Abstract
TCR-mediated specific recognition of antigenic peptides in the context of classical MHC molecules is a cornerstone of adaptive immunity of jawed vertebrate. Ancillary to these interactions, the T cell repertoire also includes unconventional T cells that recognize endogenous and/or exogenous antigens in a classical MHC-unrestricted manner. Among these, the mammalian nonclassical MHC class I-restricted invariant T cell (iT) subsets, such as iNKT and MAIT cells, are now believed to be integral to immune response initiation as well as in orchestrating subsequent adaptive immunity. Until recently the evolutionary origins of these cells were unknown. Here we review our current understanding of a nonclassical MHC class I-restricted iT cell population in the amphibian Xenopus laevis. Parallels with the mammalian iNKT and MAIT cells underline the crucial biological roles of these evolutionarily ancient immune subsets.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- XNC:
-
Xenopus non-classical
- SNC:
-
Siluriana non-classical
- MR1:
-
Major histocompatibility molecule related 1
- TCR:
-
T cell receptor
- MAIT:
-
MR1 associated invariant T cells
- iNKT:
-
Invariant natural killer T cells
- iT cells:
-
Invariant T cells
- FV3:
-
Frog virus 3
- MYA:
-
Million years ago
- CTL:
-
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- CCU-CTL:
-
Classical class Ia-unrestricted CTLs
- NKT:
-
Natural killer T cells
- αGalCer:
-
Glycolipid α-galactoceramide
- DP:
-
Double positive
- DN:
-
Double negative
- SLAM:
-
Signaling lymphocytic activation molecules
- CTX:
-
Cortical thymocyte-specific Xenopus
References
Adams EJ, Luoma AM (2013) The adaptable major histocompatibility complex (MHC) fold: structure and function of nonclassical and MHC class I-like molecules. Annu Rev Immunol 31:529–561. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-095912
Rodgers JR, Cook RG (2005) MHC class Ib molecules bridge innate and acquired immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 5(6):459–471. doi:10.1038/nri1635
Hansen TH, Huang S, Arnold PL, Fremont DH (2007) Patterns of nonclassical MHC antigen presentation. Nat Immunol 8(6):563–568. doi:10.1038/ni1475
Bendelac A (1995) Positive selection of mouse NK1+ T cells by CD1-expressing cortical thymocytes. J Exp Med 182(6):2091–2096
Bendelac A, Lantz O, Quimby ME, Yewdell JW, Bennink JR, Brutkiewicz RR (1995) CD1 recognition by mouse NK1+ T lymphocytes. Science 268(5212):863–865
Tilloy F, Treiner E, Park SH, Garcia C, Lemonnier F, de la Salle H, Bendelac A, Bonneville M, Lantz O (1999) An invariant T cell receptor alpha chain defines a novel TAP-independent major histocompatibility complex class Ib-restricted alpha/beta T cell subpopulation in mammals. J Exp Med 189(12):1907–1921
Treiner E, Duban L, Bahram S, Radosavljevic M, Wanner V, Tilloy F, Affaticati P, Gilfillan S, Lantz O (2003) Selection of evolutionarily conserved mucosal-associated invariant T cells by MR1. Nature 422(6928):164–169. doi:10.1038/nature01433
Gold MC, Eid T, Smyk-Pearson S, Eberling Y, Swarbrick GM, Langley SM, Streeter PR, Lewinsohn DA, Lewinsohn DM (2013) Human thymic MR1-restricted MAIT cells are innate pathogen-reactive effectors that adapt following thymic egress. Mucosal Immunol 6(1):35–44. doi:10.1038/mi.2012.45
Wilson SB, Delovitch TL (2003) Janus-like role of regulatory iNKT cells in autoimmune disease and tumour immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 3(3):211–222. doi:10.1038/nri1028
Miyazaki Y, Miyake S, Chiba A, Lantz O, Yamamura T (2011) Mucosal-associated invariant T cells regulate Th1 response in multiple sclerosis. Int Immunol 23(9):529–535. doi:10.1093/intimm/dxr047
Le Bourhis L, Martin E, Peguillet I, Guihot A, Froux N, Core M, Levy E, Dusseaux M, Meyssonnier V, Premel V, Ngo C, Riteau B, Duban L, Robert D, Huang S, Rottman M, Soudais C, Lantz O (2010) Antimicrobial activity of mucosal-associated invariant T cells. Nat Immunol 11(8):701–708. doi:10.1038/ni.1890
Gold MC, Cerri S, Smyk-Pearson S, Cansler ME, Vogt TM, Delepine J, Winata E, Swarbrick GM, Chua WJ, Yu YY, Lantz O, Cook MS, Null MD, Jacoby DB, Harriff MJ, Lewinsohn DA, Hansen TH, Lewinsohn DM (2010) Human mucosal associated invariant T cells detect bacterially infected cells. PLoS Biol 8(6):e1000407. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000407
