Abstract
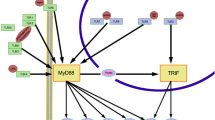
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play a central role in the regulation of the host immune system. Each TLR recognizes specific pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). TLR4 is one of the well characterized pathogen recognition receptors (PRRs) that recognizes the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of Gram-negative bacteria, some conserved structures from fungal to mycobacterial pathogens and some endogenous ligands. A complex signaling cascade initiates after the ligand binds to the TLR4 ectodomain, leading to the activation of multiple inflammatory genes. Genetic variations greatly influence immune responses towards pathogenic challenges and disease outcome. In this review, we summarize various reports regarding TLR4 polymorphisms and disease susceptibility.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lemaitre B, Nicolas E, Michaut L, Reichhart JM, Hoffmann JA. The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spatzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophila adults. Cell. 1996;86:973–83.
Beutler B. Innate immunity: an overview. Mol Immunol. 2004;40:845–59.
Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Janeway CA Jr. A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature. 1997;388:394–7.
Lemaitre B. The road to Toll. Nature Rev Immunol. 2004;4:521–7.
Tabeta K, Georgel P, Janssen E, Du X, Hoebe K, Crozat K, et al. Toll-like receptors 9 and 3 as essential components of innate immune defense against mouse cytomegalovirus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:3516–21.
Miggin SM, O’Neill LA. New insights into the regulation of TLR signaling. J Leukoc Biol. 2006;80:220–6.
Rakoff-Nahoum S, Paglino J, Eslami-Varzaneh F, Edberg S, Medzhitov R. Recognition of commensal microflora by Toll-like receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis. Cell. 2004;118:229–41.
Schnare M, Barton GM, Holt AC, Takeda K, Akira S, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptors control activation of adaptive immune responses. Nature Immunol. 2001;2:947–50.
Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:499–511.
Akira S, Yamamoto M, Takeda K. Role of adapters in Toll-like receptor signaling. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31(Pt. 3):637–42.
Vogel SN, Fitzgerald KA, Fenton MJ. TLRs: differential adapter utilization by Toll-like receptors mediates TLR-specific patterns of gene expression. Mol Interv. 2003;3:466–77.
Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in TLR4 gene. Science. 1998;282:2085–8.
Hoshino K, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Sanjo H, Ogawa T, Takeda Y, et al. Cutting edge: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient mice are hyporesponsive to lipopolysaccharide: evidence for TLR4 as the LPS gene product. J Immunol. 1999;162:3749–52.
Ohashi K, Burkart V, Flohe S, Kolb H. Cutting edge: heat shock protein 60 is a putative endogenous ligand of the toll-like receptor-4 complex. J Immunol. 2000;164:558–61.
Roelofs MF, Boelens WC, Joosten LA, Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, Geurts J, Wunderink LU, et al. Identification of small heat shock protein B8 (HSP22) as a novel TLR4 ligand and potential involvement in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 2006;176:7021–7.
Nagai Y, Akashi S, Nagafuku M, Ogata M, Iwakura Y, Akira S, et al. Essential role of MD-2 in LPS responsiveness and TLR4 distribution. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:667–72.
Jiang Z, Georgel P, Du X, Shamel L, Sovath S, Mudd S, et al. CD14 is required for MyD88-independent LPS signaling. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:565–70.
Jack RS, Fan X, Bernheiden M, Rune G, Ehlers M, Weber A, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein is required to combat a murine gram-negative bacterial infection. Nature. 1997;389:742–5.
Lye E, Mirtsos C, Suzuki N, Suzuki S, Yeh WC. The role of interleukin 1 receptor associated kinase-4 (IRAK-4) kinase activity in IRAK-4-mediated signaling. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:40653–8.
Wang C, Deng L, Hong M, Akkaraju GR, Inoue J, Chen ZJ. TAK1 is a ubiquitin dependent kinase of MKK and IKK. Nature. 2001;412:346–51.
Qian Y, Commane M, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Matsumoto K, Li X. IRAK-mediated translocation of TRAF6 and TAB 2 in the interleukin-1-induced activation of NFkappa B. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:41661–7.
Jiang Z, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Qian Y, Matsumoto K, Li X. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor associated kinase-dependent IL-1-induced signaling complexes phosphorylate TAK1 and TAB 2 at the plasma membrane and activate TAK1 in the cytosol. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:7158–67.
