Abstract
Objective
To investigate whether Nischarin participated in neuronal apoptosis induced by neuroinflammation and via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and PKB-dependent pathway.
Material
Use of male Sprague–Dawley rats, rat pheochromocytoma (PC12), and murine microglial cells (BV-2). Treatment lipopolysaccharides (LPS) were injected into the brain lateral ventricle of the rat. The BV-2 cells were treated by LPS. The PC12 cells were pretreated by or not pretreated by conditioned media and siRNA.
Methods
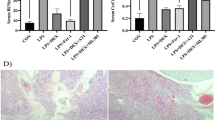
Western blotting was used for analyzing the expression level of Nischarin, pAKT, BAD and Bcl-2. Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence were used to perform the morphology and localization of Nischarin. The siRNA could down-regulate the protein level of endogenous Nischarin.
Results
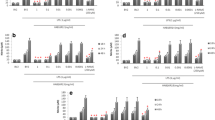
The expression level of Nischarin was elevated after LPS injection; meanwhile, Nischarin was located in the neuron. Nischarin was involved in regulating the PI3K/PKB patway.
Conclusion
Nischarin might be involved in mediating the process of PI3K/PKB pathway-dependent neuronal apoptosis. After the silencing of Nischarin in cultured PC12 (pheochromocytoma) by siRNA, these results showed that it would induce a reduction of pAKT and Bcl-2 proteins expression; meanwhile, it induces an increase of BAD and active caspase-3.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonow RH, Aid S, Zhang Y, Becker KG, Bosetti F. The brain expression of genes involved in inflammatory response, the ribosome, and learning and memory is altered by centrally injected lipopolysaccharide in mice. Pharmacogenomics J. 2009;9:116–26.
Ulevitch RJ, Tobias PS. Receptor-dependent mechanisms of cell stimulation by bacterial endotoxin. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:437–57.
Yeh SH, Hung JJ, Gean PW, Chang WC. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protects cultured cortical neurons from lipopolysaccharide-induced cell death via regulation of NR1 expression. J Neurosci. 2008;28:14259–70.
Burguillos MA, Hajji N, Englund E, Persson A, Cenci AM, Machado A, Cano J, Joseph B, Venero JL. Apoptosis-inducing factor mediates dopaminergic cell death in response to LPS-induced inflammatory stimulus: evidence in Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurobiol Dis. 2011;41:177–88.
Hauss-Wegrzyniak B, Lukovic L, Bigaud M, Stoeckel ME. Brain inflammatory response induced by intracerebroventricular infusion of lipopolysaccharide: an immunohistochemical study. Brain Res. 1998;794:211–24.
Zhang ZH, Yu Y, Wei SG, Felder RB. Centrally administered lipopolysaccharide elicits sympathetic excitation via NAD(P)H oxidase-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. J Hypertens. 2010;28:806–16.
Hu S, Peterson PK, Chao CC. Cytokine-mediated neuronal apoptosis. Neurochem Int. 1997;30:427–31.
Nagatsu T, Mogi M, Ichinose H, Togari A. Cytokines in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl. 2000;58:143–51.
Hyman BT, Yuan J. Apoptotic and non-apoptotic roles of caspases in neuronal physiology and pathophysiology. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13:395–406.
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ. Cell death: critical control points. Cell. 2004;116:205–19.
Willis SN, Fletcher JI, Kaufmann T, van Delft MF, Chen L, Czabotar PE, Ierino H, Lee EF, Fairlie WD, Bouillet P, et al. Apoptosis initiated when BH3 ligands engage multiple Bcl-2 homologs, not Bax or Bak. Science. 2007;315:856–9.
Alahari SK, Lee JW, Juliano RL. Nischarin, a novel protein that interacts with the integrin alpha5 subunit and inhibits cell migration. J Cell Biol. 2000;151:1141–54.
Yao M, Zhou XD, Zha XL, Shi DR, Fu J, He JY, Lu HF, Tang ZY. Expression of the integrin alpha5 subunit and its mediated cell adhesion in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1997;123:435–40.
Lee JW, Juliano RL. alpha5beta1 integrin protects intestinal epithelial cells from apoptosis through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and protein kinase B-dependent pathway. Mol Biol Cell. 2000;11:1973–87.
Alahari SK. Nischarin inhibits Rac induced migration and invasion of epithelial cells by affecting signaling cascades involving PAK. Exp Cell Res. 2003;288:415–24.
Alahari SK, Reddig PJ, Juliano RL. The integrin-binding protein Nischarin regulates cell migration by inhibiting PAK. EMBO J. 2004;23:2777–88.