Wu L, Gabriel CL, Parekh VV, Van Kaer L (2009) Invariant natural killer T cells: innate-like T cells with potent immunomodulatory activities. Tissue Antigens 73(6):535–545. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0039.2009.01256.x
Gold MC, Lewinsohn DM (2013) Co-dependents: MR1-restricted MAIT cells and their antimicrobial function. Nat Rev Microbiol 11(1):14–19. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2918
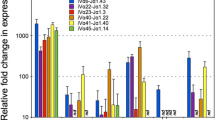
Edholm ES, Albertorio Saez LM, Gill AL, Gill SR, Grayfer L, Haynes N, Myers JR, Robert J (2013) Nonclassical MHC class I-dependent invariant T cells are evolutionarily conserved and prominent from early development in amphibians. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 110(35):14342–14347. doi:10.1073/pnas.1309840110
Flajnik MF, Kaufman JF, Hsu E, Manes M, Parisot R, Du Pasquier L (1986) Major histocompatibility complex-encoded class I molecules are absent in immunologically competent Xenopus before metamorphosis. J Immunol 137(12):3891–3899
Du Pasquier L, Weiss N (1973) The thymus during the ontogeny of the toad Xenopus laevis: growth, membrane-bound immunoglobulins and mixed lymphocyte reaction. Eur J Immunol 3(12):773–777. doi:10.1002/eji.1830031207
Rollins-Smith LA, Flajnik MF, Blair PJ, Davis AT, Green WF (1997) Involvement of thyroid hormones in the expression of MHC class I antigens during ontogeny in Xenopus. Dev Immunol 5(2):133–144
Salter-Cid L, Nonaka M, Flajnik MF (1998) Expression of MHC class Ia and class Ib during ontogeny: high expression in epithelia and coregulation of class Ia and lmp7 genes. J Immunol 160(6):2853–2861
Goyos A, Ohta Y, Guselnikov S, Robert J (2009) Novel nonclassical MHC class Ib genes associated with CD8 T cell development and thymic tumors. Mol Immunol 46(8–9):1775–1786. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2009.01.016
Salio M, Silk JD, Jones EY, Cerundolo V (2014) Biology of CD1- and MR1-restricted T cells. Annu Rev Immunol. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-032713-120243
Birkinshaw RW, Kjer-Nielsen L, Eckle SB, McCluskey J, Rossjohn J (2014) MAITs, MR1 and vitamin B metabolites. Curr Opin Immunol 26C:7–13. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2013.09.007
Le Bourhis L, Mburu YK, Lantz O (2013) MAIT cells, surveyors of a new class of antigen: development and functions. Curr Opin Immunol 25(2):174–180. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2013.01.005
Piontkivska H, Nei M (2003) Birth-and-death evolution in primate MHC class I genes: divergence time estimates. Mol Biol Evol 20(4):601–609. doi:10.1093/molbev/msg064
Adams EJ, Parham P (2001) Species-specific evolution of MHC class I genes in the higher primates. Immunol Rev 183:41–64
Nei M, Gu X, Sitnikova T (1997) Evolution by the birth-and-death process in multigene families of the vertebrate immune system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(15):7799–7806
Hughes AL, Nei M (1989) Evolution of the major histocompatibility complex: independent origin of nonclassical class I genes in different groups of mammals. Mol Biol Evol 6(6):559–579
Rogers JH (1985) Mouse histocompatibility-related genes are not conserved in other mammals. EMBO J 4(3):749–753
Joyce S, Tabaczewski P, Angeletti RH, Nathenson SG, Stroynowski I (1994) A nonpolymorphic major histocompatibility complex class Ib molecule binds a large array of diverse self-peptides. J Exp Med 179(2):579–588
Rotzschke O, Falk K, Stevanovic S, Grahovac B, Soloski MJ, Jung G, Rammensee HG (1993) Qa-2 molecules are peptide receptors of higher stringency than ordinary class I molecules. Nature 361(6413):642–644. doi:10.1038/361642a0
Lee N, Malacko AR, Ishitani A, Chen MC, Bajorath J, Marquardt H, Geraghty DE (1995) The membrane-bound and soluble forms of HLA-G bind identical sets of endogenous peptides but differ with respect to TAP association. Immunity 3(5):591–600
Diehl M, Munz C, Keilholz W, Stevanovic S, Holmes N, Loke YW, Rammensee HG (1996) Nonclassical HLA-G molecules are classical peptide presenters. Curr Biol 6(3):305–314
Fuzzi B, Rizzo R, Criscuoli L, Noci I, Melchiorri L, Scarselli B, Bencini E, Menicucci A, Baricordi OR (2002) HLA-G expression in early embryos is a fundamental prerequisite for the obtainment of pregnancy. Eur J Immunol 32(2):311–315. doi:10.1002/1521-4141(200202)32:2<311:AID-IMMU311>3.0.CO;2-8
