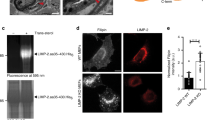
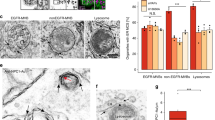
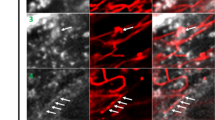
Abstract
ORP1L is an oxysterol binding homologue that regulates late endosome (LE) positioning. We show that ORP1L binds several oxysterols and cholesterol, and characterize a mutant, ORP1L Δ560–563, defective in oxysterol binding. While wild-type ORP1L clusters LE, ORP1L Δ560–563 induces LE scattering, which is reversed by disruption of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) targeting FFAT motif, suggesting that it is due to enhanced LE–ER interactions. Endosome motility is reduced upon overexpression of ORP1L. Both wild-type ORP1L and the Δ560–563 mutant induce the recruitment of both dynactin and kinesin-2 on LE. Most of the LE decorated by overexpressed ORP1L fail to accept endocytosed dextran or EGF, and the transfected cells display defective degradation of internalized EGF. ORP1L silencing in macrophage foam cells enhances endosome motility and results in inhibition of [3H]cholesterol efflux to apolipoprotein A-I. These data demonstrate that LE motility and functions in both protein and lipid transport are regulated by ORP1L.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABCA1:
-
ATP binding cassette transporter A1
- acLDL:
-
Acetylated LDL
- apoA-I:
-
Apolipoprotein A-I
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- GPF:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- GST:
-
Glutathione-S-transferase
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- LE:
-
Late endosome
- LUV:
-
Large unilamellar vesicle
- OHC:
-
Hydroxycholesterol
- ORP:
-
OSBP-related protein
- OSBP:
-
Oxysterol binding protein
- rho:
-
Rhodamine
- shRNA:
-
Short hairpin RNA
- siRNA:
-
Short interfering RNA
- VAP:
-
Vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein
- WT:
-
Wild-type
References
Taylor FR, Saucier SE, Shown EP, Parish EJ, Kandutsch AA (1984) Correlation between oxysterol binding to a cytosolic binding protein and potency in the repression of hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. J Biol Chem 259:12382–12387
Dawson PA, Ridgway ND, Slaughter CA, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1989) cDNA cloning and expression of oxysterol-binding protein, an oligomer with a potential leucine zipper. J Biol Chem 264:16798–16803
Dawson PA, Van der Westhuyzen DR, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1989) Purification of oxysterol binding protein from hamster liver cytosol. J Biol Chem 264:9046–9052
Wyles JP, McMaster CR, Ridgway ND (2002) Vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein-A (VAP-A) interacts with the oxysterol-binding protein to modify export from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 277:29908–29918
Levine TP, Munro S (1998) The pleckstrin homology domain of oxysterol-binding protein recognises a determinant specific to Golgi membranes. Curr Biol 8:729–739
Levine TP, Munro S (2002) Targeting of Golgi-specific pleckstrin homology domains involves both PtdIns 4-kinase-dependent and -independent components. Curr Biol 12:695–704
Roy A, Levine TP (2004) Multiple pools of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate detected using the pleckstrin homology domain of Osh2p. J Biol Chem 279:44683–44689
Perry RJ, Ridgway ND (2006) Oxysterol-binding protein and vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein are required for sterol-dependent activation of the ceramide transport protein. Mol Biol Cell 17:2604–2616
Wang PY, Weng J, Anderson RG (2005) OSBP is a cholesterol-regulated scaffolding protein in control of ERK 1/2 activation. Science 307:1472–1476
Wang PY, Weng J, Lee S, Anderson RG (2008) The N terminus controls sterol binding while the C terminus regulates the scaffolding function of OSBP. J Biol Chem 283:8034–8045
Yan D, Olkkonen VM (2008) Characteristics of oxysterol binding proteins. Int Rev Cytol 265:253–285
Raychaudhuri S, Prinz WA (2010) The diverse functions of oxysterol-binding proteins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.042308.113334
Ridgway ND (2010) Oxysterol-binding proteins. Subcell Biochem 51:159–182
Lehto M, Laitinen S, Chinetti G, Johansson M, Ehnholm C, Staels B, Ikonen E, Olkkonen VM (2001) The OSBP-related protein family in humans. J Lipid Res 42:1203–1213
