Abstract
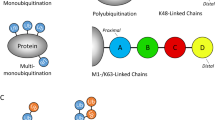
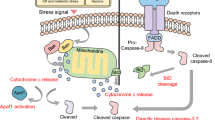
It has become apparent that ubiquitination plays a critical role in cell survival and cell death. In addition, deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) have been determined to be highly important regulators of these processes. Cells can be subjected to various stresses and respond in a variety of different ways ranging from activation of survival pathways to the promotion of cell death, which eventually eliminates damaged cells. The regulatory mechanisms of apoptosis depend on the balanced action between ubiquitination and deubiquitination systems. There is a growing recognition that DUBs play essential roles in regulating several binding partners to modulate the process of apoptosis. Thus, the interplay between the timing of DUB activity and the specificity of ubiquitin attachment and removal from its substrates during apoptosis is important to ensure cellular homeostasis. This review discusses the role of a few ubiquitin-specific DUBs that are involved in either promoting or suppressing the process of apoptosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DUB:
-
Deubiquitinating enzyme
- UPP:
-
Ubiquitin proteasomal pathway
- USP:
-
Ubiquitin specific protease
- UCH:
-
Ubiquitin carboxy terminal hydrolases
- OTU:
-
Ovarian tumor domain
- MJD:
-
Machado–Joseph disease
- JAMM:
-
Jab1/MPN domain-associated metalloisopeptidase
- UBDs:
-
Ubiquitin-binding domains
- MVB:
-
Multivesicular body
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- IFN:
-
Interferon
References
Glickman MH, Ciechanover A (2002) The ubiquitin–proteasome proteolytic pathway: destruction for the sake of construction. Physiol Rev 82:373–428
Hershko A, Ciechanover A (1998) The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem 67:425–479
Hoppe T (2005) Multiubiquitylation by E4 enzymes: ‘one size’ doesn’t fit all. Trends Biochem Sci 30:183–187
Pickart C (2000) Ubiquitin in chains. Trends Biochem Sci 25:544–548
Ikeda F, Dikic I (2008) Atypical ubiquitin chains: new molecular signals. ‘Protein Modifications: Beyond the Usual Suspects’ review series. EMBO Rep 9:536–542
Kim HT, Kim KP, Lledias F, Kisselev AF, Scaglione KM, Skowyra D, Gygi SP, Goldberg AL (2007) Certain pairs of ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s) and ubiquitin-protein ligases (E3s) synthesize nondegradable forked ubiquitin chains containing all possible isopeptide linkages. J Biol Chem 282:17375–17386
Varadan R, Assfalg M, Haririnia A, Raasi S, Pickart C, Fushman D (2004) Solution conformation of Lys63-linked di-ubiquitin chain provides clues to functional diversity of polyubiquitin signaling. J Biol Chem 279:7055–7063
Al-Hakim AK, Zagorska A, Chapman L, Deak M, Peggie M, Alessi DR (2008) Control of AMPK-related kinases by USP9X and atypical Lys(29)/Lys(33)-linked polyubiquitin chains. Biochem J 411:249–260
Bernassola F, Karin M, Ciechanover A, Melino G (2008) The HECT family of E3 ubiquitin ligases: multiple players in cancer development. Cancer Cell 14:10–21
Chastagner P, Israel A, Brou C (2006) Itch/AIP4 mediates Deltex degradation through the formation of K29-linked polyubiquitin chains. EMBO Rep 7(11):1147–1153
Wang M, Cheng D, Peng J, Pickart CM (2006) Molecular determinants of polyubiquitin linkage selection by an HECT ubiquitin ligase. EMBO J 25:1710–1719
Spence J, Sadis S, Haas AL, Finley D (1995) A ubiquitin mutant with specific defects in DNA repair and multiubiquitination. Mol Cell Biol 15:1265–1273