Marine JB, Shirakata Y, Wadsworth SA, Hooley JJ, Handy DE, Coligan JE (1993) Role of the Q10 class I regulatory element region 1 in controlling tissue-specific expression in vivo. J Immunol 151(4):1989–1997
Ellis SA, Palmer MS, McMichael AJ (1990) Human trophoblast and the choriocarcinoma cell line BeWo express a truncated HLA Class I molecule. J Immunol 144(2):731–735
Loke YW, King A, Burrows T, Gardner L, Bowen M, Hiby S, Howlett S, Holmes N, Jacobs D (1997) Evaluation of trophoblast HLA-G antigen with a specific monoclonal antibody. Tissue Antigens 50(2):135–146
Dascher CC (2007) Evolutionary biology of CD1. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 314:3–26
Huang S, Martin E, Kim S, Yu L, Soudais C, Fremont DH, Lantz O, Hansen TH (2009) MR1 antigen presentation to mucosal-associated invariant T cells was highly conserved in evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(20):8290–8295. doi:10.1073/pnas.0903196106
Zeng Z, Castano AR, Segelke BW, Stura EA, Peterson PA, Wilson IA (1997) Crystal structure of mouse CD1: an MHC-like fold with a large hydrophobic binding groove. Science 277(5324):339–345
Koch M, Stronge VS, Shepherd D, Gadola SD, Mathew B, Ritter G, Fersht AR, Besra GS, Schmidt RR, Jones EY, Cerundolo V (2005) The crystal structure of human CD1d with and without alpha-galactosylceramide. Nat Immunol 6(8):819–826. doi:10.1038/ni1225
Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Corbett AJ, Le Nours J, Meehan B, Liu L, Bhati M, Chen Z, Kostenko L, Reantragoon R, Williamson NA, Purcell AW, Dudek NL, McConville MJ, O’Hair RA, Khairallah GN, Godfrey DI, Fairlie DP, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J (2012) MR1 presents microbial vitamin B metabolites to MAIT cells. Nature 491(7426):717–723. doi:10.1038/nature11605
Yamaguchi H, Kurosawa Y, Hashimoto K (1998) Expanded genomic organization of conserved mammalian MHC class I-related genes, human MR1 and its murine ortholog. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 250(3):558–564. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9353
Shiina T, Ando A, Suto Y, Kasai F, Shigenari A, Takishima N, Kikkawa E, Iwata K, Kuwano Y, Kitamura Y, Matsuzawa Y, Sano K, Nogami M, Kawata H, Li S, Fukuzumi Y, Yamazaki M, Tashiro H, Tamiya G, Kohda A, Okumura K, Ikemura T, Soeda E, Mizuki N, Kimura M, Bahram S, Inoko H (2001) Genomic anatomy of a premier major histocompatibility complex paralogous region on chromosome 1q21-q22. Genome Res 11(5):789–802. doi:10.1101/gr.175801
Shiina T, Inoko H (2001) Comparative genome analysis of MHC region. Tanpakushitsu kakusan koso protein, nucleic acid, enzyme 46(16 Suppl):2246–2253
Flajnik MF, Kasahara M (2001) Comparative genomics of the MHC: glimpses into the evolution of the adaptive immune system. Immunity 15(3):351–362
Salomonsen J, Sorensen MR, Marston DA, Rogers SL, Collen T, van Hateren A, Smith AL, Beal RK, Skjodt K, Kaufman J (2005) Two CD1 genes map to the chicken MHC, indicating that CD1 genes are ancient and likely to have been present in the primordial MHC. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(24):8668–8673. doi:10.1073/pnas.0409213102
Miller MM, Wang C, Parisini E, Coletta RD, Goto RM, Lee SY, Barral DC, Townes M, Roura-Mir C, Ford HL, Brenner MB, Dascher CC (2005) Characterization of two avian MHC-like genes reveals an ancient origin of the CD1 family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(24):8674–8679. doi:10.1073/pnas.0500105102
Hee CS, Gao S, Loll B, Miller MM, Uchanska-Ziegler B, Daumke O, Ziegler A (2010) Structure of a classical MHC class I molecule that binds “non-classical” ligands. PLoS Biol 8(12):e1000557. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000557
Rossjohn J, Pellicci DG, Patel O, Gapin L, Godfrey DI (2012) Recognition of CD1d-restricted antigens by natural killer T cells. Nat Rev Immunol 12(12):845–857. doi:10.1038/nri3328
Nair S (2011) Whats in a name? J Maxillofac Oral Surg 10(3):183–184. doi:10.1007/s12663-011-0277-y
Lantz O, Bendelac A (1994) An invariant T cell receptor alpha chain is used by a unique subset of major histocompatibility complex class I-specific CD4+ and CD4-8− T cells in mice and humans. J Exp Med 180(3):1097–1106
