Abstract.
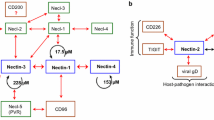
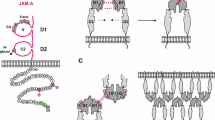
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) have been implicated in the control of a wide variety of cellular processes, such as cell adhesion, polarization, survival, movement, and proliferation. Nectins have emerged as immunoglobulin-like CAMs that participate in calcium-independent cell-cell adhesion by homophilic and heterophilic trans-interactions with nectins and nectin-like molecules. Nectin-based cell-cell adhesion exerts its function independently or in cooperation with other CAMs including cadherins and is essential for the formation of intercellular junctions, including adherens junctions, tight junctions, and puncta adherentia junctions. Nectins cis-interact with integrin αvβ3 and platelet-derived growth factor receptor and facilitate their signals to regulate the formation and integrity of intercellular junctions and cell survival. Nectins intracellularly associate with peripheral membrane proteins, including afadin and Par-3. This review focuses on recent progress in understanding the interactions of nectins with other transmembrane and peripheral membrane proteins to exert pleiotropic functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 27 June 2007; received after revision 14 August 2007; accepted 12 September 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rikitake, Y., Takai, Y. Interactions of the cell adhesion molecule nectin with transmembrane and peripheral membrane proteins for pleiotropic functions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 65, 253–263 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7290-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7290-9