Jefferies CA, Doyle S, Brunner C, Dunne A, Brint E, Wietek C, et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is a Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-binding protein that participates in nuclear factor kappaB activation by Toll-like receptor 4. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:26258–64.
Doyle SL, Jefferies CA, O’Neill LA. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is involved in p65-mediated transactivation and phosphorylation of p65 on serine 536 during NFkappaB activation by lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:23496–501.
Gray P, Dunne A, Brikos C, Jefferies CA, Doyle SL, O’Neill LA. MyD88 adapter-like (Mal) is phosphorylated by Bruton’s tyrosine kinase during TLR2 and TLR4 signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:10489–95.
Fitzgerald KA, Rowe DC, Barnes BJ, Caffrey DR, Visintin A, Latz E, et al. LPS TLR4 signaling to IRF-3/7 and NF-KB involves the Toll adapters TRAM and TRIF. J Exp Med. 2003;198:1043–55.
Jiang Z, Zamanian-Daryoush M, Nie H, Silva AM, Williams BR, Li X. Poly(I-C)-induced Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3)- mediated activation of NFkappa B and MAP kinase is through an interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK)-independent pathway employing the signaling components TLR3-TRAF6-TAK1-TAB 2-PKR. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:16713–9.
Jiang Z, Mak TW, Sen G, Li X. Toll-like receptor 3-mediated activation of NF kappaB and IRF3 diverges at Toll-IL-1 receptor domain-containing adapter inducing IFN-beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:3533–8.
Meylan E, Burns K, Hofmann K, Blancheteau V, Martinon F, Kelliher M, et al. RIP1 is an essential mediator of Toll like receptor 3 induced NF-kappa B activation. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:503–7.
Sato S, Sugiyama M, Yamamoto M, Watanabe Y, Kawai T, Takeda K, et al. Toll/IL-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-beta (TRIF) associates with TNF receptor-associated factor 6 and TANK-binding kinase 1, and activates two distinct transcription factors, NF-kappa B and IFN-regulatory factor 3, in the Toll-like receptor signaling. J Immunol. 2003;171:4304–10.
Hill AV. The genomics and genetics of human infectious disease susceptibility. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2001;2:373–400.
Notarangelo L, Casanova JL, Conley ME, Chapel H, Fischer A, Puck J, et al. Primary immunodeficiency diseases: an update from the International Union of Immunological Societies Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases Classification Committee Meeting in Budapest, 2005. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:883–96.
Schroder NW, Schumann RR. Single nucleotide polymorphisms of Toll-like receptors and susceptibility to infectious disease. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:156–64.
Orange JS, Geha RS. Finding NEMO: genetic disorders of NF-κB activation. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:983–5.
Puel A, Picard C, Ku CL, Smahi A, Casanova JL. Inherited disorders of NF-κB-mediated immunity in man. Curr Opin Immunol. 2004;16:34–41.
Smirnova I, Poltorak A, Chan EK, McBride C, Beutler B. Phylogenetic variation and polymorphism at the Toll-like receptor 4 locus (TLR4). Genome Biol. 2000;1:R002.
Smirnova I, Hamblin MT, McBride C, Beutler B, Di Rienzo A. Excess of rare amino acid polymorphisms in the Toll-like receptor 4 in humans. Genetics. 2001;158:1657–64.
Smirnova I, Mann N, Dols A, Derkx HH, Hibberd ML, Levin M, et al. Assay of locus-specific genetic load implicates rare Toll-like receptor 4 mutations in meningococcal susceptibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:6075–80.
Hawn TR, Verbon A, Janer M, Zhao LP, Beutler B, Aderem A. Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms are associated with resistance to Legionnaires’ disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:2487–9.
Arbour NC, Lorenz E, Schutte BC, Zabner J, Kline JN, Jones M, et al. TLR4 mutations are associated with endotoxin hyporesponsiveness in humans. Nat Genet. 2000;25:187–91.
Michel O, LeVan TD, Stern D, Dentener M, Thorn J, Gnat D, et al. Systemic responsiveness to lipopolysaccharide and polymorphisms in the toll-like receptor 4 gene in human beings. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;112:923–9.
Fageras Bottcher M, Hmani-Aifa M, Lindstrom A, Jenmalm MC, Mai XM, Nilsson L, et al. A TLR4 polymorphism is associated with asthma and reduced lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-12(p70) responses in Swedish children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114:561–7.