Kashiwase K, Kikuchi A, Ando Y, Nicol A, Porcelli SA, Tokunaga K, Omine M, Satake M, Juji T, Nieda M, Koezuka Y (2003) The CD1d natural killer T-cell antigen presentation pathway is highly conserved between humans and rhesus macaques. Immunogenetics 54(11):776–781. doi:10.1007/s00251-002-0527-8
Matsuura A, Kinebuchi M, Chen HZ, Katabami S, Shimizu T, Hashimoto Y, Kikuchi K, Sato N (2000) NKT cells in the rat: organ-specific distribution of NK T cells expressing distinct V alpha 14 chains. J Immunol 164(6):3140–3148
Kawano T, Cui J, Koezuka Y, Toura I, Kaneko Y, Motoki K, Ueno H, Nakagawa R, Sato H, Kondo E, Koseki H, Taniguchi M (1997) CD1d-restricted and TCR-mediated activation of valpha14 NKT cells by glycosylceramides. Science 278(5343):1626–1629
Kinjo Y, Illarionov P, Vela JL, Pei B, Girardi E, Li X, Li Y, Imamura M, Kaneko Y, Okawara A, Miyazaki Y, Gomez-Velasco A, Rogers P, Dahesh S, Uchiyama S, Khurana A, Kawahara K, Yesilkaya H, Andrew PW, Wong CH, Kawakami K, Nizet V, Besra GS, Tsuji M, Zajonc DM, Kronenberg M (2011) Invariant natural killer T cells recognize glycolipids from pathogenic Gram-positive bacteria. Nat Immunol 12(10):966–974. doi:10.1038/ni.2096
Sriram V, Du W, Gervay-Hague J, Brutkiewicz RR (2005) Cell wall glycosphingolipids of Sphingomonas paucimobilis are CD1d-specific ligands for NKT cells. Eur J Immunol 35(6):1692–1701. doi:10.1002/eji.200526157
Kinjo Y, Tupin E, Wu D, Fujio M, Garcia-Navarro R, Benhnia MR, Zajonc DM, Ben-Menachem G, Ainge GD, Painter GF, Khurana A, Hoebe K, Behar SM, Beutler B, Wilson IA, Tsuji M, Sellati TJ, Wong CH, Kronenberg M (2006) Natural killer T cells recognize diacylglycerol antigens from pathogenic bacteria. Nat Immunol 7(9):978–986. doi:10.1038/ni1380
Burrows SR, Chen Z, Archbold JK, Tynan FE, Beddoe T, Kjer-Nielsen L, Miles JJ, Khanna R, Moss DJ, Liu YC, Gras S, Kostenko L, Brennan RM, Clements CS, Brooks AG, Purcell AW, McCluskey J, Rossjohn J (2010) Hard wiring of T cell receptor specificity for the major histocompatibility complex is underpinned by TCR adaptability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(23):10608–10613. doi:10.1073/pnas.1004926107
Rudolph MG, Stanfield RL, Wilson IA (2006) How TCRs bind MHCs, peptides, and coreceptors. Annu Rev Immunol 24:419–466. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115658
Borg NA, Wun KS, Kjer-Nielsen L, Wilce MC, Pellicci DG, Koh R, Besra GS, Bharadwaj M, Godfrey DI, McCluskey J, Rossjohn J (2007) CD1d-lipid-antigen recognition by the semi-invariant NKT T-cell receptor. Nature 448(7149):44–49. doi:10.1038/nature05907
Pellicci DG, Patel O, Kjer-Nielsen L, Pang SS, Sullivan LC, Kyparissoudis K, Brooks AG, Reid HH, Gras S, Lucet IS, Koh R, Smyth MJ, Mallevaey T, Matsuda JL, Gapin L, McCluskey J, Godfrey DI, Rossjohn J (2009) Differential recognition of CD1d-alpha-galactosyl ceramide by the V beta 8.2 and V beta 7 semi-invariant NKT T cell receptors. Immunity 31(1):47–59. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2009.04.018
Scott-Browne JP, Matsuda JL, Mallevaey T, White J, Borg NA, McCluskey J, Rossjohn J, Kappler J, Marrack P, Gapin L (2007) Germline-encoded recognition of diverse glycolipids by natural killer T cells. Nat Immunol 8(10):1105–1113. doi:10.1038/ni1510
Florence WC, Xia C, Gordy LE, Chen W, Zhang Y, Scott-Browne J, Kinjo Y, Yu KO, Keshipeddy S, Pellicci DG, Patel O, Kjer-Nielsen L, McCluskey J, Godfrey DI, Rossjohn J, Richardson SK, Porcelli SA, Howell AR, Hayakawa K, Gapin L, Zajonc DM, Wang PG, Joyce S (2009) Adaptability of the semi-invariant natural killer T-cell receptor towards structurally diverse CD1d-restricted ligands. EMBO J 28(23):3781. doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.348
Godfrey DI, Rossjohn J (2011) New ways to turn on NKT cells. J Exp Med 208(6):1121–1125. doi:10.1084/jem.20110983
Venkataswamy MM, Porcelli SA (2010) Lipid and glycolipid antigens of CD1d-restricted natural killer T cells. Semin Immunol 22(2):68–78. doi:10.1016/j.smim.2009.10.003
Tsukamoto K, Deakin JE, Graves JA, Hashimoto K (2013) Exceptionally high conservation of the MHC class I-related gene, MR1, among mammals. Immunogenetics 65(2):115–124. doi:10.1007/s00251-012-0666-5
