Abstract
Background
Inflammation is a common feature in the pathogenesis of chronic kidney disease (CKD), regardless of the disease cause. Our aim was to evaluate the potential of several inflammatory biomarkers in CKD diagnosis and staging.
Methods
A total of 24 healthy controls and 92 pre-dialysis CKD patients with diverse etiologies, were enrolled in this study and grouped according to their CKD stage. We analysed the circulating levels of inflammatory molecules, C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 (TNFR2), pentraxin 3 (PTX3) and leptin, as well as the hemogram. We studied their association with parameters of kidney function and kidney injury, to evaluate their potential as early markers of the disease and/or of its worsening, as well as their interplay.
Results
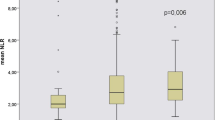
Compared to controls, patients in CKD stages 1–2 presented significantly higher IL-6 and TNFR2 levels, and higher neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio. All inflammatory cytokines and acute-phase proteins showed a trend to increase up to stage 3, stabilizing or declining thereafter, save for TNFR2, which steadily increased from stage to stage. All inflammatory molecules, apart from PTX3, were negatively and significantly correlated with eGFR, with a remarkable value for TNFR2 (r = − 0.732, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
TNFR2 might be useful for an early detection of CKD, as well as for disease staging/worsening. Still, the potential value of this biomarker in disease progression warrants further investigation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meng XM. Inflammatory mediators and renal fibrosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1165:381–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8871-2_18.
Miyamoto T, Carrero JJ, Stenvinkel P. Inflammation as a risk factor and target for therapy in chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2011;20:662–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/MNH.0b013e32834ad504.
Tsalamandris S, Antonopoulos AS, Oikonomou E, Papamikroulis G-A, Vogiatzi G, Papaioannou S, Deftereos S, Tousoulis D. The role of inflammation in diabetes: current concepts and future perspectives. Eur Cardiol. 2019;14:50–9. https://doi.org/10.15420/ecr.2018.33.1.
Ku E, Lee BJ, Wei J, Weir MR. Hypertension in CKD: core curriculum 2019. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019;74:120–31. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.12.044.
Arnold N, Lechner K, Waldeyer C, Shapiro MD, Koenig W. Inflammation and cardiovascular disease: the future. Eur Cardiol. 2021;16:e20–e20. https://doi.org/10.15420/ecr.2020.50.
Andrade-Oliveira V, Foresto-Neto O, Watanabe IKM, Zatz R, Câmara NOS. Inflammation in renal diseases: new and old players. Front Pharmacol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01192.
Akchurin OM, Kaskel F. Update on inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Blood Purif. 2015;39:84–92. https://doi.org/10.1159/000368940.
Gupta J, Mitra N, Kanetsky PA, Devaney J, Wing MR, Reilly M, Shah VO, Balakrishnan VS, Guzman NJ, Girndt M, et al. Association between albuminuria, kidney function, and inflammatory biomarker profile in CKD in CRIC. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol: CJASN. 2012;7:1938–46. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.03500412.
Schlondorff DO. Overview of factors contributing to the pathophysiology of progressive renal disease. Kidney Int. 2008;74:860–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2008.351.
Heine GH, Ortiz A, Massy ZA, Lindholm B, Wiecek A, Martínez-Castelao A, Covic A, Goldsmith D, Süleymanlar G, London GM, et al. Monocyte subpopulations and cardiovascular risk in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012;8:362–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2012.41.
Castillo-Rodríguez E, Pizarro-Sánchez S, Sanz AB, Ramos AM, Sanchez-Niño MD, Martin-Cleary C, Fernandez-Fernandez B, Ortiz A. Inflammatory cytokines as uremic toxins: “Ni Son Todos Los Que Estan, Ni Estan Todos Los Que Son.” Toxins. 2017;9:114.
Amdur RL, Feldman HI, Gupta J, Yang W, Kanetsky P, Shlipak M, Rahman M, Lash JP, Townsend RR, Ojo A, et al. Inflammation and progression of CKD: the CRIC study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11:1546–56. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.13121215.
Mihai S, Codrici E, Popescu ID, Enciu A-M, Rusu E, Zilisteanu D, Necula LG, Anton G, Tanase C. Inflammation-related patterns in the clinical staging and severity assessment of chronic kidney disease. Dis Markers. 2019;2019:1814304. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1814304.
Avesani CM, Carrero JJ, Axelsson J, Qureshi AR, Lindholm B, Stenvinkel P. Inflammation and wasting in chronic kidney disease: partners in crime. Kidney Int. 2006;70:S8–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5001969.
