Abstract:
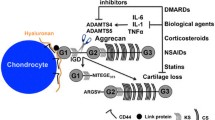
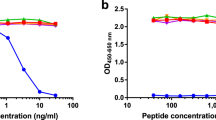
The matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) are a large group of enzymes responsible for matrix degradation. They contribute to joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) by directly degrading the cartilage and bone and indirectly promoting angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels). Inhibition of MMPs is a primary therapeutic target in RA. However, the results of limited clinical trials performed to date are disappointing. Improvements in therapeutic benefit may be achieved by targetting specific MMPs. A subclass of the MMPs, the gelatinases, contribute directly to joint destruction as well as being vital during angiogenesis. Gelatinase A is released as a latent enzyme and must be activated to degrade the matrix. It has a unique mechanism of activation on the cell surface involving membrane-type MMP (MT-MMP). Recently, the serine protease, activated protein C (APC), has been shown to directly activate gelatinase A, without requiring MT-MMP. Inhibition of APC represents a selective approach to prevent gelatinase A activation and may prove to be of therapeutic benefit in RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 6 July 2000; returned for revision 12 October 2000; accepted by R. Day 23 November 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jackson, C., Nguyen, M., Arkell, J. et al. Selective matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis - Targetting gelatinase A activation. Inflamm. res. 50, 183–186 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s000110050743
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s000110050743