Lion J, Debuysscher V, Wlodarczyk A, Hodroge A, Serriari NE, Choteau L, Ouled-haddou H, Plistat M, Lassoued K, Lantz O, Treiner E (2013) MR1B, a natural spliced isoform of the MHC-related 1 protein, is expressed as homodimers at the cell surface and activates MAIT cells. Eur J Immunol 43(5):1363–1373. doi:10.1002/eji.201242461
Reantragoon R, Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Chen Z, Illing PT, Bhati M, Kostenko L, Bharadwaj M, Meehan B, Hansen TH, Godfrey DI, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J (2012) Structural insight into MR1-mediated recognition of the mucosal associated invariant T cell receptor. J Exp Med 209(4):761–774. doi:10.1084/jem.20112095
Le Bourhis L, Guerri L, Dusseaux M, Martin E, Soudais C, Lantz O (2011) Mucosal-associated invariant T cells: unconventional development and function. Trends Immunol 32(5):212–218. doi:10.1016/j.it.2011.02.005
Dusseaux M, Martin E, Serriari N, Peguillet I, Premel V, Louis D, Milder M, Le Bourhis L, Soudais C, Treiner E, Lantz O (2011) Human MAIT cells are xenobiotic-resistant, tissue-targeted, CD161hi IL-17-secreting T cells. Blood 117(4):1250–1259. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-08-303339
Le Bourhis L, Dusseaux M, Bohineust A, Bessoles S, Martin E, Premel V, Core M, Sleurs D, Serriari NE, Treiner E, Hivroz C, Sansonetti P, Gougeon ML, Soudais C, Lantz O (2013) MAIT cells detect and efficiently lyse bacterially-infected epithelial cells. PLoS Pathog 9(10):e1003681. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003681
Flajnik MF, Kasahara M, Shum BP, Salter-Cid L, Taylor E, Du Pasquier L (1993) A novel type of class I gene organization in vertebrates: a large family of non-MHC-linked class I genes is expressed at the RNA level in the amphibian Xenopus. EMBO J 12(11):4385–4396
Goyos A, Sowa J, Ohta Y, Robert J (2011) Remarkable conservation of distinct nonclassical MHC class I lineages in divergent amphibian species. J Immunol 186(1):372–381. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1001467
Sammut B, Du Pasquier L, Ducoroy P, Laurens V, Marcuz A, Tournefier A (1999) Axolotl MHC architecture and polymorphism. Eur J Immunol 29(9):2897–2907. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199909)29:09<2897:AID-IMMU2897>3.0.CO;2-2
Bartl S, Baish MA, Flajnik MF, Ohta Y (1997) Identification of class I genes in cartilaginous fish, the most ancient group of vertebrates displaying an adaptive immune response. J Immunol 159(12):6097–6104
Wang C, Perera TV, Ford HL, Dascher CC (2003) Characterization of a divergent non-classical MHC class I gene in sharks. Immunogenetics 55(1):57–61. doi:10.1007/s00251-003-0542-4
Lukacs MF, Harstad H, Bakke HG, Beetz-Sargent M, McKinnel L, Lubieniecki KP, Koop BF, Grimholt U (2010) Comprehensive analysis of MHC class I genes from the U-, S-, and Z-lineages in Atlantic salmon. BMC Genom 11:154. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-11-154
Dijkstra JM, Katagiri T, Hosomichi K, Yanagiya K, Inoko H, Ototake M, Aoki T, Hashimoto K, Shiina T (2007) A third broad lineage of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I in teleost fish; MHC class II linkage and processed genes. Immunogenetics 59(4):305–321. doi:10.1007/s00251-007-0198-6
Star B, Nederbragt AJ, Jentoft S, Grimholt U, Malmstrom M, Gregers TF, Rounge TB, Paulsen J, Solbakken MH, Sharma A, Wetten OF, Lanzen A, Winer R, Knight J, Vogel JH, Aken B, Andersen O, Lagesen K, Tooming-Klunderud A, Edvardsen RB, Tina KG, Espelund M, Nepal C, Previti C, Karlsen BO, Moum T, Skage M, Berg PR, Gjoen T, Kuhl H, Thorsen J, Malde K, Reinhardt R, Du L, Johansen SD, Searle S, Lien S, Nilsen F, Jonassen I, Omholt SW, Stenseth NC, Jakobsen KS (2011) The genome sequence of Atlantic cod reveals a unique immune system. Nature 477(7363):207–210. doi:10.1038/nature10342
Evans BJ (2008) Genome evolution and speciation genetics of clawed frogs (Xenopus and Silurana). Front Biosci 13:4687–4706
Evans BJ, Kelley DB, Tinsley RC, Melnick DJ, Cannatella DC (2004) A mitochondrial DNA phylogeny of African clawed frogs: phylogeography and implications for polyploid evolution. Mol Phylogenet Evol 33(1):197–213. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2004.04.018
Edholm ESAG, Taran J, DeJesus Andino F, Otha Y, Robert J (2014) Unusual evolutionary conservation and specific adaptations of a large family of nonclassical MHC class Ib genes across different degrees of genome ploidy in the amphibian subfamily Xenopodinae. Immunogenetics. doi:10.1007/s0025101407745