Mazzaferro S, De Martini N, Rotondi S, Tartaglione L, Ureña-Torres P, Bover J, Pasquali M. Bone, inflammation and chronic kidney disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;506:236–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2020.03.040.
Bash LD, Erlinger TP, Coresh J, Marsh-Manzi J, Folsom AR, Astor BC. Inflammation, hemostasis, and the risk of kidney function decline in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:596–605. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.10.044.
Amdur RL, Feldman HI, Dominic EA, Anderson AH, Beddhu S, Rahman M, Wolf M, Reilly M, Ojo A, Townsend RR, et al. Use of measures of inflammation and kidney function for prediction of atherosclerotic vascular disease events and death in patients with CKD: findings from the CRIC study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019;73:344–53. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.09.012.
Menon V, Greene T, Wang X, Pereira AA, Marcovina SM, Beck GJ, Kusek JW, Collins AJ, Levey AS, Sarnak MJ. C-reactive protein and albumin as predictors of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2005;68:766–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00455.x.
Sun J, Axelsson J, Machowska A, Heimbürger O, Bárány P, Lindholm B, Lindström K, Stenvinkel P, Qureshi AR. Biomarkers of cardiovascular disease and mortality risk in patients with advanced CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11:1163–72. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.10441015.
Alix PM, Guebre-Egziabher F, Soulage CO. Leptin as an uremic toxin: deleterious role of leptin in chronic kidney disease. Biochimie. 2014;105:12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2014.06.024.
Sjöberg B, Qureshi AR, Heimbürger O, Stenvinkel P, Lind L, Larsson A, Bárány P, Ärnlöv J. Association between levels of pentraxin 3 and incidence of chronic kidney disease in the elderly. J Intern Med. 2016;279:173–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12411.
Valente MJ, Rocha S, Coimbra S, Catarino C, Rocha-Pereira P, Bronze-da-Rocha E, Oliveira JG, Madureira J, Fernandes JC, do Sameiro-Faria M, et al. Long pentraxin 3 as a broader biomarker for multiple risk factors in end-stage renal disease: association with all-cause mortality. Mediators Inflamm. 2019;2019:3295725–3295725. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3295725.
Gohda T, Niewczas MA, Ficociello LH, Walker WH, Skupien J, Rosetti F, Cullere X, Johnson AC, Crabtree G, Smiles AM, et al. Circulating TNF receptors 1 and 2 predict stage 3 CKD in type 1 diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23:516–24. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2011060628.
Niewczas MA, Gohda T, Skupien J, Smiles AM, Walker WH, Rosetti F, Cullere X, Eckfeldt JH, Doria A, Mayadas TN, et al. Circulating TNF receptors 1 and 2 predict ESRD in type 2 diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23:507–15. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2011060627.
Krolewski AS, Niewczas MA, Skupien J, Gohda T, Smiles A, Eckfeldt JH, Doria A, Warram JH. Early progressive renal decline precedes the onset of microalbuminuria and its progression to macroalbuminuria. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:226–34. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc13-0985.
Chen CC, Pedraza PL, Hao S, Stier CT, Ferreri NR. TNFR1-deficient mice display altered blood pressure and renal responses to ANG II infusion. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010;299:F1141-1150. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00344.2010.
Vielhauer V, Stavrakis G, Mayadas TN. Renal cell-expressed TNF receptor 2, not receptor 1, is essential for the development of glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:1199–209. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci23348.
Guo G, Morrissey J, McCracken R, Tolley T, Klahr S. Role of TNFR1 and TNFR2 receptors in tubulointerstitial fibrosis of obstructive nephropathy. Am J Physiol. 1999;277:F766-772. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.1999.277.5.F766.
Levin A, Stevens PE, Bilous RW, Coresh J, De Francisco ALM, De Jong PE, Griffith KE, Hemmelgarn BR, Iseki K, Lamb EJ, Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group, et al. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;3:1–150. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2009.02834.x.
Templeton G. A two-step approach for transforming continuous variables to normal: implications and recommendations for IS research. Commun Assoc Inf Syst. 2011;28:41–58. https://doi.org/10.17705/1CAIS.02804.
Hellström L, Wahrenberg H, Hruska K, Reynisdottir S, Arner P. Mechanisms behind gender differences in circulating leptin levels. J Intern Med. 2000;247:457–62. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2796.2000.00678.x.
Lv W, Booz GW, Wang Y, Fan F, Roman RJ. Inflammation and renal fibrosis: recent developments on key signaling molecules as potential therapeutic targets. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;820:65–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.12.016.