Wu CJ, Conze DB, Li T, Srinivasula SM, Ashwell JD (2006) Sensing of Lys 63-linked polyubiquitination by NEMO is a key event in NF-kappaB activation. Nat Cell Biol 8:398–406
Mukhopadhyay D, Riezman H (2007) Proteasome-independent functions of ubiquitin in endocytosis and signaling. Science 315:201–205
Arnason T, Ellison MJ (1994) Stress resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is strongly correlated with assembly of a novel type of multiubiquitin chain. Mol Cell Biol 14:7876–7883
Pickart CM (2001) Mechanisms underlying ubiquitination. Annu Rev Biochem 70:503–533
Hicke L, Riezman H (1996) Ubiquitination of a yeast plasma membrane receptor signals its ligand-stimulated endocytosis. Cell 84:277–287
Terrell J, Shih S, Dunn R, Hicke L (1998) A function for monoubiquitination in the internalization of a G protein-coupled receptor. Mol Cell 1:193–202
Galan JM, Haguenauer-Tsapis R (1997) Ubiquitin lys63 is involved in ubiquitination of a yeast plasma membrane protein. EMBO J 16:5847–5854
Hicke L, Dunn R (2003) Regulation of membrane protein transport by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-binding proteins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 19:141–172
Komada M, Kitamura N (2005) The Hrs/STAM complex in the downregulation of receptor tyrosine kinases. J Biochem 137:1–8
Duncan LM, Piper S, Dodd RB, Saville MK, Sanderson CM, Luzio JP, Lehner PJ (2006) Lysine-63-linked ubiquitination is required for endolysosomal degradation of class I molecules. EMBO J 25:1635–1645
Konstantinova IM, Tsimokha AS, Mittenberg AG (2008) Role of proteasomes in cellular regulation. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 267:59–124
Reyes-Turcu FE, Ventii KH, Wilkinson KD (2009) Regulation and cellular roles of ubiquitin-specific deubiquitinating enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem 78:363–397
Sorokin AV, Kim ER, Ovchinnikov LP (2009) Proteasome system of protein degradation and processing. Biochemistry (Mosc) 74:1411–1442
Petroski MD (2008) The ubiquitin system, disease, and drug discovery. BMC Biochem 9:S7
Amerik AY, Hochstrasser M (2004) Mechanism and function of deubiquitinating enzymes. Biochim Bio Phys Acta 1695:189–207
Baek KH (2006) Cytokine-regulated protein degradation by the ubiquitination system. Curr Protein Pept Sci 7:171–177
Nijman SM, Luna-Vargas MP, Velds A, Brummelkamp TR, Dirac AM, Sixma TK, Bernards R (2005) A genomic and functional inventory of deubiquitinating enzymes. Cell 123:773–786
Baker RT, Board PG (1987) The human ubiquitin gene family: structure of a gene and pseudogenes from the Ub B subfamily. Nucleic Acids Res 15:443–463
Pickart CM, Rose IA (1985) Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase acts on ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal amides. J Biol Chem 260:7903–7910
Wilkinson KD, Tashayev VL, O’Connor LB, Larsen CN, Kasperek E, Pickart CM (1995) Metabolism of the polyubiquitin degradation signal: structure, mechanism, and role of isopeptidase T. Biochemistry 34:14535–14546
Song L, Rape M (2008) Reverse the curse––the role of deubiquitination in cell cycle control. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20:156–163
Komada M (2008) Controlling receptor downregulation by ubiquitination and deubiquitination. Curr Drug Discov Technol 5:78–84
Kennedy RD, D’Andrea AD (2005) The Fanconi anemia/BRCA pathway: new faces in the crowd. Genes Dev 19:2925–2940
Rathaus M, Lerrer B, Cohen HY (2009) DeubiKuitylation: a novel DUB enzymatic activity for the DNA repair protein, Ku70. Cell Cycle 8:1843–1852
