Abstract.
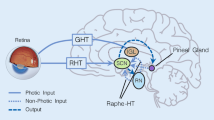
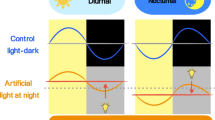
Adaptation to changes in the ambient light is of critical importance to life. In mammals, three principal photoadaptation mechanisms depend on ocular photoreception and exhibit spectral sensitivity suggestive of the opsin class of photopigment(s). These include rapid adaptation of the visual system to the ambient light by pupil constriction, direct modulation of neuroendocrine function and entrainment of the circadian clock to the day:night cycle. Surprisingly, these processes can largely function independent of classical rod/cone photoreceptors, suggesting a novel opsin-based signaling mechanism. They appear to involve a recently discovered network of intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells that make direct or indirect axonal connections to brain centers regulating photoadaptive behaviors. The discovery of a novel opsin, melanopsin, in these cells has offered an exciting entry point to explore, at the molecular level, how mammals adapt to their light environment. There is now genetic proof of a principal role for melanopsin in all three major photoadaptation processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 8 December 2005; received after revision 18 July 2006; accepted 12 October 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nayak, S.K., Jegla, T. & Panda, S. Role of a novel photopigment, melanopsin, in behavioral adaptation to light. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 64, 144–154 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-006-5581-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-006-5581-1