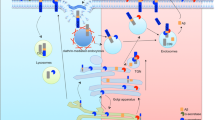
Abstract
The Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein (APP) belongs to a conserved gene family that also includes the mammalian APLP1 and APLP2, the Drosophila APPL, and the C. elegans APL-1. The biological function of APP is still not fully clear. However, it is known that the APP family proteins have redundant and partly overlapping functions, which demonstrates the importance of studying all APP family members to gain a more complete picture. When APP was first cloned, it was speculated that it could function as a receptor. This theory has been further substantiated by studies showing that APP and its homologues bind both extracellular ligands and intracellular adaptor proteins. The APP family proteins undergo regulated intramembrane proteolysis (RIP), generating secreted and cytoplasmic fragments that have been ascribed different functions. In this review, we will discuss the APP family with focus on biological functions, binding partners, and regulated processing.






Similar content being viewed by others

References
Kang J, Lemaire HG, Unterbeck A, Salbaum JM, Masters CL, Grzeschik KH, Multhaup G, Beyreuther K, Müller-Hill B (1987) The precursor of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature 325:733–736
Wasco W, Bupp K, Magendantz M, Gusella JF, Tanzi RE, Solomon F (1992) Identification of a mouse brain cDNA that encodes a protein related to the Alzheimer disease-associated amyloid beta protein precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10758–10762
Wasco W, Gurubhagavatula S, Paradis MD, Romano DM, Sisodia SS, Hyman BT, Neve RL, Tanzi RE (1993) Isolation and characterization of APLP2 encoding a homologue of the Alzheimer’s associated amyloid beta protein precursor. Nat Genet 5:95–100
Rosen DR, Martin-Morris L, Luo LQ, White K (1989) A Drosophila gene encoding a protein resembling the human β-amyloid protein precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2478–2482
Daigle I, Li C (1993) apl-1, a Caenorhabditis elegans gene encoding a protein related to the human β-amyloid protein precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:12045–12049
Glenner GG, Wong CW, Quaranta V, Eanes ED (1984) The amyloid deposits in Alzheimer’s disease: their nature and pathogenesis. Appl Pathol 2:357–369
Masters CL, Simms G, Weinman NA, Multhaup G, McDonald BL, Beyreuther K (1985) Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4245–4249
Burdick D, Soreghan B, Kwon M, Kosmoski J, Knauer M, Henschen A, Yates J, Cotman C, Glabe C (1992) Assembly and aggregation properties of synthetic Alzheimer’s A4/β amyloid peptide analogs. J Biol Chem 267:546–554
Jarrett JT, Berger EP, Lansbury PT Jr (1993) The carboxy terminus of the β amyloid protein is critical for the seeding of amyloid formation: implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochemistry 32:4693–4697
Esler WP, Wolfe MS (2001) A portrait of Alzheimer secretases—new features and familiar faces. Science 293:1449–1454
Hardy JA, Higgins GA (1992) Alzheimer’s disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science 256:184–185
Mann DM, Yates PO, Marcyniuk B (1984) Alzheimer’s presenile dementia, senile dementia of Alzheimer type and Down’s syndrome in middle age form an age related continuum of pathological changes. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 10:185–207
Dyrks T, Weidemann A, Multhaup G, Salbaum JM, Lemaire HG, Kang J, Müller-Hill B, Masters CL, Beyreuther K (1988) Identification, transmembrane orientation and biogenesis of the amyloid A4 precursor of Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO J 7:949–957
Gralle M, Ferreira ST (2007) Structure and functions of the human amyloid precursor protein: the whole is more than the sum of its parts. Prog Neurobiol 82:11–32
Paliga K, Peraus G, Kreger S, Dürrwang U, Hesse L, Multhaup G, Masters CL, Beyreuther K, Weidemann A (1997) Human amyloid precursor-like protein 1—cDNA cloning, ectopic expression in COS-7 cells and identification of soluble forms in the cerebrospinal fluid. Eur J Biochem 250:354–363
Slunt HH, Thinakaran G, Von Koch C, Lo AC, Tanzi RE, Sisodia SS (1994) Expression of a ubiquitous, cross-reactive homologue of the mouse β-amyloid precursor protein (APP). J Biol Chem 269:2637–2644
Lorent K, Overbergh L, Moechars D, De Strooper B, Van Leuven F, Van den Berghe H (1995) Expression in mouse embryos and in adult mouse brain of three members of the amyloid precursor protein family, of the α2-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein and of its ligands apolipoprotein E, lipoprotein lipase, α2-macroglobulin and the 40,000 molecular weight receptor-associated protein. Neuroscience 65:1009–1025
Hornsten A, Lieberthal J, Fadia S, Malins R, Ha L, Xu X, Daigle I, Markowitz M, O’Connor G, Plasterk R, Li C (2007) APL-1, a Caenorhabditis elegans protein related to the human β-amyloid precursor protein, is essential for viability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:1971–1976
Luo L, Martin-Morris L, White K (1990) Identification, secretion, and neural expression of APPL, a Drosophila protein similar to human amyloid protein precursor. J Neurosci 10:3849–3861
