Abstract
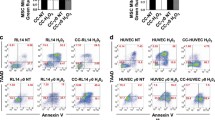
Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) home to injured tissues and have regenerative capacity. In this study, we have investigated in vitro the influence of apoptotic and necrotic cell death, thus distinct types of tissue damage, on MSC migration. Concordant with an increased overall motility, MSC migrated towards apoptotic, but not vital or necrotic neuronal and cardiac cells. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) was expressed by the apoptotic cells only. MSC, in contrast, revealed expression of the HGF-receptor, c-Met. Blocking HGF bioactivity resulted in significant reduction of MSC migration. Moreover, recombinant HGF attracted MSC in a dose-dependent manner. Thus, apoptosis initiates chemoattraction of MSC via the HGF/c-Met axis, thereby linking tissue damage to the recruitment of cells with regenerative potential.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR (1999) Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284:143–147
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A, Prockop D, Horwitz E (2006) Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The international society for cellular therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 8:315–317
Makino S, Fukuda K, Miyoshi S, Konishi F, Kodama H, Pan J, Sano M, Takahashi T, Hori S, Abe H, Hata J, Umezawa A, Ogawa S (1999) Cardiomyocytes can be generated from marrow stromal cells in vitro. J Clin Invest 103:697–705
Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, Black IB (2000) Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res 61:364–370
Sato Y, Araki H, Kato J, Nakamura K, Kawano Y, Kobune M, Sato T, Miyanishi K, Takayama T, Takahashi M, Takimoto R, Iyama S, Matsunaga T, Ohtani S, Matsuura A, Hamada H, Niitsu Y (2005) Human mesenchymal stem cells xenografted directly to rat liver are differentiated into human hepatocytes without fusion. Blood 106:756–763
Phinney DG, Prockop DJ (2007) Concise review: mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells: the state of transdifferentiation and modes of tissue repair—current views. Stem Cells 25:2896–2902
Uccelli A, Moretta L, Pistoia V (2008) Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 9:726–736
Dazzi F, Ramasamy R, Glennie S, Jones SP, Roberts I (2006) The role of mesenchymal stem cells in haemopoiesis. Blood Rev 20:161–171
Ball LM, Bernardo ME, Roelofs H, Lankester A, Cometa A, Egeler RM, Locatelli F, Fibbe WE (2007) Cotransplantation of ex vivo expanded mesenchymal stem cells accelerates lymphocyte recovery and may reduce the risk of graft failure in haploidentical hematopoietic stem–cell transplantation. Blood 110:2764–2767
Le Blanc K, Frassoni F, Ball L, Locatelli F, Roelofs H, Lewis I, Lanino E, Sundberg B, Bernardo ME, Remberger M, Dini G, Egeler RM, Bacigalupo A, Fibbe W, Ringden O (2008) Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II study. Lancet 371:1579–1586
von Bonin M, Stolzel F, Goedecke A, Richter K, Wuschek N, Holig K, Platzbecker U, Illmer T, Schaich M, Schetelig J, Kiani A, Ordemann R, Ehninger G, Schmitz M, Bornhauser M (2009) Treatment of refractory acute GVHD with third-party MSC expanded in platelet lysate-containing medium. Bone Marrow Transplant 43:245–251
Chamberlain G, Fox J, Ashton B, Middleton J (2007) Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells: their phenotype, differentiation capacity, immunological features, and potential for homing. Stem Cells 25:2739–2749
Chapel A, Bertho JM, Bensidhoum M, Fouillard L, Young RG, Frick J, Demarquay C, Cuvelier F, Mathieu E, Trompier F, Dudoignon N, Germain C, Mazurier C, Aigueperse J, Borneman J, Gorin NC, Gourmelon P, Thierry D (2003) Mesenchymal stem cells home to injured tissues when co-infused with hematopoietic cells to treat a radiation-induced multi-organ failure syndrome. J Gene Med 5:1028–1038
Ma J, Ge J, Zhang S, Sun A, Shen J, Chen L, Wang K, Zou Y (2005) Time course of myocardial stromal cell-derived factor 1 expression and beneficial effects of intravenously administered bone marrow stem cells in rats with experimental myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol 100:217–223
Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, Zhang Z, Lu D, Lu M, Chopp M (2001) Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 32:1005–1011
Herrera MB, Bussolati B, Bruno S, Morando L, Mauriello-Romanazzi G, Sanavio F, Stamenkovic I, Biancone L, Camussi G (2007) Exogenous mesenchymal stem cells localize to the kidney by means of CD44 following acute tubular injury. Kidney Int 72:430–441
Wu GD, Nolta JA, Jin YS, Barr ML, Yu H, Starnes VA, Cramer DV (2003) Migration of mesenchymal stem cells to heart allografts during chronic rejection. Transplantation 75:679–685
Spaeth E, Klopp A, Dembinski J, Andreeff M, Marini F (2008) Inflammation and tumor microenvironments: defining the migratory itinerary of mesenchymal stem cells. Gene Ther 15:730–738
Neuss S, Becher E, Woltje M, Tietze L, Jahnen-Dechent W (2004) Functional expression of HGF and HGF receptor/c-met in adult human mesenchymal stem cells suggests a role in cell mobilization, tissue repair, and wound healing. Stem Cells 22:405–414
Honda S, Kagoshima M, Wanaka A, Tohyama M, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T (1995) Localization and functional coupling of HGF and c-Met/HGF receptor in rat brain: implication as neurotrophic factor. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 32:197–210
Ono K, Matsumori A, Shioi T, Furukawa Y, Sasayama S (1997) Enhanced expression of hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met by myocardial ischemia and reperfusion in a rat model. Circulation 95:2552–2558
Miyazawa K, Shimomura T, Naka D, Kitamura N (1994) Proteolytic activation of hepatocyte growth factor in response to tissue injury. J Biol Chem 269:8966–8970
Miyazawa T, Matsumoto K, Ohmichi H, Katoh H, Yamashima T, Nakamura T (1998) Protection of hippocampal neurons from ischemia-induced delayed neuronal death by hepatocyte growth factor: a novel neurotrophic factor. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 18:345–348
Nakamura T, Mizuno S, Matsumoto K, Sawa Y, Matsuda H, Nakamura T (2000) Myocardial protection from ischemia/reperfusion injury by endogenous and exogenous HGF. J Clin Invest 106:1511–1519
Nesselmann C, Ma N, Bieback K, Wagner W, Ho A, Konttinen YT, Zhang H, Hinescu ME, Steinhoff G (2008) Mesenchymal stem cells and cardiac repair. J Cell Mol Med 12:1795–1810
Dharmasaroja P (2009) Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of ischemic stroke. J Clin Neurosci 16:12–20
Davis JB, Maher P (1994) Protein kinase C activation inhibits glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in a neuronal cell line. Brain Res 652:169–173
White SM, Constantin PE, Claycomb WC (2004) Cardiac physiology at the cellular level: use of cultured HL-1 cardiomyocytes for studies of cardiac muscle cell structure and function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H823–H829
Trapp T, Kogler G, El-Khattouti A, Sorg RV, Besselmann M, Focking M, Buhrle CP, Trompeter I, Fischer JC, Wernet P (2008) Hepatocyte growth factor/c-met-axis mediated tropism of cord blood derived unrestricted somatic stem cells for neuronal injury. J Biol Chem 283:32244–32253
Laevsky G, Knecht DA (2001) Under-agarose folate chemotaxis of Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae in permissive and mechanically inhibited conditions. Biotechniques 31:1140–1142
Sato T, Yoshinouchi T, Sakamoto T, Fujieda H, Murao S, Sato H, Kobayashi H, Ohe T (1997) Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF): a new biochemical marker for acute myocardial infarction. Heart Vessels 12:241–246
Aoki M, Morishita R, Taniyama Y, Kida I, Moriguchi A, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, Kaneda Y, Higaki J, Ogihara T (2000) Angiogenesis induced by hepatocyte growth factor in non-infarcted myocardium and infarcted myocardium: up-regulation of essential transcription factor for angiogenesis, ets. Gene Ther 7:417–427
Date I, Takagi N, Takagi K, Kago T, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, Takeo S (2004) Hepatocyte growth factor attenuates cerebral ischemia-induced learning dysfunction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 319:1152–1158
Forte G, Minieri M, Cossa P, Antenucci D, Sala M, Gnocchi V, Fiaccavento R, Carotenuto F, De Vito P, Baldini PM, Prat M, Di Nardo P (2006) Hepatocyte growth factor effects on mesenchymal stem cells: proliferation, migration, and differentiation. Stem Cells 24:23–33
