNIP1 in humans act in small RNA biogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:10073–10078
Megraw M, Baev V, Rusinov V, Jensen ST, Kalantidis K, Hatzigeorgiou AG (2006) MicroRNA promoter element discovery in Arabidopsis. RNA 12:1612–1619
Zhao X, Zhang H, Li L (2013) Identification and analysis of the proximal promoters of microRNA genes in Arabidopsis. Genomics 101:187–194
Wang L, Song X, Gu L, Li X, Cao S, Chu C, Cui X, Chen X, Cao X (2013) NOT2 proteins promote polymerase II-dependent transcription and interact with multiple MicroRNA biogenesis factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:715–727
Collart MA, Panasenko OO (2012) The Ccr4–not complex. Gene 492:42–53
Palma K, Zhao Q, Cheng YT, Bi D, Monaghan J, Cheng W, Zhang Y, Li X (2007) Regulation of plant innate immunity by three proteins in a complex conserved across the plant and animal kingdoms. Genes Dev 21:1484–1493
Zhang S, Xie M, Ren G, Yu B (2013) CDC5, a DNA binding protein, positively regulates posttranscriptional processing and/or transcription of primary microRNA transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:17588–17593
Yumul RE, Kim YJ, Liu X, Wang R, Ding J, Xiao L, Chen X (2013) POWERDRESS and diversified expression of the MIR172 gene family bolster the floral stem cell network. PLoS Genet 9:e1003218
Yant L, Mathieu J, Dinh TT, Ott F, Lanz C, Wollmann H, Chen X, Schmid M (2010) Orchestration of the floral transition and floral development in Arabidopsis by the bifunctional transcription factor APETALA2. Plant Cell 22:2156–2170
Grigorova B, Mara C, Hollender C, Sijacic P, Chen X, Liu Z (2011) LEUNIG and SEUSS co-repressors regulate miR172 expression in Arabidopsis flowers. Development 138:2451–2456
Wang F, Perry SE (2013) Identification of direct targets of FUSCA3, a key regulator of Arabidopsis seed development. Plant Physiol 161:1251–1264
Jeong DH, Park S, Zhai J, Gurazada SG, De Paoli E, Meyers BC, Green PJ (2011) Massive analysis of rice small RNAs: mechanistic implications of regulated microRNAs and variants for differential target RNA cleavage. Plant Cell 23:4185–4207
Liu HH, Tian X, Li YJ, Wu CA, Zheng CC (2008) Microarray-based analysis of stress-regulated microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. RNA 14:836–843
Zhao B, Liang R, Ge L, Li W, Xiao H, Lin H, Ruan K, Jin Y (2007) Identification of drought-induced microRNAs in rice. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 354:585–590
Liang G, He H, Yu D (2012) Identification of nitrogen starvation-responsive microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 7:e48951
Yamasaki H, Hayashi M, Fukazawa M, Kobayashi Y, Shikanai T (2009) SQUAMOSA Promoter Binding Protein-Like7 Is a central regulator for copper homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:347–361
Baek D, Kim MC, Chun HJ, Kang S, Park HC, Shin G, Park J, Shen M, Hong H, Kim WY, Kim DH, Lee SY, Bressan RA, Bohnert HJ, Yun DJ (2013) Regulation of miR399f transcription by AtMYB2 affects phosphate starvation responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 161:362–373
Valoczi A, Varallyay E, Kauppinen S, Burgyan J, Havelda Z (2006) Spatio-temporal accumulation of microRNAs is highly coordinated in developing plant tissues. Plant J 47:140–151
Breakfield NW, Corcoran DL, Petricka JJ, Shen J, Sae-Seaw J, Rubio-Somoza I, Weigel D, Ohler U, Benfey PN (2012) High-resolution experimental and computational profiling of tissue-specific known and novel miRNAs in Arabidopsis. Genome Res 22:163–176
Carlsbecker A, Lee JY, Roberts CJ, Dettmer J, Lehesranta S, Zhou J, Lindgren O, Moreno-Risueno MA, Vaten A, Thitamadee S, Campilho A, Sebastian J, Bowman JL, Helariutta Y, Benfey PN (2010) Cell signalling by microRNA165/6 directs gene dose-dependent root cell fate. Nature 465:316–321