Cao X, Südhof TC (2001) A transcriptionally active complex of APP with Fe65 and histone acetyltransferase Tip60. Science 293:115–120
Sastre M, Steiner H, Fuchs K, Capell A, Multhaup G, Condron MM, Teplow DB, Haass C (2001) Presenilin-dependent γ-secretase processing of β-amyloid precursor protein at a site corresponding to the S3 cleavage of Notch. EMBO Rep 2:835–841
Yu C, Kim SH, Ikeuchi T, Xu H, Gasparini L, Wang R, Sisodia SS (2001) Characterization of a presenilin-mediated amyloid precursor protein carboxyl-terminal fragment γ. Evidence for distinct mechanisms involved in γ-secretase processing of the APP and Notch1 transmembrane domains. J Biol Chem 276:43756–43760
Weidemann A, Eggert S, Reinhard FB, Vogel M, Paliga K, Baier G, Masters CL, Beyreuther K, Evin G (2002) A novel ε-cleavage within the transmembrane domain of the Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein demonstrates homology with Notch processing. Biochemistry 41:2825–2835
Zhao G, Mao G, Tan J, Dong Y, Cui MZ, Kim SH, Xu X (2004) Identification of a new presenilin-dependent ζ-cleavage site within the transmembrane domain of amyloid precursor protein. J Biol Chem 279:50647–50650
Esch FS, Keim PS, Beattie EC, Blacher RW, Culwell AR, Oltersdorf T, McClure D, Ward PJ (1990) Cleavage of amyloid-β peptide during constitutive processing of its precursor. Science 248:1122–1124
Sisodia SS, Koo EH, Beyreuther K, Unterbeck A, Price DL (1990) Evidence that β-amyloid protein in Alzheimer’s disease is not derived by normal processing. Science 248:492–495
Roberts SB, Ripellino JA, Ingalls KM, Robakis NK, Felsenstein KM (1994) Non-amyloidogenic cleavage of the β-amyloid precursor protein by an integral membrane metalloendopeptidase. J Biol Chem 269:3111–3116
Howard L, Lu X, Mitchell S, Griffiths S, Glynn P (1996) Molecular cloning of MADM: a catalytically active mammalian disintegrin-metalloprotease expressed in various cell types. Biochem J 317:45–50
Hussain I, Powell D, Howlett DR, Tew DG, Meek TD, Chapman C, Gloger IS, Murphy KE, Southan CD, Ryan DM, Smith TS, Simmons DL, Walsh FS, Dingwall C, Christie G (1999) Identification of a novel aspartic protease (Asp 2) as β-secretase. Mol Cell Neurosci 14:419–427
Sinha S, Anderson JP, Barbour R, Basi GS, Caccavello R, Davis D, Doan M, Dovey HF, Frigon N, Hong J, Jacobson-Croak K, Jewett N, Keim P, Knops J, Lieberburg I, Power M, Tan H, Tatsuno G, Tung J, Schenk D, Seubert P, Suomensaari SM, Wang S, Walker D, Zhao J, McConlogue L, John V (1999) Purification and cloning of amyloid precursor protein β-secretase from human brain. Nature 402:537–540
Vassar R, Bennett BD, Babu-Khan S, Kahn S, Mendiaz EA, Denis P, Teplow DB, Ross S, Amarante P, Loeloff R, Luo Y, Fisher S, Fuller J, Edenson S, Lile J, Jarosinski MA, Biere AL, Curran E, Burgess T, Louis JC, Collins F, Treanor J, Rogers G, Citron M (1999) β-secretase cleavage of Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein by the transmembrane aspartic protease BACE. Science 286:735–741
Yan R, Bienkowski MJ, Shuck ME, Miao H, Tory MC, Pauley AM, Brashier JR, Stratman NC, Mathews WR, Buhl AE, Carter DB, Tomasselli AG, Parodi LA, Heinrikson RL, Gurney ME (1999) Membrane-anchored aspartyl protease with Alzheimer’s disease β-secretase activity. Nature 402:533–537
Luo Y, Bolon B, Kahn S, Bennett BD, Babu-Khan S, Denis P, Fan W, Kha H, Zhang J, Gong Y, Martin L, Louis JC, Yan Q, Richards WG, Citron M, Vassar R (2001) Mice deficient in BACE1, the Alzheimer’s β-secretase, have normal phenotype and abolished β-amyloid generation. Nat Neurosci 4:231–232
Roberds SL, Anderson J, Basi G, Bienkowski MJ, Branstetter DG, Chen KS, Freedman SB, Frigon NL, Games D, Hu K, Johnson-Wood K, Kappenman KE, Kawabe TT, Kola I, Kuehn R, Lee M, Liu W, Motter R, Nichols NF, Power M, Robertson DW, Schenk D, Schoor M, Shopp GM, Shuck ME, Sinha S, Svensson KA, Tatsuno G, Tintrup H, Wijsman J, Wright S, McConlogue L (2001) BACE knockout mice are healthy despite lacking the primary beta-secretase activity in brain: implications for Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics. Hum Mol Genet 10:1317–1324
Ehehalt R, Keller P, Haass C, Thiele C, Simons K (2003) Amyloidogenic processing of the Alzheimer β-amyloid precursor protein depends on lipid rafts. J Cell Biol 160:113–123
Goutte C, Hepler W, Mickey KM, Priess JR (2000) aph-2 encodes a novel extracellular protein required for GLP-1-mediated signaling. Development 127:2481–2492
Yu G, Nishimura M, Arawaka S, Levitan D, Zhang L, Tandon A, Song YQ, Rogaeva E, Chen F, Kawarai T, Supala A, Levesque L, Yu H, Yang DS, Holmes E, Milman P, Liang Y, Zhang DM, Xu DH, Sato C, Rogaev E, Smith M, Janus C, Zhang Y, Aebersold R, Farrer LS, Sorbi S, Bruni A, Fraser P, St George-Hyslop P (2000) Nicastrin modulates presenilin-mediated notch/glp-1 signal transduction and βAPP processing. Nature 407:48–54
Francis R, McGrath G, Zhang J, Ruddy DA, Sym M, Apfeld J, Nicoll M, Maxwell M, Hai B, Ellis MC, Parks AL, Xu W, Li J, Gurney M, Myers RL, Himes CS, Hiebsch R, Ruble C, Nye JS, Curtis D (2002) aph-1 and pen-2 are required for Notch pathway signaling, gamma-secretase cleavage of betaAPP, and presenilin protein accumulation. Dev Cell 3:85–97