Burrows JF, McGrattan MJ, Rascle A, Humbert M, Baek KH, Johnston JA (2004) DUB-3, a cytokine-inducible deubiquitinating enzyme that blocks proliferation. J Biol Chem 279:13993–14000
Shin JM, Yoo KJ, Kim MS, Kim D, Baek KH (2006) Hyaluronan- and RNA-binding deubiquitinating enzymes of USP17 family members associated with cell viability. BMC Genom 7:292
Rytkönen A, Holden DW (2007) Bacterial interference of ubiquitination and deubiquitination. Cell Host Microbe 1:13–22
Hussain S, Zhang Y, Galardy PJ (2009) DUBs and cancer: the role of deubiquitinating enzymes as oncogenes, non-oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Cell Cycle 8:1688–1697
Liu CH, Goldberg AL, Qiu XB (2007) New insights into the role of the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway in the regulation of apoptosis. Chang Gung Med J 30:469–479
Basu A, Haldar S (2002) Signal-induced site specific phosphorylation targets Bcl2 to the proteasome pathway. Int J Oncol 21:597–601
Thompson SJ, Loftus LT, Ashley MD, Meller R (2008) Ubiquitin–proteasome system as a modulator of cell fate. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8:90–95
O’Donnell MA, Legarda-Addison D, Skountzos P, Yeh WC, Ting AT (2007) Ubiquitination of RIP1 regulates an NF-kappaB-independent cell-death switch in TNF signaling. Curr Biol 17:418–424
Zhang HG, Wang J, Yang X, Hsu HC, Mountz JD (2004) Regulation of apoptosis proteins in cancer cells by ubiquitin. Oncogene 23:2009–2015
Chang L, Kamata H, Solinas G, Luo JL, Maeda S, Venuprasad K, Liu YC, Karin M (2006) The E3 ubiquitin ligase itch couples JNK activation to TNFalpha-induced cell death by inducing c-FLIP(L) turnover. Cell 124:601–613
Brooks CL, Gu W (2006) p53 ubiquitination: Mdm2 and beyond. Mol Cell 21:307–315
Marchenko ND, Wolff S, Erster S, Becker K, Moll UM (2007) Monoubiquitylation promotes mitochondrial p53 translocation. EMBO J 26:923–934
Yang H, Dou QP (2010) Targeting apoptosis pathway with natural terpenoids: implications for treatment of breast and prostate cancer. Curr Drug Targets 11:733–744
Strasser A, O’Connor L, Dixit VM (2000) Apoptosis signaling. Annu Rev Biochem 69:217–245
Reeve JL, Duffy AM, O’Brien T, Samali A (2005) Don’t lose heart––therapeutic value of apoptosis prevention in the treatment of cardiovascular disease. J Cell Mol Med 9:609–622
Grimm LM, Osborne BA (1999) Apoptosis and the proteasome. Results Probl Cell Differ 23:209–228
Baek KH, Mondoux MA, Jaster R, Fire-Levin E, D’Andrea AD (2001) DUB-2A, a new member of the DUB subfamily of hematopoietic deubiquitinating enzymes. Blood 98:636–642
Zhu Y, Lambert K, Corless C, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, D’Andrea AD (1997) DUB-2 is a member of a novel family of cytokine-inducible deubiquitinating enzymes. J Biol Chem 272:51–57
Zhu Y, Pless M, Inhorn R, Mathey-Prevot B, D’Andrea AD (1996) The murine DUB-1 gene is specifically induced by the betac subunit of interleukin-3 receptor. Mol Cell Biol 16:4808–4817
Migone TS, Humbert M, Rascle A, Sanden D, D’Andrea A, Johnston JA (2001) The deubiquitinating enzyme DUB-2 prolongs cytokine-induced signal transducers and activators of transcription activation and suppresses apoptosis following cytokine withdrawal. Blood 98:1935–1941
Bromberg J (2002) Stat proteins and oncogenesis. J Clin Invest 109:1139–1142
Zhu Y, Carroll M, Papa FR, Hochstrasser M, D’Andrea AD (1996) DUB-1, a deubiquitinating enzyme with growth-suppressing activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:3275–3279
