Abstract
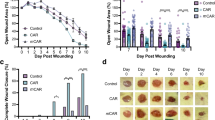
Chromogranin A (CgA), a secretory protein expressed by many neuroendocrine cells, neurons, cardiomyocytes, and keratinocytes, is the precursor of various peptides that regulate the carbohydrate/lipid metabolism and the cardiovascular system. We have found that CgA, locally administered to injured mice, can accelerate keratinocyte proliferation and wound healing. This biological activity was abolished by the Asp45Glu mutation. CgA and its N-terminal fragments, but not the corresponding Asp45Glu mutants, could selectively recognize the αvβ6-integrin on keratinocytes (a cell-adhesion receptor that is up-regulated during wound healing) and regulate keratinocyte adhesion, proliferation, and migration. No binding was observed to other integrins such as αvβ3, αvβ5, αvβ8, α5β1, α1β1, α3β1, α6β4, α6β7 and α9β1. Structure–activity studies showed that the entire CgA39–63 region is crucial for αvβ6 recognition (K i = 7 nM). This region contains an RGD site (residues CgA43–45) followed by an amphipathic α-helix (residues CgA47–63), both crucial for binding affinity and selectivity. These results suggest that the interaction of the RGD/α-helix motif of CgA with αvβ6 regulates keratinocyte physiology in wound healing.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CgA:
-
Chromogranin-A
- hCgA:
-
Human CgA
- rCgA:
-
Recombinant CgA
- VS-1:
-
Vasostatin-1
- STV:
-
Streptavidin
- HRP:
-
Peroxidase
References
Helle KB, Corti A, Metz-Boutigue MH, Tota B (2007) The endocrine role for chromogranin A: a prohormone for peptides with regulatory properties. Cell Mol Life Sci 22:2863–2886
Corti A (2010) Chromogranin A and the tumor microenvironment. Cell Mol Neurobiol 8:1163–1170
Radek KA, Lopez-Garcia B, Hupe M, Niesman IR, Elias PM, Taupenot L, Mahata SK, O’Connor DT, Gallo RL (2008) The neuroendocrine peptide catestatin is a cutaneous antimicrobial and induced in the skin after injury. J Invest Dermatol 6:1525–1534
Gayen JR, Saberi M, Schenk S, Biswas N, Vaingankar SM, Cheung WW, Najjar SM, O’Connor DT, Bandyopadhyay G, Mahata SK (2009) A novel pathway of insulin sensitivity in chromogranin A null mice: a crucial role for pancreastatin in glucose homeostasis. J Biol Chem 42:28498–28509
Gonzalez-Yanes C, Sanchez-Margalet V (2003) Pancreastatin, a chromogranin A-derived peptide, inhibits leptin and enhances UCP-2 expression in isolated rat adipocytes. Cell Mol Life Sci 12:2749–2756
Mahata SK, Mahata M, Fung MM, O’Connor DT (2010) Catestatin: a multifunctional peptide from chromogranin A. Regul Pept 1–3:33–43
Mahata SK, O’Connor DT, Mahata M, Yoo SH, Taupenot L, Wu H, Gill BM, Parmer RJ (1997) Novel autocrine feedback control of catecholamine release. A discrete chromogranin a fragment is a noncompetitive nicotinic cholinergic antagonist. J Clin Invest 6:1623–1633
Mahata SK, Mahata M, Parmer RJ, O’Connor DT (1999) Desensitization of catecholamine release. The novel catecholamine release-inhibitory peptide catestatin (chromogranin a344–364) acts at the receptor to prevent nicotinic cholinergic tolerance. J Biol Chem 5:2920–2928
Tota B, Angelone T, Mazza R, Cerra MC (2008) The chromogranin A-derived vasostatins: new players in the endocrine heart. Curr Med Chem 14:1444–1451
Lugardon K, Raffner R, Goumon Y, Corti A, Delmas A, Bulet P, Aunis D, Metz-Boutigue MH (2000) Antibacterial and antifungal activities of vasostatin-1, the N-terminal fragment of chromogranin A. J Biol Chem 275:10745–10753
Eskeland NL, Zhou A, Dinh TQ, Wu H, Parmer RJ, Mains RE, O’Connor DT (1996) Chromogranin A processing and secretion: specific role of endogenous and exogenous prohormone convertases in the regulated secretory pathway. J Clin Invest 1:148–156