Zhu G, Huang L, Song M, Yu Z, Wu X, Zhao X, Jin J, Zhao G, Chen J, Yu S (2008) Over-expression of hepatocyte growth factor in smooth muscle cells regulates endothelial progenitor cells differentiation, migration and proliferation. Int J Cardiol. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2008.10.042
Heese O, Disko A, Zirkel D, Westphal M, Lamszus K (2005) Neural stem cell migration toward gliomas in vitro. Neuro Oncol 7:476–484
Rosova I, Dao M, Capoccia B, Link D, Nolta JA (2008) Hypoxic preconditioning results in increased motility and improved therapeutic potential of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 26:2173–2182
Skoberne M, Beignon AS, Larsson M, Bhardwaj N (2005) Apoptotic cells at the crossroads of tolerance and immunity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 289:259–292
Okunishi K, Dohi M, Nakagome K, Tanaka R, Mizuno S, Matsumoto K, Miyazaki J, Nakamura T, Yamamoto K (2005) A novel role of hepatocyte growth factor as an immune regulator through suppressing dendritic cell function. J Immunol 175:4745–4753
Meng E, Guo Z, Wang H, Jin J, Wang J, Wu C, Wang L (2008) High mobility group box 1 protein inhibits the proliferation of human mesenchymal stem cells and promotes their migration and differentiation along osteoblastic pathway. Stem Cells Dev 17:805–813
Raucci A, Palumbo R, Bianchi ME (2007) HMGB1: a signal of necrosis. Autoimmunity 40:285–289
Abbott JD, Huang Y, Liu D, Hickey R, Krause DS, Giordano FJ (2004) Stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha plays a critical role in stem cell recruitment to the heart after myocardial infarction but is not sufficient to induce homing in the absence of injury. Circulation 110:3300–3305
Ji JF, He BP, Dheen ST, Tay SS (2004) Interactions of chemokines and chemokine receptors mediate the migration of mesenchymal stem cells to the impaired site in the brain after hypoglossal nerve injury. Stem Cells 22:415–427
Ip JE, Wu Y, Huang J, Zhang L, Pratt RE, Dzau VJ (2007) Mesenchymal stem cells use integrin beta1 not CXC chemokine receptor 4 for myocardial migration and engraftment. Mol Biol Cell 18:2873–2882
Sordi V, Malosio ML, Marchesi F, Mercalli A, Melzi R, Giordano T, Belmonte N, Ferrari G, Leone BE, Bertuzzi F, Zerbini G, Allavena P, Bonifacio E, Piemonti L (2005) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells express a restricted set of functionally active chemokine receptors capable of promoting migration to pancreatic islets. Blood 106:419–427
Sackstein R, Merzaban JS, Cain DW, Dagia NM, Spencer JA, Lin CP, Wohlgemuth R (2008) Ex vivo glycan engineering of CD44 programs human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cell trafficking to bone. Nat Med 14:181–187
Honczarenko M, Le Y, Swierkowski M, Ghiran I, Glodek AM, Silberstein LE (2006) Human bone marrow stromal cells express a distinct set of biologically functional chemokine receptors. Stem Cells 24:1030–1041
Li G, Zhang XA, Wang H, Wang X, Meng CL, Chan CY, Yew DT, Tsang KS, Li K, Tsai SN, Ngai SM, Han ZC, Lin MC, He ML, Kung HF (2009) Comparative proteomic analysis of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human bone marrow, umbilical cord, and placenta: implication in the migration. Proteomics 9:20–30
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by a grant from the German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF, 01GN0951). The authors would like to thank Ms. Nathalie Walter and Heike Löffler for excellent technical assistance. We are grateful to Dr. A. Methner (Department of Neurology, Heinrich Heine University Medical Center, Düsseldorf, Germany) for HT-22 cells and to Prof. Dr. A. Gödecke (Institute of Heart and Circulation Physiology, Heinrich Heine University Medical Center, Düsseldorf, Germany) for HL-1 cells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vogel, S., Trapp, T., Börger, V. et al. Hepatocyte growth factor-mediated attraction of mesenchymal stem cells for apoptotic neuronal and cardiomyocytic cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 67, 295–303 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0183-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0183-3