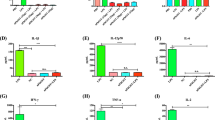
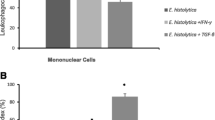
Abstract
The monocyte locomotion inhibitory factor (MLIF), a heat-stable oligopeptide found in the supernatant fluid of Entamoeba histolytica axenic cultures, may contribute to the delayed inflammation observed in amoebic hepatic abscess. This factor was isolated by ultra-filtration and high powered liquid chromatography, obtaining a primary Met-Gln-Cys-Asn-Ser structure, identified afterwards as the carboxyl-terminal (…Cys-Asn-Ser) active site. The selective anti-inflammatory effects of the pentapeptide have been observed in both in vitro and in vivo models, using a synthetic pentapeptide to maintain the same anti-inflammatory conditions during the experimental assays. Anti-inflammatory effects observed include inhibition of human monocyte locomotion and the respiratory burst in monocytes and neutrophils, increasing expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines and inhibiting expression of the adhesion molecules VLA-4 and VCAM, among others. In this review, we will describe the effects of MLIF detected so far and how it might be used as a therapeutical agent against inflammatory diseases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walsh JA. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of morbidity and mortality. Rev Infect Dis. 1986;8:228–38.
Caballero-Salcedo A, Viveros-Rogel M, Salvatierra B, Tapia-Conyer R, Sepulveda-Amor J, Gutierrez G, et al. Seroepidemiology of amebiasis in Mexico. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1994;50(4):412–9.
Tsutsumi V, Martínez-Palomo A. Inflammatory reaction in experimental hepatic amebiasis. An ultrastructural study. Am J Pathol. 1988;130:112–9.
Sepúlveda B, Martínez-Palomo A. Immunology of amebiasis by Entamoeba histolytica. In: Cohen S, Warren KS, editors. Immunology of parasitic diseases. Blackwell, Oxford; 1982. p. 172–5.
Pérez-Tamayo R, Brandt H. Amebiasis. In: Marcial Rojas RA (ed) Pathology of protozoan and helminthic disease. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore; 1971. p. 145–88.
Silva García R, Rico Rosillo G, Espinosa Cantellano M, Castañon G, Giménez Scherer J, Kretschmer R. Entamoeba dispar does not produce monocyte locomotion inhibitory factor (MLIF) produced by Entamoeba histolytica. Parasite Immunol. 2003;25:99–101.
Kretschmer R, Salinas CC, López OM, Avila M. Efecto de Entamoeba histolytica sobre la quimiotaxis de monocitos humanos. Arch Invest Med. 1980;11:147–51.
Kretschmer R, Collado ML, Pacheco MG, Salinas MC, López-Osuna M, Leucona M, et al. Inhibition of human monocyte locomotion by products of axenically grown Entamoeba histolytica. Parasite Immunol. 1985;7:527–43.
Rico G, Arellano J, Kretschmer R. The monocyte locomotion inhibitory factor produced by Entamoeba histolytica does not inhibit the locomotion of human eosinophils. Parasitol Res. 1998;84(6):522–3.
Giménez-Scherer JA, Pacheco Cano MG, Cruz de Lavin E, Hernández-Jauregui P, Merchant MT, Kretschmer RR. Ultrastructural changes associated with the inhibition of monocyte chemotaxis caused by products of axenically grown Entamoeba histolytica. Lab Invest. 1987;57:45–51.
Kretschmer RR, Castro EM, Pacheco G, Rico G, Diaz-Guerra O, Arellano J. The role of mannose in the receptor of the monocyte locomotion inhibitory factor produced by Entamoeba histolytica. Parasitol Res. 1991;77:374–8.
Rico G, Díaz-Guerra, Giménez-Scherer JA, Kretschmer RR. Effect of the monocyte locomotion inhibitory factor (MLIF) produced by Entamoeba histolytica upon the respiratory burst of human leukocytes. Arch Med Res. 1992;23:157–9.