Margis R, Fusaro AF, Smith NA, Curtin SJ, Watson JM, Finnegan EJ, Waterhouse PM (2006) The evolution and diversification of Dicers in plants. FEBS Lett 580:2442–2450
Mateos JL, Bologna NG, Chorostecki U, Palatnik JF (2010) Identification of microRNA processing determinants by random mutagenesis of Arabidopsis MIR172a precursor. Curr Biol 20:49–54
Rajagopalan R, Vaucheret H, Trejo J, Bartel DP (2006) A diverse and evolutionarily fluid set of microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes Dev 20:3407–3425
Wu L, Zhou H, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Ni F, Liu C, Qi Y (2010) DNA methylation mediated by a microRNA pathway. Mol Cell 38:465–475
Zhu H, Zhou Y, Castillo-Gonzalez C, Lu A, Ge C, Zhao YT, Duan L, Li Z, Axtell MJ, Wang XJ, Zhang X (2013) Bidirectional processing of pri-miRNAs with branched terminal loops by Arabidopsis Dicer-like1. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20:1106–1115
Song L, Axtell MJ, Fedoroff NV (2010) RNA secondary structural determinants of miRNA precursor processing in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 20:37–41
Werner S, Wollmann H, Schneeberger K, Weigel D (2010) Structure determinants for accurate processing of miR172a in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Biol 20:42–48
Bologna NG, Mateos JL, Bresso EG, Palatnik JF (2009) A loop-to-base processing mechanism underlies the biogenesis of plant microRNAs miR319 and miR159. The EMBO journal 28:3646–3656
Cuperus JT, Montgomery TA, Fahlgren N, Burke RT, Townsend T, Sullivan CM, Carrington JC (2010) Identification of MIR390a precursor processing-defective mutants in Arabidopsis by direct genome sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:466–471
Grigg SP, Canales C, Hay A, Tsiantis M (2005) SERRATE coordinates shoot meristem function and leaf axial patterning in Arabidopsis. Nature 437:1022–1026
Yang L, Liu ZQ, Lu F, Dong AW, Huang H (2006) SERRATE is a novel nuclear regulator in primary microRNA processing in Arabidopsis. Plant J 47:841–850
Lobbes D, Rallapalli G, Schmidt DD, Martin C, Clarke J (2006) SERRATE: a new player on the plant microRNA scene. EMBO Rep 7:1052–1058
Han MH, Goud S, Song L, Fedoroff N (2004) The Arabidopsis double-stranded RNA-binding protein HYL1 plays a role in microRNA-mediated gene regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:1093–1098
Vazquez F, Gasciolli V, Crete P, Vaucheret H (2004) The nuclear dsRNA binding protein HYL1 is required for microRNA accumulation and plant development, but not posttranscriptional transgene silencing. Curr Biol 14:346–351
Kurihara Y, Takashi Y, Watanabe Y (2006) The interaction between DCL1 and HYL1 is important for efficient and precise processing of pri-miRNA in plant microRNA biogenesis. RNA 12:206–212
Ren G, Xie M, Dou Y, Zhang S, Zhang C, Yu B (2012) Regulation of miRNA abundance by RNA binding protein TOUGH in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:12817–12821
Fang Y, Spector DL (2007) Identification of nuclear dicing bodies containing proteins for microRNA biogenesis in living Arabidopsis plants. Curr Biol 17:818–823
Song L, Han MH, Lesicka J, Fedoroff N (2007) Arabidopsis primary microRNA processing proteins HYL1 and DCL1 define a nuclear body distinct from the Cajal body. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:5437–5442
Fujioka Y, Utsumi M, Ohba Y, Watanabe Y (2007) Location of a possible miRNA processing site in SmD3/SmB nuclear bodies in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 48:1243–1253
