Abstract.
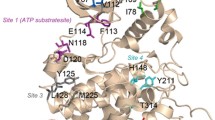
Within the last decade, 40 crystal structures corresponding to protein kinase CK2 (former name ‘casein kinase 2’), to its catalytic subunit CK2α and to its regulatory subunit CK2β were published. Together they provide a valuable, yet by far not complete basis to rationalize the biochemical features of the enzyme, such as its constitutive activity, acidophilic substrate specificity, dual-cosubstrate specificity and its heterotetrameric quarternary structure. Comprehensive sets of structural superimpositions reveal that both CK2α and CK2β are relatively rigid molecules. In CK2β the critical region of CK2α recruitment is pre-formed in the unbound state. In CK2α the activation segment – a key element of protein kinase regulation – adapts invariably the typical conformation of the active enzymes. Recent structures of human CK2α revealed a surprising plasticity in the ATP-binding region, suggesting an alternative mode of activity control.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0128-x.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niefind, K., Raaf, J. & Issinger, OG. Protein Kinase CK2 in Health and Disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 1800–1816 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-9149-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-9149-8