Rico G, Leandro E, Rojas S, Giménez-Scherer JA, Kretschmer RR. The monocyte locomotion inhibitory factor produced by Entamoeba histolytica inhibits induced nitric oxide production in human leukocytes. Parasitol Res. 2003;90:264–7.
Wang W, Keller K, Chadee K. Entamoeba histolytica modulates the nitric oxide synthase gene and nitric oxide production by macrophages for cytotoxicity against amoebae and tumour cells. Immunol. 1994;83:601–10.
Salata RA, Pearson RD, Ravdin JI. Interaction of human leucocytes and Entamoeba histolytica. Killing of virulent amebae by the activated macrophage. J Clin Invest. 1985;76:491–9.
Guerrant RL, Brush J, Ravdin JI, Sullivan JA, Mandell GL. Interaction between Entamoeba histolytica and human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1981;143:83–93.
López-Osuna M, Contreras B, Kretschmer RR. In vitro studies of the interaction of polymorphonuclear leucocytes and Entamoeba histolytica. Arch Invest Med. 1986;17:243–6.
Rico G, Ximenez C, Ramos F, Kretschmer RR. Production of the monocyte locomotion inhibitory factor (MLIF) by axenically grown Entamoeba histolytica: synthesis or degradation? Arch Med Res. 1997;28Spec:235–6.
Giménez-Scherer J, Rico R, Fernández-Diez J, Kretschmer RR. Inhibition of contact cutaneous delayed hypersensitivity reactions to DNCB in guinea pigs by the monocyte locomotion inhibitory factor (MLIF) produced by axenically grown Entamoeba histolytica. Arch Med Res. 1997;28(suppl):237–8.
Giménez-Scherer JA, Arenas E, Díaz L, Rico RG, Fernández-Diez, Kretschmer RR. Effect of the monocyte locomotion inhibitory factor (MLIF) produced by Entamoeba histolytica on the expression of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) in the Skin of Guinea Pigs. Arch Med Res. 2000;31(4suppl):92–3.
Utrera-Barillas D, Vélazquez JR, Enciso A, Cruz SM, Rico RG, Curiel Quesada E, et al. An anti-inflammatory oligopeptide produced by Entamoeba histolytica down-regulates the expression of pro-inflamamatory chemokines. Parasite Immunol. 2003;25:475–82.
Velázquez RJ, Kretschmer RR. Entamoeba histolytica, a remarkable anti-inflammatory parasite. Inmunología. 2004;23:201–7.
Giménez Scherer JA, Cárdenas G, López-Osuna M, Velázquez JR, Rico G, Isibasi A, et al. Immunization with a tetramer derivate of an anti-inflammatory pentapeptide produced by Entamoeba histolytica protects gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus) against experimental amoebic abscess of the liver. Parasite Immunol. 2004;26:343–9.
Kretschmer RR, Rico RG, Giménez-Scherer J. A novel anti-inflammatory oligopeptide produced by Entamoeba histolytica. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2001;112:201–9.
Soriano-Correa C, Sánchez-Ruiz JF, Rico-Rosillo G, Giménez-Scherer JA, Velásquez RJ, Kretschmer RR. Electronic structure and physicochemical properties of the anti-inflammatory pentapeptide produced by Entamoeba histolytica: A theoretical study. J Mol Struct Theochem. 2006;769:91–5.
Barrientos-Salcedo C, Rico-Rosillo G, Giménez-Scherer J, Soriano-Correa C. Computational study of the electronic structure characterization of a novel anti-inflammatory tripeptide derived from monocyte locomotion inhibitory factor (MLIF)-pentapeptide. Eur J Med Chem. 2009;44:3114–9.