Goyos A, Guselnikov S, Chida AS, Sniderhan LF, Maggirwar SB, Nedelkovska H, Robert J (2007) Involvement of nonclassical MHC class Ib molecules in heat shock protein-mediated anti-tumor responses. Eur J Immunol 37(6):1494–1501
Courtet M, Flajnik M, Du Pasquier L (2001) Major histocompatibility complex and immunoglobulin loci visualized by in situ hybridization on Xenopus chromosomes. Dev Comp Immunol 25(2):149–157
Nakanishi T, Toda H, Shibasaki Y, Somamoto T (2011) Cytotoxic T cells in teleost fish. Dev Comp Immunol 35(12):1317–1323
Somamoto T, Koppang EO, Fischer U (2014) Antiviral functions of CD8(+) cytotoxic T cells in teleost fish. Dev Comp Immunol 43(2):197–204. doi:10.1016/j.dci.2013.07.014
Toda H, Saito Y, Koike T, Takizawa F, Araki K, Yabu T, Somamoto T, Suetake H, Suzuki Y, Ototake M, Moritomo T, Nakanishi T (2011) Conservation of characteristics and functions of CD4 positive lymphocytes in a teleost fish. Dev Comp Immunol 35(6):650–660. doi:10.1016/j.dci.2011.01.013
Robert J, Ohta Y (2009) Comparative and developmental study of the immune system in Xenopus. Dev Dyn 238(6):1249–1270. doi:10.1002/dvdy.21891
Chida AS, Goyos A, Robert J (2011) Phylogenetic and developmental study of CD4, CD8 alpha and beta T cell co-receptor homologs in two amphibian species, Xenopus tropicalis and Xenopus laevis. Dev Comp Immunol 35(3):366–377. doi:10.1016/j.dci.2010.11.005
Laing KJ, Zou JJ, Purcell MK, Phillips R, Secombes CJ, Hansen JD (2006) Evolution of the CD4 family: teleost fish possess two divergent forms of CD4 in addition to lymphocyte activation gene-3. J Immunol 177(6):3939–3951
Dijkstra JM, Somamoto T, Moore L, Hordvik I, Ototake M, Fischer U (2006) Identification and characterization of a second CD4-like gene in teleost fish. Mol Immunol 43(5):410–419. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2005.03.005
Edholm ES, Stafford JL, Quiniou SM, Waldbieser G, Miller NW, Bengten E, Wilson M (2007) Channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, CD4-like molecules. Dev Comp Immunol 31(2):172–187. doi:10.1016/j.dci.2006.05.012
Venkatesh B, Lee AP, Ravi V, Maurya AK, Lian MM, Swann JB, Ohta Y, Flajnik MF, Sutoh Y, Kasahara M, Hoon S, Gangu V, Roy SW, Irimia M, Korzh V, Kondrychyn I, Lim ZW, Tay BH, Tohari S, Kong KW, Ho S, Lorente-Galdos B, Quilez J, Marques-Bonet T, Raney BJ, Ingham PW, Tay A, Hillier LW, Minx P, Boehm T, Wilson RK, Brenner S, Warren WC (2014) Elephant shark genome provides unique insights into gnathostome evolution. Nature 505(7482):174–179. doi:10.1038/nature12826
Ohtani M, Hayashi N, Hashimoto K, Nakanishi T, Dijkstra JM (2008) Comprehensive clarification of two paralogous interleukin 4/13 loci in teleost fish. Immunogenetics 60(7):383–397. doi:10.1007/s00251-008-0299-x
Li JH, Shao JZ, Xiang LX, Wen Y (2007) Cloning, characterization and expression analysis of pufferfish interleukin-4 cDNA: the first evidence of Th2-type cytokine in fish. Mol Immunol 44(8):2078–2086. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2006.09.010
Castro R, Bernard D, Lefranc MP, Six A, Benmansour A, Boudinot P (2011) T cell diversity and TcR repertoires in teleost fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol 31(5):644–654. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2010.08.016
Horton TL, Minter R, Stewart R, Ritchie P, Watson MD, Horton JD (2000) Xenopus NK cells identified by novel monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol 30(2):604–613. doi:10.1002/1521-4141(200002)30:2<604:AID-IMMU604>3.0.CO;2-X
Robert J, Gantress J, Rau L, Bell A, Cohen N (2002) Minor histocompatibility antigen-specific MHC-restricted CD8 T cell responses elicited by heat shock proteins. J Immunol 168(4):1697–1703
Goyos A, Cohen N, Gantress J, Robert J (2004) Anti-tumor MHC class Ia-unrestricted CD8 T cell cytotoxicity elicited by the heat shock protein gp96. Eur J Immunol 34(9):2449–2458. doi:10.1002/eji.200425105
Rau L, Cohen N, Robert J (2001) MHC-restricted and -unrestricted CD8 T cells: an evolutionary perspective. Transplantation 72(11):1830–1835
Rau L, Gantress J, Bell A, Stewart R, Horton T, Cohen N, Horton J, Robert J (2002) Identification and characterization of Xenopus CD8+ T cells expressing an NK cell-associated molecule. Eur J Immunol 32(6):1574–1583. doi:10.1002/1521-4141(200206)32:6<1574:AID-IMMU1574>3.0.CO;2-4