Ding Y, Milosavljevic T, Alahari SK. Nischarin inhibits LIM kinase to regulate cofilin phosphorylation and cell invasion. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:3742–56.
Dontenwill M, Piletz JE, Chen M, Baldwin J, Pascal G, Ronde P, Dupuy L, Greney H, Takeda K, Bousquetd P. IRAS is an anti-apoptotic protein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;1009:400–12.
Renton KW, Dibb S, Levatte TL. Lipopolysaccharide evokes the modulation of brain cytochrome P4501A in the rat. Brain Res. 1999;842:139–47.
del Peso L, Gonzalez-Garcia M, Page C, Herrera R, Nunez G. Interleukin-3-induced phosphorylation of BAD through the protein kinase Akt. Science. 1997;278:687–9.
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg ME. Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell. 1997;91:231–41.
Zha J, Harada H, Yang E, Jockel J, Korsmeyer SJ. Serine phosphorylation of death agonist BAD in response to survival factor results in binding to 14-3-3 not BCL-X(L). Cell. 1996;87:619–28.
Hoozemans JJ, Veerhuis R, Rozemuller JM, Eikelenboom P. Neuroinflammation and regeneration in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2006;24:157–65.
Bredesen DE. Neural apoptosis. Ann Neurol. 1995;38:839–51.
Naruse I, Keino H. Apoptosis in the developing CNS. Prog Neurobiol. 1995;47:135–55.
Frisch SM, Ruoslahti E. Integrins and anoikis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997;9:701–6.
Wick MJ, Dong LQ, Riojas RA, Ramos FJ, Liu F. Mechanism of phosphorylation of protein kinase B/Akt by a constitutively active 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:40400–6.
Berra E, Diaz-Meco MT, Moscat J. The activation of p38 and apoptosis by the inhibition of Erk is antagonized by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:10792–7.
Gajewski TF, Thompson CB. Apoptosis meets signal transduction: elimination of a BAD influence. Cell. 1996;87:589–92.
Green D, Kroemer G. The central executioners of apoptosis: caspases or mitochondria? Trends Cell Biol. 1998;8:267–71.
Martin LJ. Neuronal cell death in nervous system development, disease, and injury (review). Int J Mol Med. 2001;7:455–78.
Piletz JE, Ivanov TR, Sharp JD, Ernsberger P, Chang CH, Pickard RT, Gold G, Roth B, Zhu H, Jones JC, et al. Imidazoline receptor antisera-selected (IRAS) cDNA: cloning and characterization. DNA Cell Biol. 2000;19:319–29.
Dontenwill M, Pascal G, Piletz JE, Chen M, Baldwin J, Ronde P, Dupuy L, Urosevic D, Greney H, Takeda K, et al. IRAS, the human homologue of Nischarin, prolongs survival of transfected PC12 cells. Cell Death Differ. 2003;10:933–5.
Assoian RK. Anchorage-dependent cell cycle progression. J Cell Biol. 1997;136:1–4.
Zhang Z, Vuori K, Reed JC, Ruoslahti E. The alpha 5 beta 1 integrin supports survival of cells on fibronectin and up-regulates Bcl-2 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:6161–5.
Matter ML, Ruoslahti E. A signaling pathway from the alpha5beta1 and alpha(v)beta3 integrins that elevates bcl-2 transcription. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:27757–63.
Datta SR, Brunet A, Greenberg ME. Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev. 1999;13:2905–27.
Fang L, Chen B, Liu S, Wang R, Hu S, Xia G, Tian Y, Cai X. Synergistic effect of a combination of nanoparticulate Fe3O4 and gambogic acid on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/Bad pathway of LOVO cells. Int J Nanomed. 2012;7:4109–18.
Datta SR, Katsov A, Hu L, Petros A, Fesik SW, Yaffe MB, Greenberg ME. 14-3-3 proteins and survival kinases cooperate to inactivate BAD by BH3 domain phosphorylation. Mol Cell. 2000;6:41–51.
Zheng J, Hu JD, Chen YY, Chen BY, Huang Y, Zheng ZH, Liu TB. Baicalin induces apoptosis in leukemia HL-60/ADR cells via possible down-regulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13:1119–24.
Chelyshev Iu A, Cherepnev GV, Saitkulov KI. Apoptosis in the nervous system. Ontogenez. 2001;32:118–29.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31071288) and a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Graham Wallace.
X. Wu and W. Xu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Xu, W., Cui, G. et al. The expression pattern of Nischarin after lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation in rats brain cortex. Inflamm. Res. 62, 929–940 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-013-0631-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-013-0631-2