Abstract.
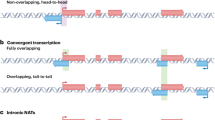
Bioinformatic analysis of the transcriptomes of diverse eukaryotes has demonstrated the ubiquity and structural diversity of complementary antisense RNAs. These include both trans-encoded microRNAs and a large population of cis-encoded antisense RNAs that encompasses both coding and non-coding RNAs. Antisense regulation has previously been characterized primarily as a post-transcriptional response affecting RNA stability, nuclear processing, export, or translation. However, the formation of double-stranded (ds) RNAs by base-pairing between complementary RNAs may elicit regulatory responses at the transcriptional level as well. Analysis of antisense transcription at several imprinted loci has suggested a number of other mechanisms that may not require formation of dsRNA. Understanding the integration of transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms represents a major challenge for understanding antisense regulation in eukaryotes. Such insight is also essential for understanding general principles of genetic regulation within the complex genomes characteristic of mouse and man as well as those of other eukaryotes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Received 13 February 2006; received after revision 19 May 2006; accepted 7 June 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munroe, S.H., Zhu, J. Overlapping transcripts, double-stranded RNA and antisense regulation: A genomic perspective. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63, 2102–2118 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-006-6070-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-006-6070-2