Erridge C, Stewart J, Poxton IR. Monocytes heterozygous for the Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile mutations in the Toll-like receptor 4 gene show no deficit in lipopolysaccharide signalling. J Exp Med. 2003;197:1787–91.
von Aulock S, Schroder NW, Gueinzius K, Traub S, Hoffmann S, Graf K, et al. Heterozygous toll-like receptor 4 polymorphism does not influence lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine release in human whole blood. J Infect Dis. 2003;188:938–43.
Schippers EF, van‘t Veer C, van Voorden S, Martina CA, Huizinga TW, le Cessie S, et al. IL-10 and toll-like receptor-4 polymorphisms and the in vivo and ex vivo response to endotoxin. Cytokine. 2005;29:215–228.
van der Graaf C, Kullberg BJ, Joosten L, Verver-Jansen T, Jacobs L, Van der Meer JW, et al. Functional consequences of the Asp299Gly Toll-like receptor-4 polymorphism. Cytokine. 2005;30:264–8.
Paulus SC, Hirschfeld AF, Victor RE, Brunstein J, Thomas E, Turvey SE. Common human Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms-Role in susceptibility to respiratory syncytial virus infection and functional immunological relevance. Clin Immunol. 2007;123:252–7.
Calvano JE, owers DJ, Coyle SM, Macor M, Reddell MT, Kumar A, et al. Response to systemic endotoxemia among humans bearing polymorphisms of the Toll-like receptor 4 (hTLR4). Clin Immunol. 2006;121:186–90.
Kim HM, Park BS, Kim JI, Kim SE, Lee J, Oh SC, et al. Crystal structure of the TLR4-MD-2 complex with bound endotoxin antagonist Eritoran. Cell. 2007;130:906–17.
Rallabhandi P, Bell J, Boukhvalova MS, Medvedev A, Lorenz E, Arditi M, et al. Analysis of TLR4 polymorphic variants: new insights into TLR4/MD-2/CD14 stoichiometry, structure, and signaling. J Immunol. 2006;177:322–32.
Read RC, Pullin J, Gregory S, Borrow R, Kaczmarski EB, di Giovine FS, et al. A functional polymorphism of toll-like receptor 4 is not associated with likelihood or severity of meningococcal disease. J Infect Dis. 2001;184:640–2.
Allen A, Obaro S, Bojang K, Awomoyi AA, Greenwood BM, Whittle H, et al. Variation in Toll-like receptor 4 and susceptibility to group A meningococcal meningitis in Gambian children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003;22:1018–9.
Faber J, Meyer CU, Gemmer C, Russo A, Finn A, Murdoch C, et al. Human toll-like receptor 4 mutations are associated with susceptibility to invasive meningococcal disease in infancy. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006;25:80–1.
Karoly E, Fekete A, Banki NF, Szebeni B, Vannay A, Szabo AJ, et al. Heatshock protein 72 (HSPA1B) gene polymorphism and Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 mutation are associated with increased risk of urinary tract infection in children. Pediatr Res. 2007;61:371–4.
Cooke GS, Segal S, Hill AV. Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms and atherogenesis. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1978–80.
Newport MJ, Allen A, Awomoyi AA, Dunstan SJ, McKinney E, Marchant A, et al. The toll-like receptor 4 Asp299Gly variant: no influence on LPS responsiveness or susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis in The Gambia. Tuberculosis. 2004;84:347–52.
Ferwerda B, Kibiki GS, Netea MG, Dolmans WM, van der Ven AJ. The toll-like receptor 4 Asp299Gly variant and tuberculosis susceptibility in HIV-infected patients in Tanzania. AIDS. 2007;21:1375–7.
Moens L, Verhaegen J, Pierik M, Vermeire S, De Boeck K, Peetermans WE, et al. Toll-like receptor 2 and Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms in invasive pneumococcal disease. Microbes Infect. 2007;9:15–20.
Barber RC, Chang LY, Arnoldo BD, Purdue GF, Hunt JL, Horton JW, et al. Innate immunity SNPs are associated with risk for severe sepsis after burn injury. Clin Med Res. 2006;4:250–5.
Child NJ, Yang IA, Pulletz MC, de Courcy-Golder K, Andrews AL, Pappachan VJ, et al. Polymorphisms in Toll-like receptor 4 and the systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31:652–3.