Jaworski CJ, Moreira E, Li A, Lee R, Rodriguez IR (2001) A family of 12 human genes containing oxysterol-binding domains. Genomics 78:185–196
Anniss AM, Apostolopoulos J, Dworkin S, Purton LE, Sparrow RL (2002) An oxysterol-binding protein family identified in the mouse. DNA Cell Biol 21:571–580
Beh CT, Cool L, Phillips J, Rine J (2001) Overlapping functions of the yeast oxysterol-binding protein homologues. Genetics 157:1117–1140
Johansson M, Bocher V, Lehto M, Chinetti G, Kuismanen E, Ehnholm C, Staels B, Olkkonen VM (2003) The two variants of oxysterol binding protein-related protein-1 display different tissue expression patterns, have different intracellular localization, and are functionally distinct. Mol Biol Cell 14:903–915
Lehto M, Tienari J, Lehtonen S, Lehtonen E, Olkkonen VM (2004) Subfamily III of mammalian oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP) homologues: the expression and intracellular localization of ORP3, ORP6, and ORP7. Cell Tissue Res 315:39–57
Ridgway ND, Dawson PA, Ho YK, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1992) Translocation of oxysterol binding protein to Golgi apparatus triggered by ligand binding. J Cell Biol 116:307–319
Wyles JP, Ridgway ND (2004) VAMP-associated protein-A regulates partitioning of oxysterol-binding protein-related protein-9 between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Exp Cell Res 297:533–547
Lehto M, Hynynen R, Karjalainen K, Kuismanen E, Hyvärinen K, Olkkonen VM (2005) Targeting of OSBP-related protein 3 (ORP3) to endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membrane is controlled by multiple determinants. Exp Cell Res 310:445–462
Johansson M, Lehto M, Tanhuanpää K, Cover TL, Olkkonen VM (2005) The oxysterol-binding protein homologue ORP1L interacts with Rab7 and alters functional properties of late endocytic compartments. Mol Biol Cell 16:5480–5492
Loewen CJ, Roy A, Levine TP (2003) A conserved ER targeting motif in three families of lipid binding proteins and in Opi1p binds VAP. EMBO J 22:2025–2035
Olkkonen VM, Levine TP (2004) Oxysterol binding proteins: in more than one place at one time? Biochem Cell Biol 82:87–98
Levine T, Loewen C (2006) Inter-organelle membrane contact sites: through a glass, darkly. Curr Opin Cell Biol 18:371–378
Johansson M, Rocha N, Zwart W, Jordens I, Janssen L, Kuijl C, Olkkonen VM, Neefjes J (2007) Activation of endosomal dynein motors by stepwise assembly of Rab7-RILP-p150Glued, ORP1L, and the receptor betalll spectrin. J Cell Biol 176:459–471
Jordens I, Fernandez-Borja M, Marsman M, Dusseljee S, Janssen L, Calafat J, Janssen H, Wubbolts R, Neefjes J (2001) The Rab7 effector protein RILP controls lysosomal transport by inducing the recruitment of dynein–dynactin motors. Curr Biol 11:1680–1685
Cantalupo G, Alifano P, Roberti V, Bruni CB, Bucci C (2001) Rab-interacting lysosomal protein (RILP): the Rab7 effector required for transport to lysosomes. EMBO J 20:683–693
Rocha N, Kuijl C, van der Kant R, Janssen L, Houben D, Janssen H, Zwart W, Neefjes J (2009) Cholesterol sensor ORP1L contacts the ER protein VAP to control Rab7-RILP-p150 Glued and late endosome positioning. J Cell Biol 185:1209–1225
Johansson M, Olkkonen VM (2005) Assays for interaction between Rab7 and oxysterol binding protein related protein 1L (ORP1L). Methods Enzymol 403:743–758
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Im YJ, Raychaudhuri S, Prinz WA, Hurley JH (2005) Structural mechanism for sterol sensing and transport by OSBP-related proteins. Nature 437:154–158
Berman H, Henrick K, Nakamura H (2003) Announcing the worldwide Protein Data Bank. Nat Struct Biol 10:980
Hynynen R, Suchanek M, Spandl J, Back N, Thiele C, Olkkonen VM (2009) OSBP-related protein 2 is a sterol receptor on lipid droplets that regulates the metabolism of neutral lipids. J Lipid Res 50:1305–1315
Ngo M, Ridgway ND (2009) Oxysterol binding protein-related Protein 9 (ORP9) is a cholesterol transfer protein that regulates Golgi structure and function. Mol Biol Cell 20:1388–1399
Basu SK, Goldstein JL, Anderson GW, Brown MS (1976) Degradation of cationized low density lipoprotein and regulation of cholesterol metabolism in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:3178–3182
Brown MS, Dana SE, Goldstein JL (1975) Receptor-dependent hydrolysis of cholesteryl esters contained in plasma low density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:2925–2929
