Abstract
Objective
We investigated the inhibitory effects of quercetin and kaempferol treatment on the suppression of immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated allergic responses in relation to intestinal epithelium barrier function in RBL-2H3 and Caco-2 cells.
Methods
RBL-2H3 cells as a model of intestinal mucosa mast cells were treated with flavonols followed by IgE-anti-dinitrophenyl sensitization. The extent of degranulation and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines were measured. Caco-2 cells were stimulated with interleukin (IL)-4 or IgE-allergen with or without flavonol pretreatment and changes in the expression of CD23 mRNA and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and chemokine release were determined.
Results
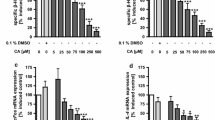
Flavonols inhibited the secretion of allergic mediators in RBL-2H3 cells and suppressed the CD23 mRNA expression and p38 MAPK activation in IL-4 stimulated Caco-2 cells. Flavonols also suppressed IgE-OVA induced extra signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) activation and chemokine release.
Conclusions
Quercetin and kaempferol effectively suppressed the development of IgE-mediated allergic inflammation of intestinal cell models.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim JW, Lee JH, Hwang BY, Mun SH, Ko NY, Kim do K, et al. Morin inhibits Fyn kinase in mast cells and IgE-mediated type I hypersensitivity response in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009;77:1506–12.
Bischoff SC, Wedemeyer J, Herrmann A, Meier PN, Trautwein C, Cetin Y, et al. Quantitative assessment of intestinal eosinophils and mast cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Histopathology. 1996;28:1–13.
Bischoff SC, Kramer S. Human mast cells, bacteria, and intestinal immunity. Immunol Rev. 2007;217:329–37.
Bischoff SC. Physiological and pathophysiological functions of intestinal mast cells. Semin Immunopathol 2009.
Bischoff SC, Sellge G, Manns MP, Lorentz A. Interleukin-4 induces a switch of human intestinal mast cells from proinflammatory cells to Th2-type cells. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001;124:151–4.
Lorentz A, Schwengberg S, Sellge G, Manns MP, Bischoff SC. Human intestinal mast cells are capable of producing different cytokine profiles: role of IgE receptor cross-linking and IL-4. J Immunol. 2000;164:43–8.
Richards ML, Katz DH. Regulation of the murine Fc epsilon RII (CD23) gene. Functional characterization of an IL-4 enhancer element. J Immunol. 1994;152:3453–66.
Yahong T, Perdue MH. CD23-mediated transport of IgE/immune complexes across human intestinal epithelium: role of p38 MAPK. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;291:G532–8.
Yu LC, Montagnac G, Yang PC, Conrad DH, Benmerah A, Perdue MH. Intestinal epithelial CD23 mediates enhanced antigen transport in allergy: evidence for novel splice forms. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003;285:G223–34.
Chacon P, Vega A, Monteseirin J, El Bekay R, Alba G, Perez-Formoso JL, et al. Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by allergens in lymphocytes from allergic patients. Eur J Immunol. 2005;35:2313–24.
Li H, Chehade M, Liu W, Xiong H, Mayer L, Berin MC. Allergen-IgE complexes trigger CD23-dependent CCL20 release from human intestinal epithelila cells. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1905–15.
Terao J. Dietary flavonoids as antioxidants. Forum Nutr. 2009;61:87–94.
Tunon MJ, Garcia-Mediavilla MV, Sanchez-Campos S, Gonzalez-Gallego J. Potential of flavonoids as anti-inflammatory agents: modulation of pro-inflammatory gene expression and signal transduction pathways. Curr Drug Metab. 2009;10:256–71.
Chun OK, Floegel A, Chung SJ, Chung CE, Song WO, Koo SI. Estimation of antioxidant intakes from diet and supplements in US adults. J Nutr 2009.
de Vries JH, Janssen PL, Hollman PC, van Staveren WA, Katan MB. Consumption of quercetin and kaempferol in free-living subjects eating a variety of diets. Cancer Lett. 1997;114:141–4.
Hertog MG, Feskens EJ, Hollman PC, Katan MB, Kromhout D. Dietary antioxidant flavonoids and risk of coronary heart disease: the Zutphen Elderly Study. Lancet. 1993;342:1007–11.
Amasheh M, Schlichter S, Amasheh S, Mankertz J, Zeitz M, Fromm M, et al. Quercetin enhances epithelial barrier function and increases claudin-4 expression in Caco-2 cells. J Nutr. 2008;138:1067–73.