Feterowski C, Emmanuilidis K, Miethke T, Gerauer K, Rump M, Ulm K, et al. Effects of functional Toll-like receptor-4 mutations on the immune response to human and experimental sepsis. Immunology. 2003;109:426–31.
Agnese DM, Calvano JE, Hahm SJ, Coyle SM, Corbett SA, Calvano SE, et al. Human toll-like receptor 4 mutations but not CD14 polymorphisms are associated with an increased risk of gram-negative infections. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:1522–5.
Lorenz E, Mira JP, Frees KL, Schwartz DA. Relevance of mutations in the TLR4 receptor in patients with gram-negative septic shock. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:1028–32.
Kurt-Jones EA, Popova L, Kwinn L, Haynes LM, Jones LP, Tripp RA, et al. Pattern recognition receptors TLR4 and CD14 mediate response to respiratory syncytial virus. Nat Immunol. 2000;1:398–401.
Haynes LM, Moore DD, Kurt-Jones EA, Finberg RW, Anderson LJ, Tripp RA. Involvement of toll-like receptor 4 in innate immunity to respiratory syncytial virus. J Virol. 2001;75:10730–7.
Gagro A, Tominac M, Krsulovic-Hresic V, Bace A, Matic M, Drazenovic V, et al. Increased Toll-like receptor 4 expression in infants with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2004;135:267–72.
Tal G, Mandelberg A, Dalal I, Cesar K, Somekh E, Tal A, et al. Association between common Toll-like receptor 4 mutations and severe respiratory syncytial virus disease. J Infect Dis. 2004;189:2057–63.
Mandelberg A, Tal G, Naugolny L, Cesar K, Oron A, Houri S, et al. Lipopolysaccharide hyporesponsiveness as a risk factor for intensive care unit hospitalization in infants with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006;144:48–52.
Awomoyi AA, Rallabhandi P, Pollin TI, Lorenz E, Sztein MB, Boukhvalova MS, et al. Association of TLR4 polymorphisms with symptomatic respiratory syncytial virus infection in high-risk infants and young children. J Immunol. 2007;179:3171–7.
Lofgren J, Marttila R, Renko M, Ramet M, Hallman M. Toll-like receptor 4 Asp299Gly polymorphism in respiratory syncytial virus epidemics. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2010;45:687–92.
Kesh S, Mensah NY, Peterlongo P, Jaffe D, Hsu K, van den Brink M, et al. TLR1 and TLR6 polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to invasive aspergillosis after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1062:95–103.
Morre SA, Murillo LS, Spaargaren J, Fennema HS, Pena AS. Role of the toll-like receptor 4 Asp299Gly polymorphism in susceptibility to Candida albicans infection. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:1377–9.
Van der Graaf CA, Netea MG, Morre SA, Den Heijer M, Verweij PE, Van der Meer JW, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 Asp299Gly/Thr399Ile polymorphisms are a risk factor for Candida bloodstream infection. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006;17:29–34.
Rezazadeh M, Hajilooi M, Rafiei A, Haidari M, Nikoopour E, Kerammat F, et al. TLR4 polymorphism in Iranian patients with brucellosis. J Infect. 2006;53:206–10.
Mockenhaupt FP, Cramer JP, Hamann L, Stegemann MS, Eckert J, Oh NR, et al. Toll-like receptor (TLR) polymorphisms in African children: common TLR-4 variants predispose to severe malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:177–82.
Mockenhaupt FP, Hamann L, von Gaertner C, Bedu-Addo G, von Kleinsorgen C, Schumann RR, et al. Common polymorphisms of toll-like receptors 4 and 9 are associated with the clinical manifestation of malaria during pregnancy. J Infect Dis. 2006;194:184–8.
Schmausser B, Andrulis M, Endrich S, Lee SK, Josenhans C, Muller-Hermelink HK, et al. Expression and subcellular distribution of Toll-like receptors TLR4, TLR5 and TLR9 on the gastric epithelium in Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 2004;136:521–6.
Kato I, Canzian F, Plummer M, Franceschi S, van Doorn LJ, Vivas J, et al. Polymorphisms in genes related to bacterial lipopolysaccharide/peptidoglycan signalling and gastric precancerous lesions in a population at high risk for gastric cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52:254–61.
Hold GL, Rabkin CS, Chow WH, Smith MG, Gammon MD, Risch HA, et al. A functional polymorphism of Toll-like receptor 4 gene increases risk of gastric carcinoma and its precursors. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:905–12.