Upadhyay A, Larson MG, Guo CY, Vasan RS, Lipinska I, O’Donnell CJ, Kathiresan S, Meigs JB, Keaney JF Jr, Rong J, et al. Inflammation, kidney function and albuminuria in the Framingham Offspring cohort. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26:920–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfq471.
Heinzelmann M, Mercer-Jones MA, Passmore JC. Neutrophils and renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis. 1999;34:384–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0272-6386(99)70375-6.
Cupp MA, Cariolou M, Tzoulaki I, Aune D, Evangelou E, Berlanga-Taylor AJ. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and cancer prognosis: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies. BMC Med. 2020;18:360. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-020-01817-1.
Angkananard T, Anothaisintawee T, McEvoy M, Attia J, Thakkinstian A. Neutrophil lymphocyte ratio and cardiovascular disease risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:2703518–2703518. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2703518.
Okyay GU, İnal S, Öneç K, Er RE, Paşaoğlu Ö, Paşaoğlu H, Derici Ü, Erten Y. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in evaluation of inflammation in patients with chronic kidney disease. Ren Fail. 2013;35:29–36. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022X.2012.734429.
Yoshitomi R, Nakayama M, Sakoh T, Fukui A, Katafuchi E, Seki M, Tsuda S, Nakano T, Tsuruya K, Kitazono T. High neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio is associated with poor renal outcomes in Japanese patients with chronic kidney disease. Ren Fail. 2019;41:238–43. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886022X.2019.1595645.
Yuan Q, Wang J, Peng Z, Zhou Q, Xiao X, Xie Y, Wang W, Huang L, Tang W, Sun D, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and incident end-stage renal disease in Chinese patients with chronic kidney disease: results from the Chinese Cohort Study of Chronic Kidney Disease (C-STRIDE). J Transl Med. 2019;17:86–86. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-019-1808-4.
Zhao W-M, Tao S-M, Liu G-L. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in relation to the risk of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ren Fail. 2020;42:1059–66. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886022X.2020.1832521.
Abraham G, Sundaram V, Sundaram V, Mathew M, Leslie N, Sathiah V. C-Reactive protein, a valuable predictive marker in chronic kidney disease. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2009;20:811–5.
Santos-Silva A, Costa E, Alves R. Chronic kidney disease. In: Palavra F, Reis F, Marado D, Sena A, editors. Biomarkers of cardiometabolic risk, inflammation and disease. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2015. p. 95–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16018-4_5.
Noor S, Alam F, Fatima SS, Khan M, Rehman R. Role of Leptin and dyslipidemia in chronic kidney disease. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2018;31:893–7.
Keller C, Katz R, Cushman M, Fried LF, Shlipak M. Association of kidney function with inflammatory and procoagulant markers in a diverse cohort: a cross-sectional analysis from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). BMC Nephrol. 2008;9:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2369-9-9.
Tonelli M, Sacks F, Pfeffer M, Jhangri GS, Curhan G. Biomarkers of inflammation and progression of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2005;68:237–45. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00398.x.
Shankar A, Sun L, Klein BEK, Lee KE, Muntner P, Nieto FJ, Tsai MY, Cruickshanks KJ, Schubert CR, Brazy PC, et al. Markers of inflammation predict the long-term risk of developing chronic kidney disease: a population-based cohort study. Kidney Int. 2011;80:1231–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2011.283.
Al-Lamki RS, Mayadas TN. TNF receptors: signaling pathways and contribution to renal dysfunction. Kidney Int. 2015;87:281–96. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2014.285.
Al-Lamki RS, Wang J, Skepper JN, Thiru S, Pober JS, Bradley JR. Expression of tumor necrosis factor receptors in normal kidney and rejecting renal transplants. Lab Invest. 2001;81:1503–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.3780364.
Gohda T, Tomino Y. Novel biomarkers for the progression of diabetic nephropathy: soluble TNF receptors. Curr Diab Rep. 2013;13:560–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-013-0385-9.
Kamei N, Yamashita M, Nishizaki Y, Yanagisawa N, Nojiri S, Tanaka K, Yamashita Y, Shibata T, Murakoshi M, Suzuki Y, et al. Association between circulating tumor necrosis factor-related biomarkers and estimated glomerular filtration rate in type 2 diabetes. Sci Rep. 2018;8:15302. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-33590-w.
Coca SG, Nadkarni GN, Huang Y, Moledina DG, Rao V, Zhang J, Ferket B, Crowley ST, Fried LF, Parikh CR. Plasma biomarkers and kidney function decline in early and established diabetic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:2786–93. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2016101101.