Morales-Martínez ME, Silva-García R, Soriano-Correa C, Giménez-Scherer J, Rojas-Dotor S, Rico-Rosillo G, et al. The Cys-Asn-Ser carboxyl-terminal end group is the pharmacophore of the amebic anti-inflammatory monocyte locomotion inhibitory factor (MLIF). Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2008;158:46–51.
Tannich E, Horstmann RD. Codon usage in pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J Mol Evol. 1992;34:272–3.
Ghosh T, Gupta S, Majumdar S. Studies on codon usage in Entamoeba histolytica. Intern J Parasitol. 2000;30:715–22.
Díaz UR, Al-Shahrour F, Dopazo J. Use of GO terms to understand the biological significance of microarray differential gene expression data. In: Johnson KF, Lin SM, editors. Microarray data analysis III. Kluwer Academic; 2003. p. 233–43.
Al-Shahrour F, Minguez F, Vaquerizas J, Conde L, Dopazo J. BABELOMICS: a suite of web-tools for functional annotation and analysis of group of genes in high-throughput experiments. Nucleic Acids Res (Web Server issue). 2005;33:W460–4.
Soldatova L, King R. Are the current ontologies in biology good ontologies? Nat Biotech. 2005;23:1095–8.
Busold C, Winter S, Hauser N, Bauer A, Dippon J, Hoheisel J, et al. Integration of GO annotations in correspondence analysis: facilitating the interpretation of microarray data. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:2424–9.
Silva-García R, Estrada-García I, Ramos-Payán R, Torres-Salazar A, Morales-Martínez E, Arenas-Aranda D, et al. The effect of an anti-inflammatory pentapeptide produced by Entamoeba histolytica on gene expression in the U-937 monocytic cell line. Inflamm Res. 2008;57:145–50.
Wolpe SD, Davatelis G, Sherry B, Beutler B, Hesse DG, Nguyen HT, et al. Macrophages secrete a novel heparin-binding protein with inflammatory and neutrophil chemokinetic properties. J Exp Med. 1988;167:570–81.
Kennedy KJ, Karpus WJ. Role of chemokines in the regulation of Th1/Th2 and autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Clin Immunol. 1999;19:273–9.
Zou W, Borvak J, Marches F. Macrophage-derived dendritic cells have strong strong Th1-polarizing potential mediated by beta-chemokines rather than IL-12. J Immunol. 2000;165:4388–96.
Schottelius AJ, Mayo MW, Sartor RB, Baldwin AS. Interleukin-10 signalling blocks inhibitor of kappa B kinase activity and nuclear factor kappa B DNA binding. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:31868–74.
Kontoyiannis D, Kotlyarov A, Carballo E, Alexopoulou L, Blackshear PJ, Gaestel M, et al. Interleukin-10 targets p38 MAPK to modulate ARE-dependent TNF mRNA translation and limit intestinal pathology. EMBO J. 2001;20:3760–70.
Muraille E, Leo O. Revisiting the Th1/Th2 paradigm. Scand J Immunol. 1998;47:1–9.
Lamont AG, Adorini L. IL-12: a key cytokine in immune regulation. Immunol Today. 1996;17:214–7.
Vancheri C, Mastruzzo C, Tomaselli V, Sortino MA, D’Amico L, Bellistri G, et al. Normal human lung fibroblasts differently modulate interleukin-10 and interleukin-12 production by monocytes: implications for an altered immune response in pulmonary chronic inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001;25:592–9.
Velazquez JR, Utrera BD, Zentella A, García BE, Ledesma SY, Kretschmer RR. The amebic anti-inflammatory monocyte locomotion inhibitory factor (MLIF) modifies the NF-κB nuclear translocation in human monocytes. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2003;14:64.
Vale W, Hsurh A, Riviel C, Yu S. The inhibin/activin family of growth factors. In: Sporn M, Roberts AB, editors. Peptide growth factors and their receptors, Handbook of experimental pharmacology. Springer Verlag, Heidelberg; 1994. p. 211–48.