Dong Z, Han MH, Fedoroff N (2008) The RNA-binding proteins HYL1 and SE promote accurate in vitro processing of pri-miRNA by DCL1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:9970–9975
Liu C, Axtell MJ, Fedoroff NV (2012) The helicase and RNaseIIIa domains of Arabidopsis Dicer-Like1 modulate catalytic parameters during microRNA biogenesis. Plant Physiol 159:748–758
Lu C, Fedoroff N (2000) A mutation in the Arabidopsis HYL1 gene encoding a dsRNA binding protein affects responses to abscisic acid, auxin, and cytokinin. Plant Cell 12:2351–2366
Yang SW, Chen HY, Yang J, Machida S, Chua NH, Yuan YA (2010) Structure of Arabidopsis HYPONASTIC LEAVES1 and its molecular implications for miRNA processing. Structure 18:594–605
Wu F, Yu L, Cao W, Mao Y, Liu Z, He Y (2007) The N-terminal double-stranded RNA binding domains of Arabidopsis HYPONASTIC LEAVES1 are sufficient for pre-microRNA processing. Plant Cell 19:914–925
Machida S, Chen HY, Adam Yuan Y (2011) Molecular insights into miRNA processing by Arabidopsis thaliana SERRATE. Nucleic Acids Res 39:7828–7836
Iwata Y, Takahashi M, Fedoroff NV, Hamdan SM (2013) Dissecting the interactions of SERRATE with RNA and DICER-LIKE 1 in Arabidopsis microRNA precursor processing. Nucleic Acids Res 41:9129–9140
Ren G, Yu B (2012) Critical roles of RNA-binding proteins in miRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis. RNA Biol 9:1424–1428
Ren G, Yu B (2012) Post-transcriptional control of miRNA abundance in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal Behav 7:1443–1446
Lau PW, Guiley KZ, De N, Potter CS, Carragher B, MacRae IJ (2012) The molecular architecture of human Dicer. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19:436–440
Raczynska KD, Stepien A, Kierzkowski D, Kalak M, Bajczyk M, McNicol J, Simpson CG, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z, Brown JW, Jarmolowski A (2014) The SERRATE protein is involved in alternative splicing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res 42:1224–1244
Laubinger S, Zeller G, Henz SR, Buechel S, Sachsenberg T, Wang JW, Ratsch G, Weigel D (2010) Global effects of the small RNA biogenesis machinery on the Arabidopsis thaliana transcriptome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:17466–17473
Lin Z, Yin K, Zhu D, Chen Z, Gu H, Qu LJ (2007) AtCDC5 regulates the G2 to M transition of the cell cycle and is critical for the function of Arabidopsis shoot apical meristem. Cell Res 17:815–828
Zhan X, Wang B, Li H, Liu R, Kalia RK, Zhu JK, Chinnusamy V (2012) Arabidopsis proline-rich protein important for development and abiotic stress tolerance is involved in microRNA biogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:18198–18203
Speth C, Willing EM, Rausch S, Schneeberger K, Laubinger S (2013) RACK1 scaffold proteins influence miRNA abundance in Arabidopsis. Plant J 76:433–445
Wu X, Shi Y, Li J, Xu L, Fang Y, Li X, Qi Y (2013) A role for the RNA-binding protein MOS2 in microRNA maturation in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 23:645–657
Ben Chaabane S, Liu R, Chinnusamy V, Kwon Y, Park JH, Kim SY, Zhu JK, Yang SW, Lee BH (2013) STA1, an Arabidopsis pre-mRNA processing factor 6 homolog, is a new player involved in miRNA biogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res 41:1984–1997
Kim W, Benhamed M, Servet C, Latrasse D, Zhang W, Delarue M, Zhou DX (2009) Histone acetyltransferase GCN5 interferes with the miRNA pathway in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 19:899–909
Xie Z, Kasschau KD, Carrington JC (2003) Negative feedback regulation of Dicer-Like1 in Arabidopsis by microRNA-guided mRNA degradation. Curr Biol 13:784–789