Suzuki T, Hara H. Quercetin enhances intestinal barrier function through the assembly of zonula occludens-2, occludin, and claudin-1 and the expression of claudin-4 in Caco-2 cells. J Nutr. 2009;139:965–74.
Amasheh M, Andres S, Amasheh S, Fromm M, Schulzke JD. Barrier effects of nutritional factors. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2009;1165:267–73.
Choi OH, Adelstein RS, Beaven MA. Secretion from rat basophilic RBL-2H3 cells is associated with diphosphorylation of myosin light chains by myosin light chain kinase as well as phosphorylation by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:536–41.
Menconi MJ, Salzman AL, Unno N. Acidosis induces hyperpermeability in Caco-2BBe cultured intestianl epithelial monolayers. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:G1007–21.
Choi OH, Kim JH, Kinet JP. Calcium mobilization via sphingosine kinase in signalling by the Fc epsilon RI antigen receptor. Nature. 1996;380:634–6.
Pearce FL, Befus AD, Bienenstock J. Mucosal mast cells III. Effect of quercetin and other flavonoids on antigen-induced histamine secretion from rat intestinal mast cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984;73:819–23.
Penissi AB, Rudolph MI, Piezzi RS. Role of mast cells in gastrointestinal mucosal defense. Biocell. 2003;27:163–72.
Fox CC, Wolf EJ, Kagey-Sobotka A, Lichtenstein LM. Comparison of human lung and intestinal mast cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1988;81:89–94.
Kempuraj D, Madhappan B, Christodoulou S, Boucher W, Cao J, Papadopoulou N, et al. Flavonols inhibit proinflammatory mediator release, intracellular calcium ion levels and protein kinase C theta phosphorylation in human mast cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2005;145:934–44.
Wadsworth TL, Koop DR. Effects of the wine polyphenolic quercetin and resveratrol on pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999;57:941–9.
Min YD, Choi CH, Bark H, Son HY, Park HH, Lee S, et al. Quercetin inhibits expression of inflammatory cytokines through attenuation of NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK in HMC-1 human mast cell line. Inflamm Res. 2007;56:210–5.
Mastuda H, Morikawa T, Ueda K, Managi H, Yoshikawa M. Structural requirements of flavonoids for inhibition of antigen-induced degranulation, TNF-α and IL-4 production from RBL-2H3 cells. Bioorg Med Chem. 2002;10:3123–8.
Hashimoto S, Amemiya E, Tomita Y, Kobayashi T, Arai K, Yamaguchi M, et al. Elevation of soluble IL-2 receptor and IL-4, and nonelevation of IFN-gamma in sera from patients with allergic asthma. Ann Allergy. 1993;71:455–8.
Marshall LA, Hansbury MJ, Bolognese BJ, Gum RJ, Peter RY, Mayer RJ. Inhibitors of the p38 mitogen-activated kinase modulate IL-4 induction of low affinity IgE receptor(CD23) in human monocytes. J Immunol. 1998;161:6005–13.
Montagnac G, Yu LC, Bevilacqua C, Heyman M, Conrad DH, Perdue MH, et al. Differential role for CD23 splice forms in apical to basolateral transcytosis of IgE/allergen complexes. Traffic. 2005;6:230–42.
Hunt AE, Williams LM, Lali FV, Foxwell BMJ. IL-4 regulation of p38 MAPK signaling is dependent on cell type. Cytokine. 2002;18:295–303.
Tu Y, Salim S, Bourgeois J, Di Leo V, Irvine EJ, Marshall JK, et al. CD23-mediated IgE trasnport across human intestinal epithelium: inhibition by blocking sites of translation or binding. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:928–40.
Lucas N. Role of chemokines in the pathogenesis of asthma. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1:108–16.
Kaplan AP. Chemokines, chemokine receptors and allergy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001;124:423–31.
Nanua S, Zick SM, Andrade JE, Sajjan US, Burgess JR, Lukacs NW, et al. Quercetin blocks airway epithelial cell chemokine expression. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006;35:602–10.
Yu LC. The epithelial gatekeeper against food allergy. Pediatr Neonatol. 2009;50:247–54.
Li H, Nowak-Wegrzyn A, Charlop-Powers Z, Shreffler W, Chehade M, Thomas S, et al. Transcytosis of IgE-antigen complexes by CD23a in human intestinal epithelial cells and its role in food allergy. Gastroenterology. 2006;131:47–58.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the grant (A080664) from the Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: A. Falus.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, EJ., Ji, GE. & Sung, MK. Quercetin and kaempferol suppress immunoglobulin E-mediated allergic inflammation in RBL-2H3 and Caco-2 cells. Inflamm. Res. 59, 847–854 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-010-0196-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-010-0196-2