Baek KH, Kim MS, Kim YS, Shin JM, Choi KH (2004) DUB-1A, a novel subfamily member of deubiquitinating enzyme, is polyubiquitinated and cytokine inducible in B-lymphocytes. J Biol Chem 279:2368–2376
Lee MY, Ajjappala BS, Kim MS, Oh YK, Baek KH (2008) DUB-1, a fate determinant of dynein heavy chain in B-lymphocytes, is regulated by the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. J Cell Biochem 105:1420–1429
Xu XM, Chen Y, Chen J, Yang S, Gao F, Underhill CB, Creswell K, Zhang L (2003) A peptide with three hyaluronan binding motifs inhibits tumor growth and induces apoptosis. Cancer Res 63:5685–5690
Burrows JF, Kelvin AA, McFarlane C, Burden RE, McGrattan MJ, De la Vega M, Govender U, Quinn DJ, Dib K, Gadina M, Scott CJ, Johnston JA (2009) USP17 regulates Ras activation and cell proliferation by blocking RCE1 activity. J Biol Chem 284:9587–9595
Pereg Y, Liu BY, O’Rourke KM, Sagolla M, Dey A, Komuves L, French DM, Dixit VM (2010) Ubiquitin hydrolase Dub3 promotes oncogenic transformation by stabilizing Cdc25A. Nat Cell Biol 12:400–406
Lin H, Keriel A, Morales CR, Bedard N, Zhao Q, Hingamp P, Lefrançois S, Combaret L, Wing SS (2000) Divergent N-terminal sequences target an inducible testis deubiquitinating enzyme to distinct subcellular structures. Mol Cell Biol 20:6568–6578
Graner E, Tang D, Rossi S, Baron A, Migita T, Weinstein LJ, Lechpammer M, Huesken D, Zimmermann J, Signoretti S, Loda M (2004) The isopeptidase USP2a regulates the stability of fatty acid synthase in prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 5:253–261
Baron A, Migita T, Tang D, Loda M (2004) Fatty acid synthase: a metabolic oncogene in prostate cancer? J Cell Biochem 91:47–53
Menendez JA, Vellon L, Mehmi I, Oza BP, Ropero S, Colomer R, Lupu R (2004) Inhibition of fatty acid synthase (FAS) suppresses HER2/neu (erbB-2) oncogene overexpression in cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:10715–10720
Stevenson LF, Sparks A, Allende-Vega N, Xirodimas DP, Lane DP, Saville MK (2007) The deubiquitinating enzyme USP2a regulates the p53 pathway by targeting Mdm2. EMBO J 26:976–986
Allende-Vega N, Sparks A, Lane DP, Saville MK (2010) MdmX is a substrate for the deubiquitinating enzyme USP2a. Oncogene 29:432–441
Meredith M, Orr A, Everett R (1994) Herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein Vmw110 binds strongly and specifically to a 135-kDa cellular protein. Virology 200:457–469
Cheon KW, Baek KH (2006) HAUSP as a therapeutic target for hematopoietic tumors (review). Int J Oncol 28:1209–1215
Li M, Brooks CL, Kon N, Gu W (2004) A dynamic role of HAUSP in the p53-Mdm2 pathway. Mol Cell 13:879–886
Cummins JM, Vogelstein B (2004) HAUSP is required for p53 destabilization. Cell Cycle 3:689–692
Lee JT, Gu W (2010) The multiple levels of regulation by p53 ubiquitination. Cell Death Differ 17:86–92
Saridakis V, Sheng Y, Sarkari F, Holowaty MN, Shire K, Nguyen T, Zhang RG, Liao J, Lee W, Edwards AM, Arrowsmith CH, Frappier L (2005) Structure of the p53 binding domain of HAUSP/USP7 bound to Epstein–Barr nuclear antigen 1 implications for EBV-mediated immortalization. Mol Cell 18:25–36
Vugmeyster Y, Borodovsky A, Maurice MM, Maehr R, Furman MH, Ploegh HL (2002) The ubiquitin–proteasome pathway in thymocyte apoptosis: caspase-dependent processing of the deubiquitinating enzyme USP7 (HAUSP). Mol Immunol 39:431–441