Achyut BR, Ghoshal UC, Moorchung N, Mittal B. Association of Toll-like receptor-4 (Asp299Gly and Thr399Ileu) gene polymorphisms with gastritis and precancerous lesions. Hum Immunol. 2007;68:901–7.
Rigoli L, Bella DI C, Fedele F, Procopio V, Amorini M, et al. TLR4 and NOD2/CARD15 genetic polymorphisms and their possible role in gastric carcinogenesis. Anticancer Res. 2010;30:513–7.
Trejo-de la OA, Torres J, Pérez-Rodriguez M, Camorlinga-Ponce M, Luna LF, Abdo-Francis JM, et al. TLR4 single-nucleotide polymorphisms alter mucosal cytokine and chemokine patterns in Mexican patients with Helicobacter pylori-associated gastroduodenal diseases. Clin Immunol. 2008;129:333–40.
Garza-Gonzalez E, Bosques-Padilla FJ, Mendoza-Ibarra SI, Flores-Gutierrez JP, Maldonado-Garza HJ, Perez–Perez GI. Assessment of the Toll-like receptor 4 Asp299Gly, Thr399Ile and interleukin-8–251 polymorphisms in the risk for the development of distal gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 2007;7:70.
Santini D, Angeletti S, Ruzzo A, Dicuonzo G, Galluzzo S, Vincenzi B, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile polymorphisms in gastric cancer of intestinal and diffuse histotypes. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008;154:360–4.
Hishida A, Matsuo K, Goto Y, Mitsuda Y, Hiraki A, Naito M, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 +3725G/C polymorphism, Helicobacter pylori seropositivity, and the risk of gastric atrophy and gastric cancer in Japanese. Helicobacter. 2009;14:47–53.
Chen YC, Giovannucci E, Lazarus R, Kraft P, Ketkar S, Hunter DJ. Sequence variants of Toll-like receptor 4 and susceptibility to prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:11771–8.
Cheng I, Plummer SJ, Casey G, Witte JS. Toll-like receptor 4 genetic variation and advanced prostate cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007;16:352–5.
Zheng SL, Augustsson-BAlter K, Chang B, Hedelin M, Li L, Adami HO, et al. Sequence variants of Toll-like receptor 4 are associated with prostate cancer risk: results from the cancer prostate in Sweden study. Cancer Res. 2004;64:2918–22.
Balistreri CR, Caruso C, Carruba G, Miceli V, Campisi I, ListÍ F, et al. A pilot study on prostate cancer risk and pro-inflammatory genotypes: pathophysiology and therapeutic implications. Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16:718–24.
Wang MH, Helzlsouer KJ, Smith MW, Hoffman-Bolton JA, Clipp SL, Grinberg V, et al. Association of IL10 and other immune response- and obesity-related genes with prostate cancer in CLUE II. Prostate. 2009;69:874–85.
Boraska Jelavic T, Barisic M, Drmic Hofman I, Boraska V, Vrdoljak E, Peruzovic M, et al. Polymorphism in the Toll-like receptor 2 is associated with colorectal cancer. Clin Genet. 2006;70:156–60.
Landi S, Gemignani F, Bottari F, Gioia-Patricola L, Guino E, Cambray M, et al. Polymorphisms within inflammatory genes and colorectal cancer. J Negat Results Biomed. 2006;5:15.
Pandey S, Mittal RD, Srivastava M, Srivastava K, Singh S, Srivastava S, Mittal B. Impact of Toll-like receptors [TLR] 2 (–196 to –174 del) and TLR 4 (Asp299Gly, Thr399Ile) in cervical cancer susceptibility in North Indian women. Gynecol Oncol. 2009;114:501–5.
Mori Y, Yoshimura A, Ukai T, Lien E, Espevik T, Hara Y. Immunohistochemical localization of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in gingival tissue from patients with periodontitis. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2003;18:54–8.
Ren L, Leung WK, Darveau RP, Jin L. The expression profile of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein, membrane-bound CD14, and toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in chronic periodontitis. J Periodontol. 2005;76:1950–9.
Wang PL, Ohura K, Fujii T, Oido-Mori M, Kowashi Y, Kikuchi M, et al. DNA microarray analysis of human gingival fibroblasts from healthy and inflammatory gingival tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;305:970–3.