Edbauer D, Winkler E, Regula JT, Pesold B, Steiner H, Haass C (2003) Reconstitution of γ-secretase activity. Nat Cell Biol 5:486–488
Yu G, Chen F, Levesque G, Nishimura M, Zhang DM, Levesque L, Rogaeva E, Xu D, Liang Y, Duthie M, St George-Hyslop PH, Fraser PE (1998) The presenilin 1 protein is a component of a high molecular weight intracellular complex that contains beta-catenin. J Biol Chem 273:16470–16475
Wolfe MS, Xia W, Ostaszewski BL, Diehl TS, Kimberly WT, Selkoe DJ (1999) Two transmembrane aspartates in presenilin-1 required for presenilin endoproteolysis and γ-secretase activity. Nature 398:513–517
Shah S, Lee SF, Tabuchi K, Hao YH, Yu C, LaPlant Q, Ball H, Dann CE, Sudhof T, Yu G (2005) Nicastrin functions as a gamma-secretase substrate receptor. Cell 122:435–447
Verdile G, Gandy SE, Martins RN (2006) The role of presenilin and its interacting proteins in the biogenesis of Alzheimer’s beta amyloid. Neurochem Res 32:609–623
Wolfe MS (2006) The γ-secretase complex: membrane-embedded proteolytic ensemble. Biochemistry 45:7931–7939
Naruse S, Thinakaran G, Luo JJ, Kusiak JW, Tomita T, Iwatsubo T, Qian X, Ginty DD, Price DL, Borchelt DR, Wong PC, Sisodia SS (1998) Effects of PS1 deficiency on membrane protein trafficking in neurons. Neuron 21:1213–1221
Gu Y, Misonou H, Sato T, Dohmae N, Takio K, Ihara Y (2001) Distinct intramembrane cleavage of the β-amyloid precursor protein family resembling γ-secretase-like cleavage of Notch. J Biol Chem 276:35235–35238
Holback S, Adlerz L, Iverfeldt K (2005) Increased processing of APLP2 and APP with concomitant formation of APP intracellular domains in BDNF and retinoic acid-differentiated human neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem 95:1059–1068
Eggert S, Paliga K, Soba P, Evin G, Masters CL, Weidemann A, Beyreuther K (2004) The proteolytic processing of the amyloid precursor protein gene family members APLP-1 and APLP-2 involves α-, β-, γ-, and ε-like cleavages: modulation of APLP-1 processing by N-glycosylation. J Biol Chem 279:18146–18156
Endres K, Postina R, Schroeder A, Mueller U, Fahrenholz F (2005) Shedding of the amyloid precursor protein-like protein APLP2 by disintegrin-metalloproteinases. FEBS J 272:5808–5820
Rooke J, Pan D, Xu T, Rubin GM (1996) KUZ, a conserved metalloprotease-disintegrin protein with two roles in Drosophila neurogenesis. Science 273:1227–1231
Carmine-Simmen K, Proctor T, Tschäpe J, Poeck B, Triphan T, Strauss R, Kretzschmar D (2008) Neurotoxic effects induced by the Drosophila amyloid-β peptide suggest a conserved toxic function. Neurobiol Dis 33:274–281
Hong CS, Koo EH (1997) Isolation and characterization of Drosophila presenilin homolog. Neuroreport 8:665–668
Boulianne GL, Livine-Bar I, Humphreys JM, Liang Y, Lin C, Rogaev E, George-Hyslop PH (1997) Cloning and characterization of the Drosophila presenilin homologue. Neuroreport 8:1025–1029
Sprecher CA, Grant FJ, Grimm G, O’Hara PJ, Norris F, Norris K, Foster DC (1993) Molecular cloning of the cDNA for a human amyloid precursor protein homolog: evidence for a multigene family. Biochemistry 32:4481–4486
Weidemann A, König Gr, Bunke D, Fischer P, Salbaum JM, Masters CL, Beyreuther K (1989) Identification, biogenesis, and localization of precursors of Alzheimer’s disease A4 amyloid protein. Cell 57:115–126
Lyckman AW, Confaloni AM, Thinakaran G, Sisodia SS, Moya KL (1998) Post-translational processing and turnover kinetics of presynaptically targeted amyloid precursor superfamily proteins in the central nervous system. J Biol Chem 273:11100–11106
Pangalos MN, Shioi J, Robakis NK (1995) Expression of the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans of amyloid precursor (appican) and amyloid precursor-like protein 2. J Neurochem 65:762–769
Thinakaran G, Sisodia SS (1994) Amyloid precursor-like protein 2 (APLP2) is modified by the addition of chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycan at a single site. J Biol Chem 269:22099–22104
Nakagawa K, Kitazume S, Oka R, Maruyama K, Saido TC, Sato Y, Endo T, Hashimoto Y (2006) Sialylation enhances the secretion of neurotoxic amyloid-β peptides. J Neurochem 96:924–933
Zhang YQ, Sarge KD (2008) Sumoylation of amyloid precursor protein negatively regulates Aβ aggregation levels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374:673–678
Gandy S, Czernik AJ, Greengard P (1988) Phosphorylation of Alzheimer disease amyloid precursor peptide by protein kinase C and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:6218–6221
Knops J, Gandy S, Greengard P, Lieberburg I, Sinha S (1993) Serine phosphorylation of the secreted extracellular domain of APP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 197:380–385
Suzuki T, Oishi M, Marshak DR, Czernik AJ, Nairn AC, Greengard P (1994) Cell cycle-dependent regulation of the phosphorylation and metabolism of the Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein. EMBO J 13:1114–1122
Oishi M, Nairn AC, Czernik AJ, Lim GS, Isohara T, Gandy SE, Greengard P, Suzuki T (1997) The cytoplasmic domain of Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein is phosphorylated at Thr654, Ser655, and Thr668 in adult rat brain and cultured cells. Mol Med 3:111–123