Pouch-Pelissier MN, Pelissier T, Elmayan T, Vaucheret H, Boko D, Jantsch MF, Deragon JM (2008) SINE RNA induces severe developmental defects in Arabidopsis thaliana and interacts with HYL1 (DRB1), a key member of the DCL1 complex. PLoS Genet 4:e1000096
Machida S, Yuan YA (2013) Crystal structure of Arabidopsis thaliana Dawdle forkhead-associated domain reveals a conserved phospho-threonine recognition cleft for dicer-like 1 binding. Mol Plant 6:1290–1300
Engelsberger WR, Schulze WX (2012) Nitrate and ammonium lead to distinct global dynamic phosphorylation patterns when resupplied to nitrogen-starved Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J 69:978–995
Manavella PA, Hagmann J, Ott F, Laubinger S, Franz M, Macek B, Weigel D (2012) Fast-forward genetics identifies plant CPL phosphatases as regulators of miRNA processing factor HYL1. Cell 151:859–870
Kruszka K, Pacak A, Swida-Barteczka A, Stefaniak AK, Kaja E, Sierocka I, Karlowski W, Jarmolowski A, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z (2013) Developmentally regulated expression and complex processing of barley pri-microRNAs. BMC Genom 14:34
Szarzynska B, Sobkowiak L, Pant BD, Balazadeh S, Scheible WR, Mueller-Roeber B, Jarmolowski A, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z (2009) Gene structures and processing of Arabidopsis thaliana HYL1-dependent pri-miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 37:3083–3093
Yan K, Liu P, Wu CA, Yang GD, Xu R, Guo QH, Huang JG, Zheng CC (2012) Stress-induced alternative splicing provides a mechanism for the regulation of microRNA processing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Cell 48:521–531
Jia F, Rock CD (2013) MIR846 and MIR842 comprise a cistronic MIRNA pair that is regulated by abscisic acid by alternative splicing in roots of Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 81:447–460
Hirsch J, Lefort V, Vankersschaver M, Boualem A, Lucas A, Thermes C, d’Aubenton-Carafa Y, Crespi M (2006) Characterization of 43 non-protein-coding mRNA genes in Arabidopsis, including the MIR162a-derived transcripts. Plant Physiol 140:1192–1204
Bielewicz D, Kalak M, Kalyna M, Windels D, Barta A, Vazquez F, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z, Jarmolowski A (2013) Introns of plant pri-miRNAs enhance miRNA biogenesis. EMBO Rep 14:622–628
Schwab R, Speth C, Laubinger S, Voinnet O (2013) Enhanced microRNA accumulation through stemloop-adjacent introns. EMBO Rep 14:615–621
Raczynska KD, Simpson CG, Ciesiolka A, Szewc L, Lewandowska D, McNicol J, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z, Brown JW, Jarmolowski A (2010) Involvement of the nuclear cap-binding protein complex in alternative splicing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res 38:265–278
Gregory BD, O’Malley RC, Lister R, Urich MA, Tonti-Filippini J, Chen H, Millar AH, Ecker JR (2008) A link between RNA metabolism and silencing affecting Arabidopsis development. Dev Cell 14:854–866
Laubinger S, Sachsenberg T, Zeller G, Busch W, Lohmann JU, Ratsch G, Weigel D (2008) Dual roles of the nuclear cap-binding complex and SERRATE in pre-mRNA splicing and microRNA processing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:8795–8800
Kim S, Yang JY, Xu J, Jang IC, Prigge MJ, Chua NH (2008) Two cap-binding proteins CBP20 and CBP80 are involved in processing primary MicroRNAs. Plant Cell Physiol 49:1634–1644
Gruber JJ, Zatechka DS, Sabin LR, Yong J, Lum JJ, Kong M, Zong WX, Zhang Z, Lau CK, Rawlings J, Cherry S, Ihle JN, Dreyfuss G, Thompson CB (2009) Ars2 links the nuclear cap-binding complex to RNA interference and cell proliferation. Cell 138:328–339
Levine E, McHale P, Levine H (2007) Small regulatory RNAs may sharpen spatial expression patterns. PLoS Comput Biol 3:e233
