Abstract.
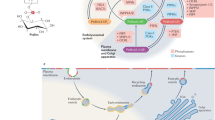
Phosphoinositides comprise a family of eight minor membrane lipids which play important roles in many signal transducing pathways in the cell. Signaling through various phosphoinositides has been shown to mediate cell growth and proliferation, apoptosis, cytoskeletal changes, insulin action and vesicle trafficking. A number of advances in signal transduction in the last decade has resulted in the discovery of a growing list of proteins which directly interact with high affinity and specificity with distinct phosphoinositides. Equally important, a number of phosphoinositide binding domains such as the pleckstrin homology domain have emerged as critical mediators of phosphoinositide signaling. Here, recent advances in phosphoinositide signaling are discussed. The aim of this review is to highlight particularly exciting advances made in the field over the last few years. The regulation of phosphoinositide metabolism by lipid kinases, phosphatases and phospholipases is reviewed, and considerable emphasis is placed on phosphoinositide-binding proteins. Finally, the role of these lipids in regulating signaling pathways and cell function is described.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toker, A. Phosphoinositides and signal transduction. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 59, 761–779 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-002-8465-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-002-8465-z