Lee MS, Kao SC, Lemere CA, Xia W, Tseng HC, Zhou Y, Neve R, Ahlijanian MK, Tsai LH (2003) APP processing is regulated by cytoplasmic phosphorylation. J Cell Biol 163:83–95
Kimberly WT, Zheng JB, Town T, Flavell RA, Selkoe DJ (2005) Physiological regulation of the beta-amyloid precursor protein signalling domain byc-Jun N-terminal kinase JNK3 during neuronal differentiation. J Neurosci 25:5533–5543
Iijima K, Ando K, Takeda S, Satoh Y, Seki T, Itohara S, Greengard P, Kirino Y, Nairn AC, Suzuki T (2000) Neuron-specific phosphorylation of Alzheimer’s β-amyloid precursor protein by cyclin-dependent kinase 5. J Neurochem 75:1085–1091
Aplin AE, Gibb GM, Jacobsen JS, Gallo JM, Anderton BH (1996) In vitro phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic domain of the amyloid precursor protein by glycogen synthase kinase-3β. J Neurochem 67:699–707
Muresan Z, Muresan V (2005) Coordinated transport of phosphorylated amyloid-β precursor protein and c-Jun NH2 terminal kinase-interacting protein-1. J Cell Biol 171:615–625
Sano Y, Nakaya T, Pedrini S, Takeda S, Iijima-Ando K, Iijima K, Mathews PM, Shigeyoshi I, Gandy S, Suzuki T (2006) Physiological mouse brain Aβ levels are not correlated to the phosphorylation state of threonine-668 of Alzheimer’s APP. PLoS ONE 1:e51
Feyt C, Pierrot N, Tasiaux B, Hees JV, Kienlen-Campard P, Courtoy PJ, Octave JN (2007) Phosphorylation of APP695 at Thr668 decreases γ-cleavage and extracellular Aβ. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 357:1004–1010
Takahashi K, Niidome T, Akaike A, Kihara T, Sugimoto H (2008) Phosphorylation of amyloid protein (APP) at Tyr687 regulates APP processing by α- and γ-secretase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 377:544–549
Suzuki T, Ando K, Isohara T, Oishi M, Lim GS, Satoh Y, Wasco W, Tanzi RE, Nairn AC, Greengard P, Gandy SE, Kirino Y (1997) Phosphorylation of Alzheimer β-amyloid precursor-like proteins. Biochemistry 36:4643–4649
Taru H, Suzuki T (2004) Facilitation of stress-induced phosphorylation of beta-amyloid precursor protein family members by X11-like/Mint2 protein. J Biol Chem 279:21628–21636
Ando K, Iijima K, Elliott JI, Kirino Y, Suzuki T (2001) Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of the interaction of amyloid precursor protein with Fe65 affects the production of β-amyloid. J Biol Chem 276:40353–40361
Pastorino L, Sun A, Lu PJ, Zhou XZ, Balastik M, Finn G, Wulf G, Lim J, Li SH, Li X, Xia W, Nicholson LK, Lu KP (2006) The prolyl isomerase Pin1 regulates amyloid precursor protein processing and amyloid-β production. Nature 440:528–533
Liou YC, Sun A, Ryo A, Zhou XZ, Yu ZX, Huang HK, Uchida T, Bronson R, Bing G, Li X, Hunter T, Lu KP (2003) Role of the isomerase Pin1 in protecting against age-dependent neurododegeneration. Nature 424:556–561
Zheng H, Jiang M, Trumbauer ME, Sirinathsinghji DJ, Hopkins R, Smith DW, Heavens RP, Dawson GR, Boyce S, Conner MW, Stevens KA, Slunt HH, Sisoda SS, Chen HY, Van der Ploeg LH (1995) β-Amyloid precursor protein-deficient mice show reactive gliosis and decreased locomotor activity. Cell 81:525–531
von Koch CS, Zheng H, Chen H, Trumbauer M, Thinakaran G, van der Ploeg LH, Price DL, Sisodia SS (1997) Generation of APLP2 KO mice and early postnatal lethality in APLP2/APP double KO mice. Neurobiol Aging 18:661–669
Heber S, Herms J, Gajic V, Hainfellner J, Aguzzi A, Rülicke T, von Kretzschmar H, von Koch C, Sisodia S, Tremml P, Lipp HP, Wolfer DP, Müller U (2000) Mice with combined gene knock-outs reveal essential and partially redundant functions of amyloid precursor protein family members. J Neurosci 20:7951–7963
Herms J, Anliker B, Heber S, Ring S, Fuhrmann M, Kretzschmar H, Sisodia S, Müller U (2004) Cortical dysplasia resembling human type 2 lissencephaly in mice lacking all three APP family members. EMBO J 23:4106–4115
Schubert D, Jin LW, Saitoh T, Cole G (1989) The regulation of amyloid beta protein precursor secretion and its modulatory role in cell adhesion. Neuron 3:689–694
Narindrasorasak S, Lowery DE, Altman RA, Gonzalez-DeWhitt P, Greenberg B, Kisilevsky R (1992) Characterization of high affinity binding between laminin and Alzheimer’s disease amyloid precursor proteins. Lab Invest 67:643–652
Wang Y, Ha Y (2004) X-ray structure of an antiparallel dimer of the human amyloid precursor protein E2 domain. Mol Cell 15:343–353
Soba P, Eggert S, Wagner K, Zentgraf H, Siehl K, Kreger S, Löwer A, Langer A, Merdes G, Paro R, Masters CL, Müller U, Kins S, Beyreuther K (2005) Homo- and heterodimerization of APP family members promotes intercellular adhesion. EMBO J 24:3624–3634
Kaden D, Munter L, Joshi M, Treiber C, Weise C, Bethge T, Voigt P, Schaefer M, Beyermann M, Reif B, Multhaup G (2008) Homophilic interactions of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) ectodomain are regulated by the loop region and affect β-secretase cleavage of APP. J Biol Chem 283:7271–7279
Small D, Nurcombe V, Reed G, Clarris H, Moir R, Beyreuther K, Masters CL (1994) A heparin-binding domain in the amyloid protein precursor of Alzheimer’s disease is involved in the regulation of neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci 14:2117–2127