Muraro D, Mellor N, Pound MP, Help H, Lucas M, Chopard J, Byrne HM, Godin C, Hodgman TC, King JR, Pridmore TP, Helariutta Y, Bennett MJ, Bishopp A (2014) Integration of hormonal signaling networks and mobile microRNAs is required for vascular patterning in Arabidopsis roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:857–862
Yang ZY, Ebright YW, Yu B, Chen XM (2006) HEN1 recognizes 21-24 nt small RNA duplexes and deposits a methyl group onto the 2′ OH of the 3′ terminal nucleotide. Nucleic Acids Res 34:667–675
Boutet S, Vazquez F, Liu J, Beclin C, Fagard M, Gratias A, Morel JB, Crete P, Chen X, Vaucheret H (2003) Arabidopsis HEN1: a genetic link between endogenous miRNA controlling development and siRNA controlling transgene silencing and virus resistance. Curr Biol 13:843–848
Li J, Yang Z, Yu B, Liu J, Chen X (2005) Methylation protects miRNAs and siRNAs from a 3′-end uridylation activity in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 15:1501–1507
Zhai J, Zhao Y, Simon SA, Huang S, Petsch K, Arikit S, Pillay M, Ji L, Xie M, Cao X, Yu B, Timmermans M, Yang B, Chen X, Meyers BC (2013) Plant microRNAs display differential 3′ truncation and tailing modifications that are ARGONAUTE1 dependent and conserved across species. Plant Cell 25:2417–2428
Huang Y, Ji L, Huang Q, Vassylyev DG, Chen X, Ma JB (2009) Structural insights into mechanisms of the small RNA methyltransferase HEN1. Nature 461:823–827
Ren G, Chen X, Yu B (2012) Uridylation of miRNAs by hen1 suppressor1 in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 22:695–700
Zhao Y, Yu Y, Zhai J, Ramachandran V, Dinh TT, Meyers BC, Mo B, Chen X (2012) The Arabidopsis nucleotidyl transferase HESO1 uridylates unmethylated small RNAs to trigger their degradation. Curr Biol 22:689–694
Ren G, Xie M, Zhang S, Vinovskis C, Chen X, Yu B (2014) Methylation protects microRNAs from an AGO1-associated activity that uridylates 5′ RNA fragments generated by AGO1 cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:6365–6370
Ibrahim F, Rymarquis LA, Kim EJ, Becker J, Balassa E, Green PJ, Cerutti H (2010) Uridylation of mature miRNAs and siRNAs by the MUT68 nucleotidyltransferase promotes their degradation in Chlamydomonas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:3906–3911
Ramachandran V, Chen X (2008) Degradation of microRNAs by a family of exoribonucleases in Arabidopsis. Science 321:1490–1492
Yan J, Gu Y, Jia X, Kang W, Pan S, Tang X, Chen X, Tang G (2012) Effective small RNA destruction by the expression of a short tandem target mimic in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24:415–427
Han BW, Hung JH, Weng Z, Zamore PD, Ameres SL (2011) The 3′-to-5′ exoribonuclease Nibbler shapes the 3′ ends of microRNAs bound to Drosophila Argonaute1. Curr Biol 21:1878–1887
Liu N, Abe M, Sabin LR, Hendriks GJ, Naqvi AS, Yu Z, Cherry S, Bonini NM (2011) The exoribonuclease Nibbler controls 3′ end processing of microRNAs in Drosophila. Curr Biol 21:1888–1893
Vaucheret H (2008) Plant argonautes. Trends Plant Sci 13:350–358
Tolia NH, Joshua-Tor L (2007) Slicer and the argonautes. Nat Chem Biol 3:36–43
Rivas FV, Tolia NH, Song JJ, Aragon JP, Liu J, Hannon GJ, Joshua-Tor L (2005) Purified Argonaute2 and an siRNA form recombinant human RISC. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12:340–349
Hutvagner G, Simard MJ (2008) Argonaute proteins: key players in RNA silencing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:22–32
Liu X, Lu T, Dou Y, Yu B, Zhang C (2014) Identification of RNA silencing components in soybean and sorghum. BMC Bioinformatics 15:4
