Abstract.
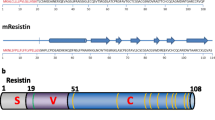
Resistin is a newly discovered adipocyte hormone. It is related to resistin-like molecules α, β and γ in structure and function. Resistin is produced by white and brown adipose tissues but has also has been identified in several other tissues, including the hypothalamus, pituitary and adrenal glands, pancreas, gastrointestinal tract, myocytes, spleen, white blood cells and plasma. The tissue level of resistin is decreased by insulin, cytokines such as tumour necrosis factor α, endothelin-1 and increased by growth and gonadal hormones, hyperglycaemia, male gender and some proinflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-6 and lipopolysaccharide. Resistin antagonizes insulin action, and it is downregulated by rosiglitazone and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ agonists. Since evidence of a direct link between resistin genotype and human diabetes is still weak, more molecular, physiological and clinical studies are needed to determine the role of resistin in the aetiology of type 2 diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 26 February 2004; received after revision 26 April 2004; accepted 7 June 2004
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adeghate, E. An update on the biology and physiology of resistin. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 61, 2485–2496 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4083-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4083-2