Milward EA, Papadopoulos R, Fuller SJ, Moir RD, Small D, Beyreuther K, Masters CL (1992) The amyloid protein precursor of Alzheimer’s disease is a mediator of the effects of nerve growth factor on neurite outgrowth. Neuron 9:129–137
Perez RG, Zheng H, Van der Ploeg LH, Koo EH (1997) The β-amyloid precursor protein of Alzheimer’s disease enhances neuron viability and modulates neuronal polarity. J Neurosci 17:9407–9414
Young-Pearse TL, Chen AC, Chang R, Marquez C, Selkoe DJ (2008) Secreted APP regulates the function of full-length APP in neurite outgrowth through interactions with integrin beta 1. Neural Develop 3:1–13
Li Y, Liu T, Peng Y, Yuan C, Guo A (2004) Specific functions of Drosophilia amyloid precursor-like protein in the development of nervous sydtem and nonneuronal tissues. J Neurobiol 61:343–358
Roch JM, Masliah E, Roch-Levecq AC, Sundsmo MP, Otero DA, Veinbergs I, Saitoh T (1994) Increase of synaptic density and memory retention by a peptide representing the trophic domain of the amyloid β/A4 protein precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:7450–7454
Moya KL, Benowitz LI, Schneider GE, Allinquant B (1994) The amyloid precursor protein is developmentally regulated and correlated with synaptogenesis. Dev Biol 161:597–603
Young-Pearse TL, Bai J, Chang R, Zheng JB, LoTurco JJ, Selkoe DJ (2007) A critical function for beta-amyloid precursor protein in neuronal migration revealed by in utero RNA interference. J Neurosci 27:14459–14469
Ma QH, Futagawa T, Yang WL, Jiang XD, Zeng L, Takeda Y, Xu RX, Bagnard D, Schachner M, Furley AJ, Karagogeos D, Watanabe K, Dawe GS, Xiao ZC (2008) A TAG1-APP signalling pathway through Fe65 negatively modulates neurogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 10:283–294
Leyssen M, Ayaz D, Hebert SS, Reeve S, De Strooper B, Hassan BA (2005) Amyloid precursor protein promotes post-developmental neurite arborization in the Drosophila brain. EMBO J 24:2944–2955
Araki W, Kitaguchi N, Tokushima Y, Ishii K, Aratake H, Shimohama S, Nakamura S, Kimura J (1991) Trophic effect of β-amyloid precursor protein on cerebral cortical neurons in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 181:265–271
Mattson MP, Cheng B, Culwell AR, Esch FS, Lieberburg I, Rydel RE (1993) Evidence for excitoprotective and intraneuronal calcium-regulating roles for secreted forms of the β-amyloid precursor protein. Neuron 10:243–254
Goodman Y, Mattson MP (1994) Secreted forms of beta-amyloid precursor protein protect hippocampal neurons against amyloid beta-peptide-induced oxidative injury. Exp Neurol 128:1–12
Kinoshita A, Whelan CM, Berezovska O, Hyman BT (2002) The γ secretase carboxyl-terminal domain of the amyloid precursor protein induces apoptrosis via Top60 in H4 cells. J Biol Chem 277:28530–28536
Nakayama K, Ohkawara T, Hiratochi M, Koh CS, Nagase H (2008) The intracellular domain of amyloid precursor protein induces neuron-specific apoptosis. Neurosci Lett 44:127–131
Kim HS, Kim EM, Lee JP, Park CH, Kim S, Seo JH, Chang KA, Yu E, Jeong SJ, Chong YH, Suh YH (2003) C-terminal fragments of amyloid precursor protein exert neurotoxicity by inducing glycogen synthase kinase-3β expression. FASEB J 17:1951–1953
Ozaki T, Li Y, Kikuchi H, Tomita T, Iwatsubo T, Nakagawara A (2006) The intracellular domain of the amyloid precursor protein (AICD) enhances the p53-mediated apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 351:57–63
Tang X, Milayavsky M, Goldfinger N, Rotter V (2007) Amyloid-beta precursor-like protein APLP1 is a novel p53 transcriptional target gene that augments neuroblastoma cell death upon genotoxic stress. Oncogene 26:7302–7312
Furukawa K, Mattson MP (1997) Secreted amyloid precursor protein alpha selectively suppresses NMDA currents in hippocampal neurons: involvement of cyclic GMP. Neuroscience 83:429–438
Furukawa K, Barger SW, Blalock EM, Mattson MP (1996) Activation of K+ channels and suppression of neuronal activity by secreted β-amyloid-precursor protein. Nature 379:74–78
Doyle E, Bruce MT, Breen KC, Smith DC, Anderton B, Regan CM (1990) Intraventricular infusions of antibodies to amyloid-beta-protein precursor impair the acquisition of a passive avoidance response in the rat. Neurosci Lett 115:97–102
Huber G, Martin JR, Loffler J, Moreau JL (1993) Involvement of amyloid precursor protein in memory formation in the rat: an indirect antibody approach. Brain Res 603:348–352
Fazeli MS, Breen K, Errington ML, Bliss TV (1994) Increase in extracellular NCAM and amyloid precursor protein following induction of long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus of anaesthetized rats. Neurosci Lett 169:77–80
Nabeshima T, Nitta A (1994) Memory impairment and neuronal dysfunction induced by beta-amyloid protein in rats. J Exp Med 174:241–249
Chen QS, Kagan BL, Hirakura Y, Xie CW (2000) Impairment of hippocampal long-term potentiation by Alzheimer amyloid beta-peptides. J Neurosci Res 60:65–72
Puzzo D, Privitera L, Leznik E, Fa M, Staniszewski A, Palmeri A, Arancio O (2008) Picomolar amyloid-beta positively modulates synaptic plasticity and memory in hippocampus. J Neurosci 28:14537–14545