Perttilä J, Merikanto K, Naukkarinen J, Surakka I, Martin NW, Tanhuanpää K, Grimard V, Taskinen MR, Thiele C, Salomaa V, Jula A, Perola M, Virtanen I, Peltonen L, Olkkonen VM (2009) OSBPL10, a novel candidate gene for high triglyceride trait in dyslipidemic Finnish subjects, regulates cellular lipid metabolism. J Mol Med 87:825–835
Yan D, Mäyränpää MI, Wong J, Perttilä J, Lehto M, Jauhiainen M, Kovanen PT, Ehnholm C, Brown AJ, Olkkonen VM (2008) OSBP-related protein 8 (ORP8) suppresses ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux from macrophages. J Biol Chem 283:332–340
Suchanek M, Hynynen R, Wohlfahrt G, Lehto M, Johansson M, Saarinen H, Radzikowska A, Thiele C, Olkkonen VM (2007) The mammalian oxysterol-binding protein-related proteins (ORPs) bind 25-hydroxycholesterol in an evolutionarily conserved pocket. Biochem J 405:473–480
Yan D, Jauhiainen M, Hildebrand RB, Willems van Dijk K, Van Berkel TJ, Ehnholm C, Van Eck M, Olkkonen VM (2007) Expression of human OSBP-related protein 1L in macrophages enhances atherosclerotic lesion development in LDL receptor-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:1618–1624
Xu Y, Liu Y, Ridgway ND, McMaster CR (2001) Novel members of the human oxysterol-binding protein family bind phospholipids and regulate vesicle transport. J Biol Chem 276:18407–18414
Wyles JP, Perry RJ, Ridgway ND (2007) Characterization of the sterol-binding domain of oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP)-related protein 4 reveals a novel role in vimentin organization. Exp Cell Res 313:1426–1437
Brown CL, Maier KC, Stauber T, Ginkel LM, Wordeman L, Vernos I, Schroer TA (2005) Kinesin-2 is a motor for late endosomes and lysosomes. Traffic 6:1114–1124
Garcia-Cruset S, Carpenter KL, Guardiola F, Stein BK, Mitchinson MJ (2001) Oxysterol profiles of normal human arteries, fatty streaks and advanced lesions. Free Radic Res 35:31–41
Maor I, Kaplan M, Hayek T, Vaya J, Hoffman A, Aviram M (2000) Oxidized monocyte-derived macrophages in aortic atherosclerotic lesion from apolipoprotein E-deficient mice and from human carotid artery contain lipid peroxides and oxysterols. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 269:775–780
Vaya J, Aviram M, Mahmood S, Hayek T, Grenadir E, Hoffman A, Milo S (2001) Selective distribution of oxysterols in atherosclerotic lesions and human plasma lipoproteins. Free Radic Res 34:485–497
Laitinen S, Olkkonen VM, Ehnholm C, Ikonen E (1999) Family of human oxysterol binding protein (OSBP) homologues. A novel member implicated in brain sterol metabolism. J. Lipid Res 40:2204–2211
Björkhem I (2007) Rediscovery of cerebrosterol. Lipids 42:5–14
Raychaudhuri S, Im YJ, Hurley JH, Prinz WA (2006) Nonvesicular sterol movement from plasma membrane to ER requires oxysterol-binding protein-related proteins and phosphoinositides. J Cell Biol 173:107–119
Brown AJ, Jessup W (1999) Oxysterols and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 142:1–28
Lebrand C, Corti M, Goodson H, Cosson P, Cavalli V, Mayran N, Faure J, Gruenberg J (2002) Late endosome motility depends on lipids via the small GTPase Rab7. EMBO J 21:1289–1300
Eden ER, White IJ, Tsapara A, Futter CE (2010) Membrane contacts between endosomes and ER provide sites for PTP1B-epidermal growth factor receptor interaction. Nat Cell Biol 12:267–272
Schulz TA, Choi MG, Raychaudhuri S, Mears JA, Ghirlando R, Hinshaw JE, Prinz WA (2009) Lipid-regulated sterol transfer between closely apposed membranes by oxysterol-binding protein homologues. J Cell Biol 187:889–903
Hynynen R, Laitinen S, Käkelä R, Tanhuanpää K, Lusa S, Ehnholm C, Somerharju P, Ikonen E, Olkkonen VM (2005) Overexpression of OSBP-related protein 2 (ORP2) induces changes in cellular cholesterol metabolism and enhances endocytosis. Biochem J 390:273–283
Yvan-Charvet L, Wang N, Tall AR (2010) Role of HDL, ABCA1, and ABCG1 transporters in cholesterol efflux and immune responses. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30:139–143
Chen W, Sun Y, Welch C, Gorelik A, Leventhal AR, Tabas I, Tall AR (2001) Preferential ATP-binding cassette transporter A1-mediated cholesterol efflux from late endosomes/lysosomes. J Biol Chem 276:43564–43569
