Abstract
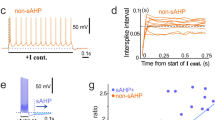
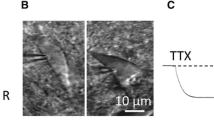
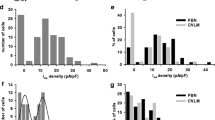
A hyperpolarization-activated current recorded from the pyramidal cells of the dorsal cochlear nucleus was investigated in the present study by using 150- to 200-μm-thick brain slices prepared from 6- to 14-day-old Wistar rats. The pyramidal neurones exhibited a slowly activating inward current on hyperpolarization. The reversal potential of this component was –32 ± 3 mV (mean ± SE, n = 6), while its half-activation voltage was –99 ± 1 mV with a slope factor of 10.9 ± 0.4 mV (n = 27). This current was highly sensitive to the extracellular application of both 1 mM Cs+ and 10 μM ZD7288. The electrophysiological properties and the pharmacological sensitivity of this current indicated that it corresponded to a hyperpolarization-activated non-specific cationic current (Ih). Our experiments showed that there was a correlation between the availability of the h-current and the spontaneous activity of the pyramidal cells, suggesting that this conductance acts as a pacemaker current in these neurones. Immunocytochemical experiments were also conducted on freshly isolated pyramidal cells to demonstrate the possible subunit composition of the channels responsible for the genesis of the pyramidal h-current. These investigations indicated the presence of HCN1, HCN2 and HCN4 subunits in the pyramidal cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 15 May 2003; received after revision 26 June 2003; accepted 21 July 2003
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paál, B., Oór, Á., Szücs, G. et al. HCN channels contribute to the intrinsic activity of cochlear pyramidal cells. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 60, 2189–2199 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-003-3187-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-003-3187-4