Yoo KJ, Lee HJ, Lee H, Lee KY, Lee SH, Chung HM, Baek KH (2005) Expression and functional analyses of mHAUSP regulating apoptosis of cervical adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Oncol 27:97–104
Colland F, Formstecher E, Jacq X, Reverdy C, Planquette C, Conrath S, Trouplin V, Bianchi J, Aushev VN, Camonis J, Calabrese A, Borg-Capra C, Sippl W, Collura V, Boissy G, Rain JC, Guedat P, Delansorne R, Daviet L (2009) Small-molecule inhibitor of USP7/HAUSP ubiquitin protease stabilizes and activates p53 in cells. Mol Cancer Ther 8:2286–2295
Burgering BM, Kops GJ (2002) Cell cycle and death control: long live Forkheads. Trends Biochem Sci 27:352–360
Medema RH, Kops GJ, Bos JL, Burgering BM (2000) AFX-like Forkhead transcription factors mediate cell-cycle regulation by Ras and PKB through p27kip1. Nature 404:782–787
van der Horst A, de Vries-Smits AM, Brenkman AB, van Triest MH, van den Broek N, Colland F, Maurice M, Burgering BM (2006) FOXO4 transcriptional activity is regulated by monoubiquitination and USP7/HAUSP. Nat Cell Biol 8:1064–1073
Brenkman AB, de Keizer PL, van den Broek NJ, Jochemsen AG, Burgering BM (2008) Mdm2 induces mono-ubiquitination of FOXO4. PLoS One 3:e2819
Yuan J, Luo K, Zhang L, Cheville JC, Lou Z (2010) USP10 regulates p53 localization and stability by deubiquitinating p53. Cell 140:384–396
Naviglio S, Mattecucci C, Matoskova B, Nagase T, Nomura N, Di Fiore PP, Draetta GF (1998) UBPY: a growth-regulated human ubiquitin isopeptidase. EMBO J 17:3241–3250
Qiu XB, Markant SL, Yuan J, Goldberg AL (2004) Nrdp1-mediated degradation of the gigantic IAP, BRUCE, is a novel pathway for triggering apoptosis. EMBO J 23:800–810
Wu X, Yen L, Irwin L, Sweeney C, Carraway KL (2004) Stabilization of the E3 ubiquitin ligase Nrdp1 by the deubiquitinating enzyme USP8. Mol Cell Biol 24:7748–7757
Huang Y, Baker RT, Fischer-Vize JA (1995) Control of cell fate by a deubiquitinating enzyme encoded by the fat facets gene. Science 270:1828–1831
Noguchi T, Ishii K, Fukutomi H, Naguro I, Matsuzawa A, Takeda K, Ichijo H (2008) Requirement of reactive oxygen species-dependent activation of ASK1-p38 MAPK pathway for extracellular ATP-induced apoptosis in macrophage. J Biol Chem 283:7657–7665
Matsuzawa A, Saegusa K, Noguchi T, Sadamitsu C, Nishitoh H, Nagai S, Koyasu S, Matsumoto K, Takeda K, Ichijo H (2005) ROS-dependent activation of the TRAF6-ASK1–p38 pathway is selectively required for TLR4-mediated innate immunity. Nat Immunol 6:587–592
Nagai H, Noguchi T, Homma K, Katagiri K, Takeda K, Matsuzawa A, Ichijo H (2009) Ubiquitin-like sequence in ASK1 plays critical roles in the recognition and stabilization by USP9X and oxidative stress-induced cell death. Mol Cell 36:805–818
van Delft MF, Wei AH, Mason KD, Vandenberg CJ, Chen L, Czabotar PE, Willis SN, Scott CL, Day CL, Cory S, Adams JM, Roberts AW, Huang DC (2006) The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell 10:389–399
Akgul C (2009) Mcl-1 is a potential therapeutic target in multiple types of cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:1326–1336
Schwickart M, Huang X, Lill JR, Liu J, Ferrando R, French DM, Maecker H, O’Rourke K, Bazan F, Eastham-Anderson J, Yue P, Dornan D, Huang DC, Dixit VM (2010) Deubiquitinase USP9X stabilizes MCL1 and promotes tumour cell survival. Nature 463:103–107
Hetfeld BK, Helfrich A, Kapelari B, Scheel H, Hofmann K, Guterman A, Glickman M, Schade R, Kloetzel PM, Dubiel W (2005) The zinc finger of the CSN-associated deubiquitinating enzyme USP15 is essential to rescue the E3 ligase Rbx1. Curr Biol 15:1217–1221