Yang S, Wang J, Brand DD, Zheng SG. Role of TNF-TNF receptor 2 signal in regulatory T cells and its therapeutic implications. Front Immunol. 2018;9:784. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00784.
Gough P, Myles IA. Tumor necrosis factor receptors: pleiotropic signaling complexes and their differential effects. Front Immunol. 2020;11:585880–585880. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.585880.
Bruggeman LA, Drawz PE, Kahoud N, Lin K, Barisoni L, Nelson PJ. TNFR2 interposes the proliferative and NF-κB-mediated inflammatory response by podocytes to TNF-α. Lab Invest. 2011;91:413–25. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2010.199.
Saha S, Buttari B, Panieri E, Profumo E, Saso L. An overview of Nrf2 signaling pathway and its role in inflammation. Molecules. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225474.
Juul-Nielsen C, Shen J, Stenvinkel P, Scholze A. Systematic review of the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) system in human chronic kidney disease: alterations, interventions, and relation to morbidity. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfab031.
Stenvinkel P, Chertow GM, Devarajan P, Levin A, Andreoli SP, Bangalore S, Warady BA. Chronic inflammation in chronic kidney disease progression: role of Nrf2. Kidney Int Rep. 2021;6:1775–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2021.04.023.
Martini S, Nair V, Keller BJ, Eichinger F, Hawkins JJ, Randolph A, Böger CA, Gadegbeku CA, Fox CS, Cohen CD, et al. Integrative biology identifies shared transcriptional networks in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25:2559–72. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2013080906.
Hoffmann U, Bergler T, Rihm M, Pace C, Krüger B, Rümmele P, Stoelcker B, Banas B, Männel DN, Krämer BK. Upregulation of TNF receptor type 2 in human and experimental renal allograft rejection. Am J Transplant. 2009;9:675–86. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2008.02536.x.
Stuveling EM, Hillege HL, Bakker SJ, Gans RO, De Jong PE, De Zeeuw D. C-reactive protein is associated with renal function abnormalities in a non-diabetic population. Kidney Int. 2003;63:654–61. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00762.x.
Su H, Lei CT, Zhang C. Interleukin-6 signaling pathway and its role in kidney disease: an update. Front Immunol. 2017;8:405. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00405.
Soleimani A, Soleimani M, Farzadnejad F, Tamadon M. The relationship between urinary and plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha and various stages of chronic kidney disease in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. J Nephropathol. 2020;9:e39–e39. https://doi.org/10.34172/jnp.2020.39.
Navarro JF, Mora C, Maca M, Garca J. Inflammatory parameters are independently associated with urinary albumin in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;42:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0272-6386(03)00408-6.
Zwiech R. Predictive value of conjointly examined IL-1ra, TNF-R I, TNF-R II, and RANTES in patients with primary glomerulonephritis. J Korean Med Sci. 2013;28:261–7. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.2.261.
Iglesias J, Marik PE, Levine JS. Elevated serum levels of the type I and type II receptors for tumor necrosis factor-alpha as predictive factors for ARF in patients with septic shock. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41:62–75. https://doi.org/10.1053/ajkd.2003.50024.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Applied Molecular Biosciences Unit (UCIBIO), which is financed by national funds from FCT & MCTES; by FEDER COMPETE2020 funds UIDP/04539/2020 (CIBB); by PTDC/SAU-NUT/31712/2017, POCI-01-0145-FEDER-007440 and POCI-01-0145-FEDER-031712, and by FCT doctoral grant SFRH/BD/145939/2019; by funds from Portugal Regional Coordination and Development Commissions (Norte-01-0145-FEDER-000024; Centro-01-0145-FEDER-000012); by REQUIMTE-Rede de Química e Tecnologia-Associação in the form of a researcher [(S. Rocha – project Dial4Life co-financed by FCT/MCTES (PTDC/MEC-CAR/31322/2017) and FEDER/COMPETE 2020 (POCI-01-0145-FEDER-031322)].
Funding
This work was financially supported by national funds from FCT—Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P., in the scope of the project UIDP/04378/2020 and UIDB/04378/2020 of the Research Unit on Applied Molecular Biosciences—UCIBIO and the project LA/P/0140/2020 of the Associate Laboratory Institute for Health and Bioeconomy—i4HB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Wissam H Faour.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lousa, I., Belo, L., Valente, M.J. et al. Inflammatory biomarkers in staging of chronic kidney disease: elevated TNFR2 levels accompanies renal function decline. Inflamm. Res. 71, 591–602 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-022-01574-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-022-01574-2