Behar SM, Podrebarac TA, Roy CJ, Wang CR, Brenner MB (1999) Diverse TCRs recognize murine CD1. J Immunol 162(1):161–167
Zhao J, Weng X, Bagchi S, Wang CR (2014) Polyclonal type II natural killer T cells require PLZF and SAP for their development and contribute to CpG-mediated antitumor response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(7):2674–2679. doi:10.1073/pnas.1323845111
Nieuwkoop PD, Faber J (1967) Normal tables of Xenopus laevis (Daudin). In: Nieuwkoop PD (ed) A systematic and chronological survey of the development from the fertilized egg till the end of metamorphosis, 2nd edn. North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp 162–188
Grayfer L, Andino FDJ, Chen G, Chinchar GV, Robert J (2012) Immune evasion strategies of ranaviruses and innate immune responses to these emerging pathogens. Viruses 4(7):1075–1092. doi:10.3390/v4071075
De Jesus Andino F, Chen G, Li Z, Grayfer L, Robert J (2012) Susceptibility of Xenopus laevis tadpoles to infection by the ranavirus Frog-Virus 3 correlates with a reduced and delayed innate immune response in comparison with adult frogs. Virology 432(2):435–443. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2012.07.001
Haynes-Gilmore N, Banach M, Edholm ES, Lord E, Robert J (2014) A critical role of nonclassical MHC in tumor immune evasion in the amphibian Xenopus model. Carcinogenesis. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgu100
Bjorkman PJ, Saper MA, Samraoui B, Bennett WS, Strominger JL, Wiley DC (1987) Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2. Nature 329(6139):506–512. doi:10.1038/329506a0
Madden DR (1995) The three-dimensional structure of peptide–MHC complexes. Annu Rev Immunol 13:587–622. doi:10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.003103
Hughes AL, Nei M (1988) Pattern of nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class I loci reveals overdominant selection. Nature 335(6186):167–170. doi:10.1038/335167a0
O’Callaghan CA, Tormo J, Willcox BE, Braud VM, Jakobsen BK, Stuart DI, McMichael AJ, Bell JI, Jones EY (1998) Structural features impose tight peptide binding specificity in the nonclassical MHC molecule HLA-E. Mol Cell 1(4):531–541
O’Callaghan CA, Tormo J, Willcox BE, Blundell CD, Jakobsen BK, Stuart DI, McMichael AJ, Bell JI, Jones EY (1998) Production, crystallization, and preliminary X-ray analysis of the human MHC class Ib molecule HLA-E. Protein Sci 7(5):1264–1266. doi:10.1002/pro.5560070525
Wang CR, Lindahl KF, Deisenhofer J (1996) Crystal structure of the MHC class Ib molecule H2-M3. Res Immunol 147(5):313–321
Patel O, Kjer-Nielsen L, Le Nours J, Eckle SB, Birkinshaw R, Beddoe T, Corbett AJ, Liu L, Miles JJ, Meehan B, Reantragoon R, Sandoval-Romero ML, Sullivan LC, Brooks AG, Chen Z, Fairlie DP, McCluskey J, Rossjohn J (2013) Recognition of vitamin B metabolites by mucosal-associated invariant T cells. Nat Commun 4:2142. doi:10.1038/ncomms3142
Saper MA, Bjorkman PJ, Wiley DC (1991) Refined structure of the human histocompatibility antigen HLA-A2 at 2.6 A resolution. J Mol Biol 219(2):277–319
Anderson G, Moore NC, Owen JJ, Jenkinson EJ (1996) Cellular interactions in thymocyte development. Annu Rev Immunol 14:73–99. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.14.1.73
Jameson SC, Hogquist KA, Bevan MJ (1995) Positive selection of thymocytes. Annu Rev Immunol 13:93–126. doi:10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.000521
Urdahl KB, Sun JC, Bevan MJ (2002) Positive selection of MHC class Ib-restricted CD8(+) T cells on hematopoietic cells. Nat Immunol 3(8):772–779. doi:10.1038/ni814
Kisielow J, Tortola L, Weber J, Karjalainen K, Kopf M (2011) Evidence for the divergence of innate and adaptive T-cell precursors before commitment to the alphabeta and gammadelta lineages. Blood 118(25):6591–6600. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-05-352732
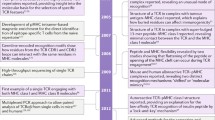
Turpen JB, Smith PB (1989) Precursor immigration and thymocyte succession during larval development and metamorphosis in Xenopus. J Immunol 142(1):41–47
Gravenor I, Horton TL, Ritchie P, Flint E, Horton JD (1995) Ontogeny and thymus-dependence of T cell surface antigens in Xenopus: flow cytometric studies on monoclonal antibody-stained thymus and spleen. Dev Comp Immunol 19(6):507–523
