Abstract.
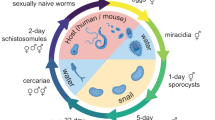
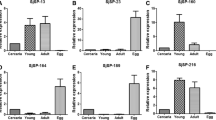
The schistosomulum is the main target of vaccine-induced protective immunity; however, most studies have utilized schistosomula produced by mechanical transformation of infective larvae followed by in vitro culture rather than larvae isolated directly from the lungs of infected mammals. Using transmission electron microscopy, we demonstrated that there was little difference in the ultrastructure of Schistosoma japonicum schistosomula obtained by the two methods. However, significant differences in gene expression profiles were apparent when we used an oligonucleotide microarray to compare the gene expression profiles of schistosomula obtained in vivo from lung tissue with those maintained in vitro, and with adult worms of S. japonicum. It is likely that host environmental factors, which cannot be reliably reproduced in vitro, do influence the growth, development and overall biology of schistosomes. Thus caution is urged when using in vitro-cultured schistosomes and mechanically transformed/cultured schistosomula in molecular, biochemical and immunological studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 6 December 2005; received after revision 19 January 2006; accepted 3 February 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chai, M., McManus, D.P., McInnes, R. et al. Transcriptome profiling of lung schistosomula,in vitro cultured schistosomula and adult Schistosoma japonicum. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63, 919–929 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5578-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5578-1