Koo EH, Sisodia SS, Archer DR, Martin LJ, Weidemann A, Beyreuther K, Fischer P, Masters CL, Price DL (1990) Precursor of amyloid protein in Alzheimer disease undergoes fast anterograde axonal transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1561–1565
Schubert W, Prior R, Weidemann A, Dircksen H, Multhaup G, Masters CL, Beyreuther K (1990) Localization of Alzheimer ßA4 amyloid precursor protein at central and peripheral synaptic sites. Brain Res 563:184–194
Kamal A, Stokin GB, Yang Z, Xia CH, Goldstein LS (2000) Axonal transport of amyloid precursor protein is mediated by direct binding to the kinesin light chain subunit of kinesin-I. Neuron 28:449–459
Gunawardena S, Goldstein LS (2001) Disruption of axonal transport and neuronal viability by amyloid precursor protein mutations in Drosophilia. Neuron 32:389–401
Lazarov O, Morfini GD, Lee EB, Farah MH, Szodorai A, DeBoer SR, Koliatsos VE, Kins S, Lee VM, Wong PC, Price DL, Brady ST, Sisoda SS (2005) Axonal transport, amyloid precursor protein, kinesin-1, and the processing apparatus: revisited. J Neurosci 25:2386–2395
Needham BE, Wlodek ME, Ciccotosto GD, Fam BC, Masters CL, Proietto J, Andrikopoulos S, Cappai R (2008) Identification of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid precursor protein (APP) and its homologue APLP2 as essential modulators of glucose and insulin homeostasis and growth. J Pathol 215:155–163
Lee Y, Tharp WG, Maple RL, Nair S, Permana PA, Pratley RE (2008) Amyloid precursor protein expression is upregulated in adipocytes in obesity. Obesity 16:1493–1500
Fiore F, Zambrano N, Minopoli G, Donini V, Duilio A, Russo T (1995) The regions of the Fe65 protein homologous to the phosphotyrosine interaction/phosphotyrosine binding domain of Shc bind the intracellular domain of the Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein. J Biol Chem 270:30853–30856
Guénette SY, Chen J, Jondro PD, Tanzi RE (1996) Association of a novel human FE65-like protein with the cytoplasmic domain of the β-amyloid precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10832–10837
Duilio A, Faraonio R, Minopoli G, Zambrano N, Russo T (1998) Fe65L2: a new member of Fe65 protein family interacting with the intracellular domain of Alzheimer’s β-amyloid precursor protein. Biochem J 330:513–519
Scheinfeld MH, Ghersi E, Laky K, Fowlkes BJ, D’Adamio L (2002) Processing of β-amyloid precursor-like protein-1 and -2 by γ-secretase regulates transcription. J Biol Chem 277:44195–44201
Zambrano N, Bimonte M, Arbucci S, Gianni D, Russo T, Bazzicalupo P (2002) feh-1 and apl-1, the Caenorhabditis elegans orthologues of mammalian Fe65 and β-amyloid precursor protein genes, are involved in the same pathway that controls nematode pharyngeal pumping. J Cell Sci 115:1411–1422
Guénette S, Chang Y, Hiesberger T, Richardson JA, Eckman CB, Eckman EA, Hammer RE, Herz J (2006) Essential roles for the FE65 amyloid precursor protein-interacting proteins in brain development. EMBO J 25:420–431
Borg JP, Ooi J, Levy E, Margolis B (1996) The phosphotyrosine interaction domain of X11 and FE65 bind to distinct sites on the YENPTY motif of amyloid precursor protein. Mol Cell Biol 16:6229–6241
Sabo SL, Lanier LM, Ikin AF, Khorkova O, Sahasrabudhe S, Greengard P, Buxbaum JD (1999) Regulation of β-amyloid secretion by FE65, an amyloid protein precursor-binding protein. J Biol Chem 274:7952–7957
Hu Q, Wang L, Yang Z, Cool BH, Zitnik G, Martin GM (2005) Endoproteolytic cleavage of FE65 converts the adaptor protein to a potent suppressor of the sAPPα pathway in primates. J Biol Chem 280:12548–12558
Chang KA, Kim HS, Ha TY, Ha JW, Shin KY, Jeong YH, Lee JP, Park CH, Kim S, Baik TK, Suh YH (2006) Phosphorylation of amyloid precursor protein (APP) at Thr668 regulates the nuclear translocation of the APP intracellular domain and induces neurodegeneration. Mol Cell Biol 26:4327–4338
Nakaya T, Kawai T, Suzuki T (2008) Regulation of FE65 nuclear translocation and function by amyloid β-protein precursor in osmotically stressed cells. J Biol Chem 283:19119–19131
Nakaya T, Suzuki T (2006) Role of APP phosphorylation in FE65-dependent gene transactivation mediated by AICD. Genes Cells 11:633–645
Radzimanowski J, Simon B, Sattler M, Beyreuther K, Sinning I, Wild K (2008) Structure of the intracellular domain of the amyloid precursor protein in complex with Fe65-PTB2. EMBO Rep 9:1134–1140
Tanahashi H, Tabira T (1999) X11L2, a new member of the X11 protein family, interacts with Alzheimer’s β-amyloid precursor protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 255:663–667
Borg JP, Yang Y, De Taddéo-Borg M, Margolis B, Turner RS (1998) The X11α protein slows cellular amyloid precursor protein processing and reduces Aβ40 and Aβ42 secretion. J Biol Chem 273:14761–14766
Sastre M, Turner RS, Levy E (1998) X11 interaction with β-amyloid precursor protein modulates its cellular stabilization and reduces amyloid β-protein secretion. J Biol Chem 273:22351–22357
Lee JH, Lau KF, Perkinton MS, Standen CL, Shemilt SJA, Mercken L, Cooper JD, McLoughlin DM, Miller CCJ (2003) The neuronal adaptor protein X11α reduces Aβ levels in the brains of Alzheimer’s APPswe Tg2576 transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 278:47025–47029
