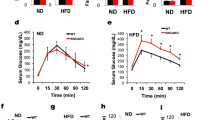
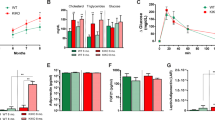
Abstract
Insulin is the main glucoregulator that promotes the uptake of glucose by tissues and the subsequent utilization of glucose as an energy source. In this paper, we describe a novel glucoregulator, the alpha-synuclein (SNCA) protein, that has previously been linked to Parkinson’s disease. Treatment with recombinant SNCA promotes glucose uptake in vitro in preadipocytes and in vivo in the adipose tissues and skeletal muscles of mice through the LPAR2/Gab1/PI3K/Akt pathway; these effects occur independently of the insulin receptor. This function of SNCA represents a new mechanistic insight that creates novel avenues of research with respect to the process of glucose regulation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goedert M (2001) Alpha-synuclein and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:492–501
Burre J, Sharma M, Tsetsenis T, Buchman V, Etherton MR, Sudhof TC (2010) Alpha-synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science 329:1663–1667
Chandra S, Gallardo G, Fernandez-Chacon R, Schluter OM, Sudhof TC (2005) Alpha-synuclein cooperates with CSPalpha in preventing neurodegeneration. Cell 123:383–396
Duran R, Barrero FJ, Morales B, Luna JD, Ramirez M, Vives F (2010) Plasma alpha-synuclein in patients with Parkinson’s disease with and without treatment. Mov Disord 25:489–493
Barbour R, Kling K, Anderson JP, Banducci K, Cole T, Diep L, Fox M, Goldstein JM, Soriano F, Seubert P et al (2008) Red blood cells are the major source of alpha-synuclein in blood. Neurodegener Dis 5:55–59
Park SM, Jung HY, Kim HO, Rhim H, Paik SR, Chung KC, Park JH, Kim J (2002) Evidence that alpha-synuclein functions as a negative regulator of Ca(++)-dependent alpha-granule release from human platelets. Blood 100:2506–2514
Hong S, Lee HK, Kim CY, Seong GJ (2008) Identification and localization of alpha-synuclein in human cornea. Korean J Ophthalmol 22:145–146
Kurz A, Rabbani N, Walter M, Bonin M, Thornalley P, Auburger G, Gispert S (2011) Alpha-synuclein deficiency leads to increased glyoxalase I expression and glycation stress. Cell Mol Life Sci 68:721–733
Seo JH, Rah JC, Choi SH, Shin JK, Min K, Kim HS, Park CH, Kim S, Kim EM, Lee SH et al (2002) Alpha-synuclein regulates neuronal survival via Bcl-2 family expression and PI3/Akt kinase pathway. FASEB J 16:1826–1828
Geng X, Lou H, Wang J, Li L, Swanson AL, Sun M, Beers-Stolz D, Watkins S, Perez RG, Drain P (2011) alpha-Synuclein binds the K(ATP) channel at insulin-secretory granules and inhibits insulin secretion. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 300:E276–E286
Hayashi H, Nakagami H, Takami Y, Koriyama H, Mori M, Tamai K, Sun J, Nagao K, Morishita R, Kaneda Y (2009) FHL-2 suppresses VEGF-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt activation via interaction with sphingosine kinase-1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:909–914
Abeliovich A, Schmitz Y, Farinas I, Choi-Lundberg D, Ho WH, Castillo PE, Shinsky N, Verdugo JM, Armanini M, Ryan A et al (2000) Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron 25:239–252
Begriche K, Massart J, Abbey-Toby A, Igoudjil A, Letteron P, Fromenty B (2008) Beta-aminoisobutyric acid prevents diet-induced obesity in mice with partial leptin deficiency. Obesity (Silver Spring) 16:2053–2067
Shiuchi T, Nakagami H, Iwai M, Takeda Y, Cui T, Chen R, Minokoshi Y, Horiuchi M (2001) Involvement of bradykinin and nitric oxide in leptin-mediated glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. Endocrinology 142:608–612
Shiuchi T, Haque MS, Okamoto S, Inoue T, Kageyama H, Lee S, Toda C, Suzuki A, Bachman ES, Kim YB et al (2009) Hypothalamic orexin stimulates feeding-associated glucose utilization in skeletal muscle via sympathetic nervous system. Cell Metab 10:466–480
Heart E, Choi WS, Sung CK (2000) Glucosamine-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278:E103–E112
Jiang ZY, Zhou QL, Coleman KA, Chouinard M, Boese Q, Czech MP (2003) Insulin signaling through Akt/protein kinase B analyzed by small interfering RNA-mediated gene silencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:7569–7574
Taniguchi CM, Emanuelli B, Kahn CR (2006) Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:85–96
Holgado-Madruga M, Emlet DR, Moscatello DK, Godwin AK, Wong AJ (1996) A Grb2-associated docking protein in EGF- and insulin-receptor signalling. Nature 379:560–564
Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E, Vande Woude GF (2003) Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:915–925
Saltiel AR, Kahn CR (2001) Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 414:799–806
Wohrle FU, Daly RJ, Brummer T (2009) Function, regulation and pathological roles of the Gab/DOS docking proteins. Cell Commun Signal 7:22
Miinea CP, Sano H, Kane S, Sano E, Fukuda M, Peranen J, Lane WS, Lienhard GE (2005) AS160, the Akt substrate regulating GLUT4 translocation, has a functional Rab GTPase-activating protein domain. Biochem J 391:87–93