Huang X, Langelotz C, Hetfeld-Pechoc BK, Schwenk W, Dubiel W (2009) The COP9 signalosome mediates beta-catenin degradation by deneddylation and blocks adenomatous polyposis coli destruction via USP15. J Mol Biol 391:691–702
Xu M, Takanashi M, Oikawa K, Tanaka M, Nishi H, Isaka K, Kudo M, Kuroda M (2009) USP15 plays an essential role for caspase-3 activation during paclitaxel-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 388:366–371
Cai SY, Babbitt RW, Marchesi VT (1999) A mutant deubiquitinating enzyme (Ubp-M) associates with mitotic chromosomes and blocks cell division. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:2828–2833
Joo HY, Zhai L, Yang C, Nie S, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Chang C, Wang H (2007) Regulation of cell cycle progression and gene expression by H2A deubiquitination. Nature 449:1068–1072
Mimnaugh EG, Kayastha G, McGovern NB, Hwang SG, Marcu MG, Trepel J, Cai SY, Marchesi VT, Neckers L (2001) Caspase-dependent deubiquitination of monoubiquitinated nucleosomal histone H2A induced by diverse apoptogenic stimuli. Cell Death Differ 8:1182–1196
Potu H, Sgorbissa A, Brancolini C (2010) Identification of USP18 as an important regulator of the susceptibility to IFN-alpha and drug-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 70:655–665
Zhang D, Zaugg K, Mak TW, Elledge SJ (2006) A role for the deubiquitinating enzyme USP28 in control of the DNA-damage response. Cell 126:529–542
Gewies A, Grimm S (2003) UBP41 is a proapoptotic ubiquitin-specific protease. Cancer Res 63:682–688
Peschiaroli A, Skaar JR, Pagano M, Melino G (2010) The ubiquitin-specific protease USP47 is a novel beta-TRCP interactor regulating cell survival. Oncogene 29:1384–1393
Fuchs SY, Spiegelman VS, Kumar KG (2004) The many faces of beta-TrCP E3 ubiquitin ligases: reflections in the magic mirror of cancer. Oncogene 23:2028–2036
Bignell GR, Warren W, Seal S, Takahashi M, Rapley E, Barfoot R, Green H, Brown C, Biggs PJ, Lakhani SR, Jones C, Hansen J, Blair E, Hofmann B, Siebert R, Turner G, Evans DG, Schrander-Stumpel C, Beemer FA, van Den Ouweland A, Halley D, Delpech B, Cleveland MG, Leigh I, Leisti J, Rasmussen S (2000) Identification of the familial cylindromatosis tumour-suppressor gene. Nat Genet 25:160–165
Massoumi R, Chmielarska K, Hennecke K, Pfeifer A, Fassler R (2006) Cyld inhibits tumor cell proliferation by blocking Bcl-3-dependent NF-κB signaling. Cell 125:665–677
Sun SC (2010) CYLD: a tumor suppressor deubiquitinase regulating NF-kappaB activation and diverse biological processes. Cell Death Differ 17:25–34
Wright A, Reiley WW, Chang M, Jin W, Lee AJ, Zhang M, Sun SC (2007) Regulation of early wave of germ cell apoptosis and spermatogenesis by deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD. Dev Cell 13:705–716
Print CG, Loveland KL (2000) Germ cell suicide: new insights into apoptosis during spermatogenesis. Bioessays 22:423–430
Wang L, Du F, Wang X (2008) TNF-alpha induces two distinct caspase-8 activation pathways. Cell 133:693–703
Bloom J, Pagano M (2003) Deregulated degradation of the cdk inhibitor p27 and malignant transformation. Semin Cancer Biol 13:41–47
Lu Y, Adegoke OA, Nepveu A, Nakayama KI, Bedard N, Cheng D, Peng J, Wing SS (2009) USP19 deubiquitinating enzyme supports cell proliferation by stabilizing KPC1, a ubiquitin ligase for p27Kip1. Mol Cell Biol 29:547–558
Gong L, Kamitani T, Millas S, Yeh ET (2000) Identification of a novel isopeptidase with dual specificity for ubiquitin- and NEDD8-conjugated proteins. J Biol Chem 275:14212–14216