Lee JH, Lau KF, Perkinton MS, Standen CL, Rogelj B, Falinska A, McLoughlin DM, Miller CCJ (2004) The neuronal adaptor protein X11β reduces amyloid β-protein levels and amyloid plaque formation in the brains of transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 279:49099–49104
Saito Y, Sano Y, Vassar R, Gandy S, Nakaya T, Yamamoto T, Suzuki T (2008) X11 proteins regulate the translocation of APP into detergent resistant membrane and suppress the amyloidgenic cleavage of APP by BACE in brain. J Biol Chem 283:35763–35771
Araki Y, Tomita S, Yamaguchi H, Miyagi N, Sumioka A, Kirino Y, Suzuki T (2003) Novel cadherin-related membrane proteins, Alcadeins, enhance the X11-like protein-mediated stabilization of amyloid beta-protein precursor metabolism. J Biol Chem 278:49448–49458
King GD, Turner S (2004) Adaptor protein interactions: modulators of amyloid precursor protein metabolism and Alzheimer’s disease risk? Exp Neurol 185:208–219
Hase M, Yagi Y, Taru H, Tomita S, Sumioka A, Hiori K, Miyamoto K, Sasamura T, Nakamura M, Matsuno K, Suzuki T (2002) Expression and characterization of the Drosophilia X11-like/Mint protein during neural development. J Neurochem 81:1223–1232
Matsuda S, Yasukawa T, Homma Y, Ito Y, Niikura T, Hiraki T, Hirai S, Ohno S, Kita Y, Kawasumi M, Kouyama K, Yamamoto T, Kyriakis JM, Nishimoto I (2001) c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-interacting protein-1b/islet-brain-1 scaffolds Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein with JNK. J Neurosci 21:6597–6607
Scheinfeld MH, Roncarati R, Vito P, Lopez PA, Abdallah M, D’Adamio L (2002) Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) interacting protein 1 (JIP1) binds the cytoplasmic domain of the Alzheimer’s β-amyloid precursor protein (APP). J Biol Chem 277:3767–3775
Taru H, Kirino Y, Suzuki T (2002) Differential roles of JIP scaffold proteins in the modulation of amyloid precursor protein metabolism. J Biol Chem 277:27567–27574
Inomata H, Nakamura Y, Hayakawa A, Takata H, Suzuki T, Miyazawa K, Kitamura N (2003) A scaffold protein JIP-1b enhances amyloid precursor protein phosphorylation by JNK and its association with kinesin light chain 1. J Biol Chem 278:22946–22955
Araki Y, Kawano T, Taru H, Saito Y, Wada S, Miyamoto K, Kobayashi H, Ishikawa HO, Ohsugi Y, Yamamoto T, Matsuno K, Kinjo M, Suzuki T (2007) The novel cargo Alcadein induces vesicle association of kinesin-1 motor components and activates axonal transport. EMBO J 26:1475–1486
Horiuchi D, Collins CA, Bhat P, Barkus RV, Diantonio A, Saxton WM (2007) Control of a kinesin-cargo linkage mechanism by JNK pathway kinases. Curr Biol 17:1313–1317
Tarr PE, Roncarati R, Pelicci G, Pelicci PG, D’Adamio L (2002) Tyrosine phosphorylation of the β-amyloid precursor protein cytoplasmic tail promotes interaction with Shc. J Biol Chem 277:16798–16804
Xie Z, Dong Y, Maeda U, Xia W, Tanzi RE (2007) RNA interference silencing of the adaptor molecules ShcC and Fe65 differentially affect amyloid precursor protein processing and Aβ generation. J Biol Chem 282:4318–4325
Russo C, Dolcini V, Salis S, Venezia V, Zambrano N, Russo T, Schettini G (2002) Signal transduction through tyrosine-phosphorylated C-terminal fragments of amyloid precursor protein via an enhanced interaction with Shc/Grb2 adaptor proteins in reactive astrocytes of Alzheimer’s diease brain. J Biol Chem 277:35282–35288
Zhou D, Noviello C, D’Ambrosio C, Scaloni A, D’Adamio L (2004) Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 interaction with the tyrosine-phosphorylated tail of amyloid β precursor protein is mediated by its Src homology 2 domain. J Biol Chem 279:25374–25380
Nizzari M, Venezia V, Repetto E, Caorsi V, Magrassi R, Gagliani MC, Carlo P, Florio T, Schettini G, Tacchetti C, Russo T, Diaspro A, Russo C (2007) Amyloid precursor protein and presenelin 1 interact with the adaptor GRB2 and modulate Erk1, 2 signaling. J Biol Chem 282:13833–13844
Howell BW, Lanier LM, Frank R, Gertler FB, Cooper JA (1999) The disabled 1 phosphotyrosine-binding domain binds to the internalization signals of transmembrane glycoproteins and to phospholipids. Mol Cell Biol 19:5179–5188
Homayouni R, Rice DS, Sheldon M, Curran T (1999) Disabled-1 binds to the cytoplasmic domain of amyloid precursor-like protein 1. J Neurosci 19:7507–7515
Hoe HS, Train TS, Matsuoka Y, Howell BW, Rebeck W (2006) DAB1 and Reelin effects on amyloid precursor protein and ApoE receptor 2 trafficking and processing. J Biol Chem 281:35176–35185
Hoe HS, Minami SS, Makarova A, Lee J, Hyman BT, Matsuoka Y, Rebeck GW (2008) Fyn modulation of Dab1 effects on amyloid precursor protein and ApoE receptor 2 processing. J Biol Chem 283:6288–6299
Roncarati R, Sestan N, Scheinfeld MH, Berechid BE, Lopez PA, Meucci O, McGlade JC, Rakic P, D’Adamio L (2002) The γ-secretase-generated intracellular domain of β-amyloid precursor protein binds Numb and inhibits Notch signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:7102–7107