Doblinger A, Becker A, Seidah NG, Laslop A (2003) Proteolytic processing of chromogranin A by the prohormone convertase PC2. Regul Pept 1–3:111–116
Colombo B, Curnis F, Foglieni C, Monno A, Arrigoni G, Corti A (2002) Chromogranin A expression in neoplastic cells affects tumor growth and morphogenesis in mouse models. Cancer Res 3:941–946
Biswas N, Rodriguez-Flores JL, Courel M, Gayen JR, Vaingankar SM, Mahata M, Torpey JW, Taupenot L, O’Connor DT, Mahata SK (2009) Cathepsin L colocalizes with chromogranin A in chromaffin vesicles to generate active peptides. Endocrinology 8:3547–3557
Gasparri A, Sidoli A, Sanchez LP, Longhi R, Siccardi AG, Marchisio PC, Corti A (1997) Chromogranin A fragments modulate cell adhesion. Identification and characterization of a pro-adhesive domain. J Biol Chem 33:20835–20843
Ratti S, Curnis F, Longhi R, Colombo B, Gasparri A, Magni F, Manera E, Metz-Boutigue MH, Corti A (2000) Structure–activity relationships of chromogranin A in cell adhesion. Identification and characterization of an adhesion site for fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 38:29257–29263
Colombo B, Longhi R, Marinzi C, Magni F, Cattaneo A, Yoo SH, Curnis F, Corti A (2002) Cleavage of chromogranin A N-terminal domain by plasmin provides a new mechanism for regulating cell adhesion. J Biol Chem 48:45911–45919
Dondossola E, Gasparri A, Bachi A, Longhi R, Metz-Boutigue MH, Tota B, Helle KB, Curnis F, Corti A (2010) Role of vasostatin-1 C-terminal region in fibroblast cell adhesion. Cell Mol Life Sci 12:2107–2118
Ferrero E, Magni E, Curnis F, Villa A, Ferrero ME, Corti A (2002) Regulation of endothelial cell shape and barrier function by chromogranin A. Ann N Y Acad Sci 971:355–358
Ferrero E, Scabini S, Magni E, Foglieni C, Belloni D, Colombo B, Curnis F, Villa A, Ferrero ME, Corti A (2004) Chromogranin A protects vessels against tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced vascular leakage. FASEB J 3:554–556
Belloni D, Scabini S, Foglieni C, Veschini L, Giazzon A, Colombo B, Fulgenzi A, Helle KB, Ferrero ME, Corti A, Ferrero E (2007) The vasostatin-I fragment of chromogranin A inhibits VEGF-induced endothelial cell proliferation and migration. FASEB J 12:3052–3062
Plow EF, Haas TA, Zhang L, Loftus J, Smith JW (2000) Ligand binding to integrins. J Biol Chem 29:21785–21788
Humphries JD, Byron A, Humphries MJ (2006) Integrin ligands at a glance. J Cell Sci 119(Pt 19):3901–3903
Barczyk M, Carracedo S, Gullberg D (2010) Integrins. Cell Tissue Res 1:269–280
Thomas GJ, Nystrom ML, Marshall JF (2006) Alphavbeta6 integrin in wound healing and cancer of the oral cavity. J Oral Pathol Med 1:1–10
Curnis F, Gasparri A, Sacchi A, Cattaneo A, Magni F, Corti A (2005) Targeted delivery of IFNgamma to tumor vessels uncouples antitumor from counterregulatory mechanisms. Cancer Res 7:2906–2913
D’Alessio S, Gerasi L, Blasi F (2008) uPAR-deficient mouse keratinocytes fail to produce EGFR-dependent laminin-5, affecting migration in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Sci 121(Pt 23):3922–3932
Corti A, Longhi R, Gasparri A, Chen F, Pelagi M, Siccardi AG (1996) Antigenic regions of human chromogranin A and their topographic relationships with structural/functional domains. Eur J Biochem 235(1–2):275–280
Corti A, Sanchez LP, Gasparri A, Curnis F, Longhi R, Brandazza A, Siccardi AG, Sidoli A (1997) Production and structure characterisation of recombinant chromogranin A N-terminal fragments (vasostatins)—evidence of dimer–monomer equilibria. Eur J Biochem 3:692–699
Fields GB, Noble RL (1990) Solid phase peptide synthesis utilizing 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl amino acids. Int J Pept Protein Res 3:161–214
Curnis F, Cattaneo A, Longhi R, Sacchi A, Gasparri AM, Pastorino F, Di Matteo P, Traversari C, Bachi A, Ponzoni M, Rizzardi GP, Corti A (2010) Critical role of flanking residues in NGR-to-isoDGR transition and CD13/integrin receptor switching. J Biol Chem 12:9114–9123