Wang Y, Feng W, Xue W, Tan Y, Hein DW, Li XK, Cai L (2009) Inactivation of GSK-3beta by metallothionein prevents diabetes-related changes in cardiac energy metabolism, inflammation, nitrosative damage, and remodeling. Diabetes 58:1391–1402
Mariappan MM, Shetty M, Sataranatarajan K, Choudhury GG, Kasinath BS (2008) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta is a novel regulator of high glucose- and high insulin-induced extracellular matrix protein synthesis in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 283:30566–30575
Eulenfeld R, Schaper F (2009) A new mechanism for the regulation of Gab1 recruitment to the plasma membrane. J Cell Sci 122:55–64
Minokoshi Y, Alquier T, Furukawa N, Kim YB, Lee A, Xue B, Mu J, Foufelle F, Ferre P, Birnbaum MJ et al (2004) AMP-kinase regulates food intake by responding to hormonal and nutrient signals in the hypothalamus. Nature 428:569–574
Rose AJ, Richter EA (2005) Skeletal muscle glucose uptake during exercise: how is it regulated? Physiology (Bethesda) 20:260–270
Bertrand L, Ginion A, Beauloye C, Hebert AD, Guigas B, Hue L, Vanoverschelde JL (2006) AMPK activation restores the stimulation of glucose uptake in an in vitro model of insulin-resistant cardiomyocytes via the activation of protein kinase B. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H239–H250
O’Neill HM, Maarbjerg SJ, Crane JD, Jeppesen J, Jorgensen SB, Schertzer JD, Shyroka O, Kiens B, van Denderen BJ, Tarnopolsky MA et al (2011) AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) beta1beta2 muscle null mice reveal an essential role for AMPK in maintaining mitochondrial content and glucose uptake during exercise. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:16092–16097
Cabin DE, Shimazu K, Murphy D, Cole NB, Gottschalk W, McIlwain KL, Orrison B, Chen A, Ellis CE, Paylor R et al (2002) Synaptic vesicle depletion correlates with attenuated synaptic responses to prolonged repetitive stimulation in mice lacking alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci 22:8797–8807
Hogberg H, Engblom L, Ekdahl A, Lidell V, Walum E, Alberts P (2006) Temperature dependence of O2 consumption; opposite effects of leptin and etomoxir on respiratory quotient in mice. Obesity (Silver Spring) 14:673–682
Pronin AN, Morris AJ, Surguchov A, Benovic JL (2000) Synucleins are a novel class of substrates for G protein-coupled receptor kinases. J Biol Chem 275:26515–26522
Bisotto S, Fixman ED (2001) Src-family tyrosine kinases, phosphoinositide 3-kinase and Gab1 regulate extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 activation induced by the type A endothelin-1 G-protein-coupled receptor. Biochem J 360:77–85
Lin SH, Civelli O (2004) Orphan G protein-coupled receptors: targets for new therapeutic interventions. Ann Med 36:204–214
Ohta H, Sato K, Murata N, Damirin A, Malchinkhuu E, Kon J, Kimura T, Tobo M, Yamazaki Y, Watanabe T et al (2003) Ki16425, a subtype-selective antagonist for EDG-family lysophosphatidic acid receptors. Mol Pharmacol 64:994–1005
Haque F, Pandey AP, Cambrea LR, Rochet JC, Hovis JS (2010) Adsorption of alpha-synuclein on lipid bilayers: modulating the structure and stability of protein assemblies. J Phys Chem B 114:4070–4081
Ward Y, Lake R, Yin JJ, Heger CD, Raffeld M, Goldsmith PK, Merino M, Kelly K (2011) LPA receptor heterodimerizes with CD97 to amplify LPA-initiated RHO-dependent signaling and invasion in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 71:7301–7311
Choi JW, Herr DR, Noguchi K, Yung YC, Lee CW, Mutoh T, Lin ME, Teo ST, Park KE, Mosley AN et al (2010) LPA receptors: subtypes and biological actions. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 50:157–186
Kwakkenbos MJ, Kop EN, Stacey M, Matmati M, Gordon S, Lin HH, Hamann J (2004) The EGF-TM7 family: a postgenomic view. Immunogenetics 55:655–666
Vaughan TY, Verma S, Bunting KD (2011) Grb2-associated binding (Gab) proteins in hematopoietic and immune cell biology. Am J Blood Res 1:130–134
Bertola A, Bonnafous S, Cormont M, Anty R, Tanti JF, Tran A, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Gual P (2007) Hepatocyte growth factor induces glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through A Gab1/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Glut4 pathway. J Biol Chem 282:10325–10332
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of the Japanese Government (Monbukagakusho).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests with respect to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodriguez-Araujo, G., Nakagami, H., Hayashi, H. et al. Alpha-synuclein elicits glucose uptake and utilization in adipocytes through the Gab1/PI3K/Akt transduction pathway. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 70, 1123–1133 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1198-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1198-8