Abstract
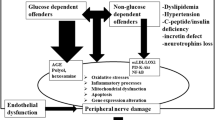
Diabetic polyneuropathy is the most common complication of diabetes mellitus. Several interactive pathogenetic mechanisms have been identified mainly in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats and have been ascribed to hyperglycemia. Over the last number of years it is becoming increasingly clear that diabetic neuropathy differs in type 1 and type 2 diabetes in humans and in murine models that more accurately mimic the human disorders. Beside hyperglycemia, attention is increasingly being paid to the pathogenetic roles of insulin and C-peptide deficiencies, particularly in type 1 diabetic neuropathy. There is now evidence to suggest that insulin and C-peptide deficiencies are mainly responsible for perturbations of neurotrophic factors and contribute to oxidative stress in diabetic nerve. This may also be true for apoptotic phenomena afflicting both the peripheral and central nervous systems in diabetes. The new data have lead to re-evaluations of pathogenetic components in this complex disorder, and their further exploration is likely to form a more refined basis for future therapeutic and preventive measures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 25 February 2003; received after revision 12 May 2003; accepted 19 May 2003
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sima, A.A.F. New insights into the metabolic and molecular basis for diabetic neuropathy. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 60, 2445–2464 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-003-3084-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-003-3084-x