Endo A, Matsumoto M, Inada T, Yamamoto A, Nakayama KI, Kitamura N, Komada M (2009) Nucleolar structure and function are regulated by the deubiquitylating enzyme USP36. J Cell Sci 122:678–686
Wilkinson KD, Lee KM, Deshpande S, Duerksen-Hughes P, Boss JM, Pohl J (1989) The neuron-specific protein PGP 9.5 is a ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase. Science 246:670–673
Kwon J, Wang YL, Setsuie R, Sekiguchi S, Sakurai M, Sato Y, Lee WW, Ishii Y, Kyuwa S, Noda M, Wada K, Yoshikawa Y (2004) Developmental regulation of ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase isozyme expression during spermatogenesis in mice. Biol Reprod 71:515–521
Kwon J (2007) The new function of two ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase isozymes as reciprocal modulators of germ cell apoptosis. Exp Anim 56:71–77
Chow MK, Mackay JP, Whisstock JC, Scanlon MJ, Bottomley SP (2004) Structural and functional analysis of the Josephin domain of the polyglutamine protein ataxin-3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 322:387–394
Ferro A, Carvalho AL, Teixeira-Castro A, Almeida C, Tomé RJ, Cortes L, Rodrigues AJ, Logarinho E, Sequeiros J, Macedo-Ribeiro S, Maciel P (2007) NEDD8: a new ataxin-3 interactor. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773:1619–1627
Burnett B, Li F, Pittman RN (2003) The polyglutamine neurodegenerative protein ataxin-3 binds polyubiquitylated proteins and has ubiquitin protease activity. Hum Mol Genet 12:3195–3205
Rodrigues AJ, Neves-Carvalho A, Ferro A, Rokka A, Corthals G, Logarinho E, Maciel P (2009) ATX-3, CDC-48 and UBXN-5: a new trimolecular complex in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 386:575–581
Wang H, Jia N, Fei E, Wang Z, Liu C, Zhang T, Fan J, Wu M, Chen L, Nukina N, Zhou J, Wang G (2007) p45, an ATPase subunit of the 19S proteasome, targets the polyglutamine disease protein ataxin-3 to the proteasome. J Neurochem 101:1651–1661
Wang Q, Li L, Ye Y (2006) Regulation of retrotranslocation by p97-associated deubiquitinating enzyme ataxin-3. J Cell Biol 174:963–971
Kobayashi T, Kakizuka A (2003) Molecular analyses of Machado–Joseph disease. Cytogenet Genome Res 100:261–275
Yoshizawa T, Yamagishi Y, Koseki N, Goto J, Yoshida H, Shibasaki F, Shoji S, Kanazawa I (2000) Cell cycle arrest enhances the in vitro cellular toxicity of the truncated Machado–Joseph disease gene product with an expanded polyglutamine stretch. Hum Mol Genet 9:69–78
Tsai HF, Tsai HJ, Hsieh M (2004) Full-length expanded ataxin-3 enhances mitochondrial-mediated cell death and decreases Bcl-2 expression in human neuroblastoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 324:1274–1282
Berke SJ, Schmied FA, Brunt ER, Ellerby LM, Paulson HL (2004) Caspase-mediated proteolysis of the polyglutamine disease protein ataxin-3. J Neurochem 89:908–918
Chou AH, Yeh TH, Kuo YL, Kao YC, Jou MJ, Hsu CY, Tsai SR, Kakizuka A, Wang HL (2006) Polyglutamine-expanded ataxin-3 activates mitochondrial apoptotic pathway by upregulating Bax and downregulating Bcl-xL. Neurobiol Dis 21:333–345
Choo YS, Johnson GV, MacDonald M, Detloff PJ, Lesort M (2004) Mutant huntingtin directly increases susceptibility of mitochondria to the calcium-induced permeability transition and cytochrome c release. Hum Mol Genet 13:1407–1420
Wang X, Zhu S, Drozda M, Zhang W, Stavrovskaya IG, Cattaneo E, Ferrante RJ, Kristal BS, Friedlander RM (2003) Minocycline inhibits caspase-independent and -dependent mitochondrial cell death pathways in models of Huntington’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:10483–10487
