Abstract.
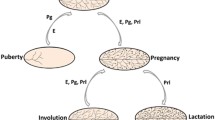
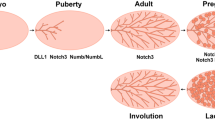
The mammary gland undergoes major developmental changes during puberty and pregnancy. It is thought that stem cells drive mammary gland development during puberty and are responsible for tissue maintenance as well as the major growth and remodelling that occurs with every pregnancy. The use of sophisticated cell separation procedures has facilitated the prospective isolation of mammary epithelial stem and differentiated cell subpopulations from the mouse mammary gland, while studies of primary human breast cancers have described sub-populations of tumourigenic cells capable of initiating tumour growth in immuno-compromised mice. These potential tumour ‘stem cells’ constitute an important therapeutic target population with respect to cancer therapy, as these are likely to be the cells which maintain tumour growth. Understanding the origin of these cells, their relationship to breast cancer subtypes, and how and why they differ from normal breast stem cells will lead to a revolution in tumour understanding, treatment and prevention. (Part of a Multi-author Review)
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molyneux, G., Regan, J. & Smalley, M.J. Common Molecular Mechanisms of Mammary Gland Development and Breast Cancer. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 64, 3248–3260 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7391-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7391-5