Mi S, Cai T, Hu Y, Chen Y, Hodges E, Ni F, Wu L, Li S, Zhou H, Long C, Chen S, Hannon GJ, Qi Y (2008) Sorting of small RNAs into Arabidopsis argonaute complexes is directed by the 5′ terminal nucleotide. Cell 133:116–127
Montgomery TA, Howell MD, Cuperus JT, Li D, Hansen JE, Alexander AL, Chapman EJ, Fahlgren N, Allen E, Carrington JC (2008) Specificity of argonaute7-miR390 interaction and dual functionality in TAS3 trans-acting siRNA formation. Cell 133:128–141
Mallory A, Vaucheret H (2010) Form, function, and regulation of argonaute proteins. Plant Cell 22:3879–3889
Rhoades MW, Reinhart BJ, Lim LP, Burge CB, Bartel B, Bartel DP (2002) Prediction of plant microRNA targets. Cell 110:513–520
Vaucheret H, Vazquez F, Crete P, Bartel DP (2004) The action of ARGONAUTE1 in the miRNA pathway and its regulation by the miRNA pathway are crucial for plant development. Genes Dev 18:1187–1197
Earley K, Smith M, Weber R, Gregory B, Poethig R (2010) An endogenous F-box protein regulates argonaute1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Silence 1:15
Derrien B, Baumberger N, Schepetilnikov M, Viotti C, De Cillia J, Ziegler-Graff V, Isono E, Schumacher K, Genschik P (2012) Degradation of the antiviral component argonaute1 by the autophagy pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:15942–15946
Zhu H, Hu F, Wang R, Zhou X, Sze SH, Liou LW, Barefoot A, Dickman M, Zhang X (2011) Arabidopsis Argonaute10 specifically sequesters miR166/165 to regulate shoot apical meristem development. Cell 145:242–256
Eamens AL, Smith NA, Curtin SJ, Wang MB, Waterhouse PM (2009) The Arabidopsis thaliana double-stranded RNA binding protein DRB1 directs guide strand selection from microRNA duplexes. RNA 15:2219–2235
Smith MR, Willmann MR, Wu G, Berardini TZ, Moller B, Weijers D, Poethig RS (2009) Cyclophilin 40 is required for microRNA activity in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:5424–5429
Iki T, Yoshikawa M, Meshi T, Ishikawa M (2012) Cyclophilin 40 facilitates HSP90-mediated RISC assembly in plants. EMBO J 31:267–278
Iki T, Yoshikawa M, Nishikiori M, Jaudal MC, Matsumoto-Yokoyama E, Mitsuhara I, Meshi T, Ishikawa M (2010) In vitro assembly of plant RNA-induced silencing complexes facilitated by molecular chaperone HSP90. Mol Cell 39:282–291
Earley KW, Poethig RS (2011) Binding of the cyclophilin 40 ortholog SQUINT to Hsp90 protein is required for SQUINT function in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 286:38184–38189
Kwak PB, Tomari Y (2012) The N domain of Argonaute drives duplex unwinding during RISC assembly. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19:145–151
Mallory AC, Reinhart BJ, Jones-Rhoades MW, Tang G, Zamore PD, Barton MK, Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNA control of PHABULOSA in leaf development: importance of pairing to the microRNA 5′ region. EMBO J 23:3356–3364
Liu Q, Wang F, Axtell MJ (2014) Analysis of complementarity requirements for plant MicroRNA targeting using a Nicotiana benthamiana quantitative transient assay. Plant Cell 26:741–753
Li J, Reichel M, Millar AA (2014) Determinants beyond both complementarity and cleavage govern microR159 efficacy in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 10:e1004232
Carbonell A, Fahlgren N, Garcia-Ruiz H, Gilbert KB, Montgomery TA, Nguyen T, Cuperus JT, Carrington JC (2012) Functional analysis of three Arabidopsis argonautes using slicer-defective mutants. Plant Cell 24:3613–3629
Llave C, Xie Z, Kasschau KD, Carrington JC (2002) Cleavage of Scarecrow-like mRNA targets directed by a class of Arabidopsis miRNA. Science 297:2053–2056
Souret FF, Kastenmayer JP, Green PJ (2004) AtXRN4 degrades mRNA in Arabidopsis and its substrates include selected miRNA targets. Mol Cell 15:173–183