Azuma Y, Takada M, Shin HW, Kioka N, Nakayama K, Ueda K (2009) Retroendocytosis pathway of ABCA1/apoA-I contributes to HDL formation. Genes Cells 14:191–204
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Lea Puhakka, Seija Puomilahti and Pirjo Ranta for skilled technical assistance, Jaakko Ilola for skilled assistance in endosome motility quantitation, and to Drs. Matti Jauhiainen and Marianna Maranghi for the lipoprotein preparations. Dr. Jacques Neefjes (The Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam) is thanked for kindly providing the GFP-RILP cDNA construct. This study was supported by the Minerva Foundation (Helsinki), the Sigrid Juselius Foundation, the Academy of Finland (grant 121457 to V.M.O. and 131429 to E.I.), the Finnish Foundation for Cardiovascular Research, the Magnus Ehrnrooth Foundation, the European Union FP7 (LipidomicNet, agreement no. 202272), the Finnish Concordia Fund (T.V.), and the Finnish Atherosclerosis Society (T.V.). Terhi Vihervaara is a member of Helsinki Biomedical Graduate School. Riikka-Liisa Uronen is a member of Helsinki Graduate School in Biotechnology and Molecular Biology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
18_2010_470_MOESM2_ESM.mpeg
Supplemental video 1. Motility of LE/lysosomes in control transfected cells. LEs were labeled by overnight internalization of Alexa568-dextran in HeLa cells transfected with empty GFP vector. Cells were imaged with live cell confocal microscope by taking 1 frame/second for a total of 1 minute. (MPEG 476 kb)
18_2010_470_MOESM3_ESM.mpeg
Supplemental video 2. Motility of LE/lysosomes in cells overexpressing WT ORP1L. LEs were labeled by overnight internalization of Alexa568-dextran in HeLa cells transfected with GFP-ORP1L. Cells were imaged with live cell confocal microscope by taking 1 frame/second for a total of 1 minute. (MPEG 936 kb)
18_2010_470_MOESM4_ESM.mpeg
Supplemental video 3. Motility of LE/lysosomes in cells overexpressing ORP1L Δ560-563. LEs were labeled by overnight internalization of Alexa568-dextran in HeLa cells transfected with GFP-ORP1L Δ560-563. Cells were imaged with live cell confocal microscope by taking 1 frame/second for a total of 1 minute. (MPEG 968 kb)
18_2010_470_MOESM5_ESM.mpeg
Supplemental video 4. Motility of LE/lysosomes in cells overexpressing the double mutant ORP1L Δ560-563 mFFAT. LEs were labeled by overnight internalization of Alexa568-dextran in HeLa cells transfected with GFP-ORP1L Δ560-563 mFFAT. Cells were imaged with live cell confocal microscope by taking 1 frame/second for a total of 1 minute. (MPEG 472 kb)
18_2010_470_MOESM6_ESM.mpeg
Supplemental video 5. Motility of LE/lysosomes in cells overexpressing ORP1L mFFAT. LEs were labeled by overnight internalization of Alexa568-dextran in HeLa cells transfected with GFP-ORP1L mFFAT. Cells were imaged with live cell confocal microscope by taking 1 frame/second for a total of 1 minute. (MPEG 492 kb)
18_2010_470_MOESM7_ESM.mpeg
Supplemental video 6. Motility of LE/lysosomes in control macrophage. LEs were labeled by internalization of DiI-acLDL in RAW264.7 cells treated with non-targeting shRNA encoding lentivirus. Cells were imaged with live cell confocal microscope by taking 1 frame/second for a total of 1 minute. (MPEG 1110 kb)
18_2010_470_MOESM8_ESM.mpeg
Supplemental video 7. Motility of LE/lysosomes in ORP1L silenced macrophage. LEs were labeled by internalization of DiI-acLDL in RAW264.7 cells treated with ORP1L specific shRNA (shORP1L.1) encoding lentivirus. Cells were imaged with live cell confocal microscope by taking 1 frame/second for a total of 1 minute. (MPEG 1110 kb)
18_2010_470_MOESM9_ESM.mpeg
Supplemental video 8. Motility of LE/lysosomes in ORP1L silenced macrophage. LEs were labeled by internalization of DiI-acLDL in RAW264.7 cells treated with ORP1L specific shRNA (shORP1L.2) encoding lentivirus. Cells were imaged with live cell confocal microscope by taking 1 frame/second for a total of 1 minute. (MPEG 1112 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vihervaara, T., Uronen, RL., Wohlfahrt, G. et al. Sterol binding by OSBP-related protein 1L regulates late endosome motility and function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68, 537–551 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0470-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0470-z