Spitaleri A, Mari S, Curnis F, Traversari C, Longhi R, Bordignon C, Corti A, Rizzardi GP, Musco G (2008) Structural basis for the interaction of isoDGR with the RGD-binding site of alphavbeta3 integrin. J Biol Chem 28:19757–19768
Lugardon K, Chasserot-Golaz S, Kieffer AE, Maget-Dana R, Nullans G, Kieffer B, Aunis D, Metz-Boutigue MH (2001) Structural and biological characterization of chromofungin, the antifungal chromogranin A-(47–66)-derived peptide. J Biol Chem 38:35875–35882
Dechantsreiter MA, Planker E, Matha B, Lohof E, Holzemann G, Jonczyk A, Goodman SL, Kessler H (1999) N-Methylated cyclic RGD peptides as highly active and selective alpha(V)beta(3) integrin antagonists. J Med Chem 16:3033–3040
Elayadi AN, Samli KN, Prudkin L, Liu YH, Bian A, Xie XJ, Wistuba II, Roth JA, McGuire MJ, Brown KC (2007) A peptide selected by biopanning identifies the integrin alphavbeta6 as a prognostic biomarker for nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 12:5889–5895
Hausner SH, DiCara D, Marik J, Marshall JF, Sutcliffe JL (2007) Use of a peptide derived from foot-and-mouth disease virus for the noninvasive imaging of human cancer: generation and evaluation of 4-[18F]fluorobenzoyl A20FMDV2 for in vivo imaging of integrin alphavbeta6 expression with positron emission tomography. Cancer Res 16:7833–7840
DiCara D, Rapisarda C, Sutcliffe JL, Violette SM, Weinreb PH, Hart IR, Howard MJ, Marshall JF (2007) Structure-function analysis of Arg-Gly-Asp helix motifs in alpha v beta 6 integrin ligands. J Biol Chem 13:9657–9665
Huang X, Wu J, Spong S, Sheppard D (1998) The integrin alphavbeta6 is critical for keratinocyte migration on both its known ligand, fibronectin, and on vitronectin. J Cell Sci 111:2189–2195
Breuss JM, Gallo J, DeLisser HM, Klimanskaya IV, Folkesson HG, Pittet JF, Nishimura SL, Aldape K, Landers DV, Carpenter W et al (1995) Expression of the beta 6 integrin subunit in development, neoplasia and tissue repair suggests a role in epithelial remodeling. J Cell Sci 108:2241–2251
Logan D, Abu-Ghazaleh R, Blakemore W, Curry S, Jackson T, King A, Lea S, Lewis R, Newman J, Parry N et al (1993) Structure of a major immunogenic site on foot-and-mouth disease virus. Nature 6420:566–568
Kraft S, Diefenbach B, Mehta R, Jonczyk A, Luckenbach GA, Goodman SL (1999) Definition of an unexpected ligand recognition motif for alphav beta6 integrin. J Biol Chem 4:1979–1985
Clark RA, Ashcroft GS, Spencer MJ, Larjava H, Ferguson MW (1996) Re-epithelialization of normal human excisional wounds is associated with a switch from alpha v beta 5 to alpha v beta 6 integrins. Br J Dermatol 1:46–51
Hakkinen L, Hildebrand HC, Berndt A, Kosmehl H, Larjava H (2000) Immunolocalization of tenascin-C, alpha9 integrin subunit, and alphavbeta6 integrin during wound healing in human oral mucosa. J Histochem Cytochem 7:985–998
Busk M, Pytela R, Sheppard D (1992) Characterization of the integrin alpha v beta 6 as a fibronectin-binding protein. J Biol Chem 9:5790–5796
Koivisto L, Larjava K, Hakkinen L, Uitto VJ, Heino J, Larjava H (1999) Different integrins mediate cell spreading, haptotaxis and lateral migration of HaCaT keratinocytes on fibronectin. Cell Adhes Commun 3:245–257
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC 9965 and 9180), and Alleanza Contro il Cancro (ACC) of Italy.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Curnis, F., Gasparri, A.M., Longhi, R. et al. Chromogranin A binds to αvβ6-integrin and promotes wound healing in mice. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 69, 2791–2803 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-0955-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-0955-z