Ibrahim F, Rohr J, Jeong WJ, Hesson J, Cerutti H (2006) Untemplated oligoadenylation promotes degradation of RISC-cleaved transcripts. Science 314:1893
Franco-Zorrilla JM, Valli A, Todesco M, Mateos I, Puga MI, Rubio-Somoza I, Leyva A, Weigel D, Garcia JA, Paz-Ares J (2007) Target mimicry provides a new mechanism for regulation of microRNA activity. Nat Genet 39:1033–1037
Schwab R, Palatnik JF, Riester M, Schommer C, Schmid M, Weigel D (2005) Specific effects of microRNAs on the plant transcriptome. Dev Cell 8:517–527
Brodersen P, Sakvarelidze-Achard L, Bruun-Rasmussen M, Dunoyer P, Yamamoto YY, Sieburth L, Voinnet O (2008) Widespread translational inhibition by plant miRNAs and siRNAs. Science 320:1185–1190
Li S, Liu L, Zhuang X, Yu Y, Liu X, Cui X, Ji L, Pan Z, Cao X, Mo B, Zhang F, Raikhel N, Jiang L, Chen X (2013) MicroRNAs inhibit the translation of target mRNAs on the endoplasmic reticulum in Arabidopsis. Cell 153:562–574
Lanet E, Delannoy E, Sormani R, Floris M, Brodersen P, Crete P, Voinnet O, Robaglia C (2009) Biochemical evidence for translational repression by Arabidopsis microRNAs. Plant Cell 21:1762–1768
Reynoso MA, Blanco FA, Bailey-Serres J, Crespi M, Zanetti ME (2012) Selective recruitment of mRNAs and miRNAs to polyribosomes in response to rhizobia infection in Medicago truncatula. Plant J 73:289–301
Iwakawa HO, Tomari Y (2013) Molecular insights into microRNA-mediated translational repression in plants. Mol Cell 52:591–601
Liu J, Valencia-Sanchez MA, Hannon GJ, Parker R (2005) MicroRNA-dependent localization of targeted mRNAs to mammalian P-bodies. Nat Cell Biol 7:719–723
Yang L, Wu G, Poethig RS (2012) Mutations in the GW-repeat protein SUO reveal a developmental function for microRNA-mediated translational repression in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:315–320
Behm-Ansmant I, Rehwinkel J, Doerks T, Stark A, Bork P, Izaurralde E (2006) mRNA degradation by miRNAs and GW182 requires both CCR4:NOT deadenylase and DCP1:DCP2 decapping complexes. Genes Dev 20:1885–1898
Wu L, Fan J, Belasco JG (2006) MicroRNAs direct rapid deadenylation of mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:4034–4039
Motomura K, Le QT, Kumakura N, Fukaya T, Takeda A, Watanabe Y (2012) The role of decapping proteins in the miRNA accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. RNA Biol 9:644–652
Li JF, Chung HS, Niu Y, Bush J, McCormack M, Sheen J (2013) Comprehensive protein-based artificial microRNA screens for effective gene silencing in plants. Plant Cell 25:1507–1522
Grant-Downton R, Kourmpetli S, Hafidh S, Khatab H, Le Trionnaire G, Dickinson H, Twell D (2013) Artificial microRNAs reveal cell-specific differences in small RNA activity in pollen. Curr Biol 23:R599–R601
Stoppin-Mellet V, Gaillard J, Vantard M (2006) Katanin’s severing activity favors bundling of cortical microtubules in plants. Plant J 46:1009–1017
Brodersen P, Sakvarelidze-Achard L, Schaller H, Khafif M, Schott G, Bendahmane A, Voinnet O (2012) Isoprenoid biosynthesis is required for miRNA function and affects membrane association of argonaute 1 in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:1778–1783
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a National Science Foundation Grant MCB-1121193 (to B. Y).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. Xie and S. Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, M., Zhang, S. & Yu, B. microRNA biogenesis, degradation and activity in plants. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 72, 87–99 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1728-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1728-7