Du Pasquier L, Flajnik MF (1990) Expression of MHC class II antigens during Xenopus development. Dev Immunol 1(2):85–95
Rollins-Smith LA, Barker KS, Davis AT (1997) Involvement of glucocorticoids in the reorganization of the amphibian immune system at metamorphosis. Dev Immunol 5(2):145–152
Berzins SP, Uldrich AP, Pellicci DG, McNab F, Hayakawa Y, Smyth MJ, Godfrey DI (2004) Parallels and distinctions between T and NKT cell development in the thymus. Immunol Cell Biol 82(3):269–275. doi:10.1111/j.0818-9641.2004.01256.x
Gapin L (2009) Where do MAIT cells fit in the family of unconventional T cells? PLoS Biol 7(3):e70. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000070
Tilloy F, Di Santo JP, Bendelac A, Lantz O (1999) Thymic dependence of invariant V alpha 14+ natural killer-T cell development. Eur J Immunol 29(10):3313–3318
Bix M, Raulet D (1992) Inefficient positive selection of T cells directed by haematopoietic cells. Nature 359(6393):330–333. doi:10.1038/359330a0
Gapin L, Matsuda JL, Surh CD, Kronenberg M (2001) NKT cells derive from double-positive thymocytes that are positively selected by CD1d. Nat Immunol 2(10):971–978. doi:10.1038/ni710
Robert J, Cohen N (1998) Ontogeny of CTX expression in Xenopus. Dev Comp Immunol 22(5–6):605–612
Robert J, Cohen N (1999) In vitro differentiation of a CD4/CD8 double-positive equivalent thymocyte subset in adult Xenopus. Int Immunol 11(4):499–508
Chretien I, Robert J, Marcuz A, Garcia-Sanz JA, Courtet M, Du Pasquier L (1996) CTX, a novel molecule specifically expressed on the surface of cortical thymocytes in Xenopus. Eur J Immunol 26(4):780–791. doi:10.1002/eji.1830260409
Russ JH, Horton JD (1987) Cytoarchitecture of the Xenopus thymus following gamma-irradiation. Development 100(1):95–105
Robert J, Chretien I, Guiet C, Du Pasquier L (1997) Cross-linking CTX, a novel thymocyte-specific molecule, inhibits the growth of lymphoid tumor cells in Xenopus. Mol Immunol 34(2):133–143
Chung B, Aoukaty A, Dutz J, Terhorst C, Tan R (2005) Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule-associated protein controls NKT cell functions. J Immunol 174(6):3153–3157
Griewank K, Borowski C, Rietdijk S, Wang N, Julien A, Wei DG, Mamchak AA, Terhorst C, Bendelac A (2007) Homotypic interactions mediated by Slamf1 and Slamf6 receptors control NKT cell lineage development. Immunity 27(5):751–762. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2007.08.020
Coles MC, Raulet DH (2000) NK1.1+ T cells in the liver arise in the thymus and are selected by interactions with class I molecules on CD4+ CD8+ cells. J Immunol 164(5):2412–2418
Godfrey DI, Berzins SP (2007) Control points in NKT-cell development. Nat Rev Immunol 7(7):505–518. doi:10.1038/nri2116
Chun T, Page MJ, Gapin L, Matsuda JL, Xu H, Nguyen H, Kang HS, Stanic AK, Joyce S, Koltun WA, Chorney MJ, Kronenberg M, Wang CR (2003) CD1d-expressing dendritic cells but not thymic epithelial cells can mediate negative selection of NKT cells. J Exp Med 197(7):907–918. doi:10.1084/jem.20021366
Martin E, Treiner E, Duban L, Guerri L, Laude H, Toly C, Premel V, Devys A, Moura IC, Tilloy F, Cherif S, Vera G, Latour S, Soudais C, Lantz O (2009) Stepwise development of MAIT cells in mouse and human. PLoS Biol 7(3):e54. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000054
Kishimoto H, Sprent J (1997) Negative selection in the thymus includes semimature T cells. J Exp Med 185(2):263–271
Pellicci DG, Uldrich AP, Kyparissoudis K, Crowe NY, Brooks AG, Hammond KJ, Sidobre S, Kronenberg M, Smyth MJ, Godfrey DI (2003) Intrathymic NKT cell development is blocked by the presence of alpha-galactosylceramide. Eur J Immunol 33(7):1816–1823. doi:10.1002/eji.200323894
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Nicolas Cohen for helpful discussions and critical reading of the manuscript. This research was supported by Grants R24-AI-059830 from National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIH/NIAID).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edholm, ES., Grayfer, L. & Robert, J. Evolution of nonclassical MHC-dependent invariant T cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 71, 4763–4780 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1701-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1701-5