Evert BO, Wüllner U, Schulz JB, Weller M, Groscurth P, Trottier Y, Brice A, Klockgether T (1999) High level expression of expanded full-length ataxin-3 in vitro causes cell death and formation of intranuclear inclusions in neuronal cells. Hum Mol Genet 8:1169–1176
Huynh DP, Yang HT, Vakharia H, Nguyen D, Pulst SM (2003) Expansion of the polyQ repeat in ataxin-2 alters its Golgi localization, disrupts the Golgi complex and causes cell death. Hum Mol Genet 12:1485–1496
Wiedemeyer R, Westermann F, Wittke I, Nowock J, Schwab M (2003) Ataxin-2 promotes apoptosis of human neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene 22:401–411
Dixit VM, Green S, Sarma V, Holzman LB, Wolf FW, O’Rourke K, Ward PA, Prochownik EV, Marks RM (1990) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induction of novel gene products in human endothelial cells including a macrophage-specific chemotaxin. J Biol Chem 265:2973–2978
Heyninck K, Beyaert R (2005) A20 inhibits NF-kappaB activation by dual ubiquitin-editing functions. Trends Biochem Sci 30:1–4
Makarova KS, Aravind L, Koonin EV (2000) A novel superfamily of predicted cysteine proteases from eukaryotes, viruses and Chlamydia pneumoniae. Trends Biochem Sci 25:50–52
Cooper JT, Stroka DM, Brostjan C, Palmetshofer A, Bach FH, Ferran C (1996) A20 blocks endothelial cell activation through a NF-kappaB-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 271:18068–18073
Hoffmann A, Baltimore D (2006) Circuitry of nuclear factor kappaB signaling. Immunol Rev 210:171–186
Opipari AW Jr, Hu HM, Yabkowitz R, Dixit VM (1992) The A20 zinc finger protein protects cells from tumor necrosis factor cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem 267:12424–12427
Lee EG, Boone DL, Chai S, Libby SL, Chien M, Lodolce JP, Ma A (2000) Failure to regulate TNF-induced NF-kappaB and cell death responses in A20-deficient mice. Science 289:2350–2354
Daniel S, Arvelo MB, Patel VI, Longo CR, Shrikhande G, Shukri T, Mahiou J, Sun DW, Mottley C, Grey ST, Ferran C (2004) A20 protects endothelial cells from TNF-, Fas-, and NK-mediated cell death by inhibiting caspase 8 activation. Blood 104:2376–2384
Longo CR, Arvelo MB, Patel VI, Daniel S, Mahiou J, Grey ST, Ferran C (2003) A20 protects from CD40-CD40 ligand-mediated endothelial cell activation and apoptosis. Circulation 108:1113–1118
Boone DL, Turer EE, Lee EG, Ahmad RC, Wheeler MT, Tsui C, Hurley P, Chien M, Chai S, Hitotsumatsu O, McNally E, Pickart C, Ma A (2004) The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat Immunol 5:1052–1060
Li HL, Zhuo ML, Wang D, Wang AB, Cai H, Sun LH, Yang Q, Huang Y, Wei YS, Liu PP, Liu DP, Liang CC (2007) Targeted cardiac overexpression of A20 improves left ventricular performance and reduces compensatory hypertrophy after myocardial infarction. Circulation 115:1885–1894
Acknowledgments
The authors thank members of Baek laboratory at CHA University and CHA General Hospital for their critical comments on the manuscript. This study was supported by a grant from the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family affairs, Republic of Korea (00001602).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramakrishna, S., Suresh, B. & Baek, KH. The role of deubiquitinating enzymes in apoptosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68, 15–26 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0504-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0504-6