Bilezikjian LM, Blount AL, Donaldson CJ, Vale WW. Pituitary actions of ligands of the TGF-beta family: activins and inhibins. Reproduction. 2006;132:207–15.
de Kretser DM, Hedger MP, Phillips DJ. Activin A and follistatin: their role in the acute phase reaction and inflammation. J Endocrinol. 1999;161:195–8.
Brosh N, Sternberg D, Honigwachs-Sha’anani J, Lee BC, Shav-Tal Y, Tzehoval E, et al. The plasmacytoma growth inhibitor restrictin-P is an antagonist of interleukin 6 and interleukin 11. Identification as a stroma-derived activin A. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:29594–600.
Ohguchi M, Yamato K, Ishihara Y, Koide M, Ueda N, Okahashi N, et al. Activin A regulates the production of mature interleukin-1beta and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in human monocytic cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1998;18:491–8.
Hubner G, Brauchle M, Gregor M, Werner S. Activin A: a novel player and inflammatory marker in inflammatory bowel disease? Lab Invest. 1997;77:311–8.
Kozian DH, Ziche M, Augustin HG. The activin-binding protein follistatin regulates autocrine endothelial cell activity and induces angiogenesis. Lab Invest. 1997;76:267–76.
Sugiyama M, Ichida T, Sato T, Ishikawa T, Matsuda Y, Asakura H. Expression of activin A is increased in cirrhotic and fibrotic rat livers. Gastroenterology. 1998;114:550–8.
Munz B, Hubner G, Tretter Y, Alzheimer C, Werner S. A novel role of activin in inflammation and repair. J Endocrinol. 1999;161:187–93.
de Bleser PJ, Niki T, Xu G, Rogiers V, Geerts A. Localization and cellular sources of activins in normal and fibrotic rat liver. Hepatology. 1997;26:905–12.
Hubner G, Hu Q, Smola H, Werner S. Strong induction of activin expression after injury suggests an important role of activin in wound repair. Dev Biol. 1996;173:490–8.
Balemans W, Van HW. Extracellular regulation of BMP signaling in vertebrates: a cocktail of modulators. Dev Biol. 2002;250:231–50.
Thompson TB, Lerch TF, Cook RW, Woodruff TK, Jardetzky TS. The structure of the follistatin: activin complex reveals antagonism of both type I and type II receptor binding. Dev Cell. 2005;9:535–43.
Phillips DJ, Jones KL, Scheerlinck JY, Hedger MP, de Kretser DM. Evidence for activin A and follistatin involvement in the systemic inflammatory response. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001;180:155–62.
Mashasiro S, Masayuki K, Takefumi I, Akiko W, Noriko I, Masaki S, et al. Differential regulation of metalloproteinase production, proliferation and chemotaxis of human lung fibroblasts by PDGF, interleukin-1β and TNF-α. Mediators Inflamm. 2000;9:1551–60.
Mehrnaz G, Sem HP. Role of cytokines and cytokine therapy in wound healing and fibrotic disease. Curr Pharm Desigs. 2001;7:1083–103.
Jenssen H, Hamill P, Hancock R. Peptide antimicrobial agents. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;13:491–511.
Lien S, Lowman H. Therapeutic peptides. Trends Biotechnol. 2003;21:556–62.
Adessi C, Soto C. Converting a peptide into a drug: strategies to improve stability and bioavailability. Curr Med Chem. 2002;9:96366.
Braughler JM, Hall DE. Involvement of lipid peroxidation in CNS injury. J Neurotrauma. 1992;Suppl 1:1–7.
Hamada Y, Ikata T, Katoh S, Tsuchiya K, Niwa M, Tsutsunishita Y, et al. Roles of nitric oxide in compression injury of rat spinal cord. J Free Rad. Biom Med. 1996;20:1–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kumar Visvanathan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva-García, R., Rico-Rosillo, G. Anti-inflammatory defense mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica . Inflamm. Res. 60, 111–117 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-010-0261-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-010-0261-x