Kinane DF, Peterson M, Stathopoulou PG. Environmental and other modifying factors of the periodontal diseases. Periodontol 2000. 2006;40:107–119.
Kinane DF, Shiba H, Stathopoulou PG, Zhao H, Lappin DF, Singh A, et al. Gingival epithelial cells heterozygous for Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms Asp299Gly and Thr399ile are hypo-responsive to Porphyromonas gingivalis. Genes Immun. 2006;7:190–200.
Ozturk A, Vieira AR. TLR4 as a risk factor for periodontal disease: a reappraisal. J Clin Periodontol. 2009;36:279–86.
Michelsen KS, Doherty TM, Shah PK, Arditi M. TLR signaling: an emerging bridge from innate immunity to atherogenesis. J Immunol. 2004;173:5901–7.
Michelsen KS, Doherty TM, Shah PK, Arditi M. Role of Toll-like receptors in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2004;95:e96–7.
Kalayoglu MV, Libby P, Byrne GI. Chlamydia pneumoniae as an emerging risk factor in cardiovascular disease. JAMA. 2002;288:2724–31.
Lehr HA, Sagban TA, Ihling C, Zahringer U, Hungerer KD, Blumrich M, et al. Immunopathogenesis of atherosclerosis: endotoxin accelerates atherosclerosis in rabbits on hypercholesterolemic diet. Circulation. 2001;104:914–20.
Xu XH, Shah PK, Faure E, Equils O, Thomas L, Fishbein MC, et al. Toll-like receptor-4 is expressed by macrophages in murine and human lipid-rich atherosclerotic plaques and upregulated by oxidized LDL. Circulation. 2001;104:3103–8.
Kiechl S, Lorenz E, Reindl M, Wiedermann CJ, Oberhollenzer F, Bonora E, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms and atherogenesis. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:185–92.
Ameziane N, Beillat T, Verpillat P, Chollet-Martin S, Aumont MC, Seknadji P, et al. Association of the Toll-like receptor 4 gene Asp299Gly polymorphism with acute coronary events. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23:e61–4.
Balistreri CR, Candore G, Colonna-Romano G, Lio D, Caruso M, Hoffmann E, et al. Role of Toll like receptor 4 in acute myocardial infarction and longevity. JAMA. 2004;292:2339–40.
Yang IA, Holloway JW, Ye S. TLR4 Asp299Gly polymorphism is not associated with coronary artery stenosis. Atherosclerosis. 2003;170:187–90.
Reismann P, Lichy C, Rudofsky G, Humpert PM, Genius J, Si TD, et al. Lack of association between polymorphisms of the toll-like receptor 4 gene and cerebral ischemia. J Neurol. 2004;251:853–8.
Edfeldt K, Bennet AM, Eriksson P, Frostegard J, Wiman B, Hamsten A, et al. Association of hyporesponsive toll-like receptor 4 variants with risk of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2004;25:1447–53.
Lorenz E, Hallman M, Marttila R, Haataja R, Schwartz DA. Association between the Asp299Gly polymorphisms in the Toll-like receptor 4 and premature births in the Finnish population. Pediatr Res. 2002;52:373–6.
Torok HP, Glas J, Tonenchi L, Mussack T, Folwaczny C. Polymorphisms of the lipopolysaccharide-signaling complex in inflammatory bowel disease: association of a mutation in the Toll-like receptor 4 gene with ulcerative colitis. Clin Immunol. 2004;112:85–91.
Yang IA, Barton SJ, Rorke S, Cakebread JA, Keith TP, Clough JB, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphism and severity of atopy in asthmatics. Genes Immun. 2004;5:41–5.
Radstake TR, Franke B, Hanssen S, Netea MG, Welsing P, Barrera P, et al. The Toll-like receptor 4 Asp299Gly functional variant is associated with decreased rheumatoid arthritis disease susceptibility but does not influence disease severity and/or outcome. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:999–1001.
Rudofsky G Jr, Reismann P, Witte S, Humpert PM, Isermann B, Chavakis T, et al. Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile genotypes of the TLR4 gene are associated with a reduced prevalence of diabetic neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:179–83.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kumar Visvanathan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noreen, M., Shah, M.A.A., Mall, S.M. et al. TLR4 polymorphisms and disease susceptibility. Inflamm. Res. 61, 177–188 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-011-0427-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-011-0427-1