Kyriazis GA, Wei Z, Vandermey M, Jo DG, Xin O, Mattson MP, Chan SL (2008) Numb endocytic adapter proteins regulate the transport and processing of the amyloid precursor protein in an isoform-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 283:25492–25502
Zheng P, Eastman J, Pol SV, Pimplikar SW (1998) PAT1, a microtubule-interacting protein, recognizes the basolateral sorting signal of amyloid precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14745–14750
Kuan YH, Gruebl T, Soba P, Eggert S, Nesic I, Back S, Kirsch J, Beyreuther K, Kins S (2006) PAT1a modulates intracellular transport and processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP), APLP1 and APLP2. J Biol Chem 281:40114–40123
Gordon WR, Arnett KL, Blacklow SC (2008) The molecular logic of Notch signaling–a structural and biochemical perspective. J Cell Sci 121:3109–3119
Müller T, Meyer HE, Egensperger R, Marcus K (2008) The amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain (AICD) as a modulator of gene transcription, apoptosis, and cytoskeletal dynamics—relevance for Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 85:393–406
Baek SH, Ohgi KA, Rose DW, Koo EH, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG (2002) Exchange of N-CoR corepressor and Tip60 coactivator complexes links gene expression by NF-κB and β-amyloid precursor protein. Cell 110:55–67
Pardossi-Piquard R, Dunys J, Kawarai T, Sunyach C, Ring S, D’Adamio L, Shen J, Müller U, Hyslop P, Checler F (2005) Presenelin-dependent transcriptional control of the Aβ-degrading enzyme neprilysin by intracellular domains of βAPP and APLP. Neuron 46:541–554
Hébert SS, Serneels L, Tolia A, Craessaerts K, Derks C, Filippov MA, Müller U, De Strooper B (2006) Regulated intramembrane proteolysis of amyloid precursor protein and regulation of expression of putative target genes. EMBO Rep 7:737–745
Ho A, Sudhof T (2004) Binding of F-spondin to amyloid-beta precursor protein: a candidate amyloid-beta precursor protein ligand that modulates amyloid-beta precursor protein cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:2548–2553
Hoe HS, Wessner D, Beffert U, Becker AG, Matsuoka Y, Rebeck GW (2005) F-spondin interaction with the apolipoprotein E receptor ApoEr2 affects processing of amyloid precursor protein. Mol Cell Biol 25:9259–9268
Buxbaum JD, Gandy SE, Cicchetti P, Ehrlich ME, Czernik AJ, Fracasso RP, Ramabhadran TV, Unterbeck AJ, Greengard P (1990) Processing of Alzheimer βA4 amyloid precursor protein: modulation by agents that regulate protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6003–6006
Caporaso GL, Gandy SE, Buxbaum JD, Ramabhadran TV, Greengard P (1992) Protein phosphorylation rgeulates secretion of Alzheimer β/A4 amyloid precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:3055–3059
Buxbaum JD, Koo EH, Greengard P (1993) Protein phosphorylation inhibits production of Alzheimer amyloid β/A4 peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:9195–9198
Nitsch RM, Slack BE, Wurtman RJ, Growdon JH (1992) Release of Alzheimer amyloid precursor derivatives stimulated by activation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Science 258:304–307
Lee RK, Wurtman RJ, Cox AJ, Nitsch RM (1995) Amyloid precursor protein processing is stimulated by metabotropic glutamate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8083–8087
Slack BE, Breu J, Muchnicki L, Wurtman RJ (1997) Rapid stimulation of amyloid precursor protein release by epidermal growth factor: role of protein kinase C. Biochem J 327:245–249
Slack BE, Ma LK, Seah CC (2001) Constitutive shedding of the amyloid precursor protein ectodomain is up-regulated by tumour necrosis factor-α converting enzyme. Biochem J 357:787–794
da Cruz e Silva OA, Iverfeldt K, Oltersdorf T, Sinha S, Lieberburg I, Ramabhadran TV, Suzuki T, Sisodia S, Gandy S, Greengard P (1993) Regulated cleavage of Alzheimer beta-amyloid precursor protein in the absence of the cytoplasmic tail. Neuroscience 57:873–877
Hung AY, Selkoe DJ (1994) Selective ectodomain phosphorylation and regulated cleavage of β-amyloid precursor protein. EMBO J 13:534–542
Holback S, Adlerz L, Gatsinzi T, Jacobsen KT, Iverfeldt K (2007) PI3-K- and PKC-dependent up-regulation of APP processing enzymes by retinoic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 365:298–303
Torres-Aleman I (2007) Targeting insulin-like growth factor-1 to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets 12:1535–1542
Adlerz L, Holback S, Multhaup G, Iverfeldt K (2007) IGF-1-induced processing of the amyloid precursor protein family is mediated by different signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 282:10203–10209
Petanceska S, Gandy S (1999) The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor Wortmannin alters the metabolism of the Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein. J Neurochem 73:2316–2320
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacobsen, K.T., Iverfeldt, K. Amyloid precursor protein and its homologues: a family of proteolysis-dependent receptors. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 2299–2318 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0020-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0020-8